Sailboat Parts Explained: Illustrated Guide (with Diagrams)
When you first get into sailing, there are a lot of sailboat parts to learn. Scouting for a good guide to all the parts, I couldn't find any, so I wrote one myself.
Below, I'll go over each different sailboat part. And I mean each and every one of them. I'll walk you through them one by one, and explain each part's function. I've also made sure to add good illustrations and clear diagrams.
This article is a great reference for beginners and experienced sailors alike. It's a great starting point, but also a great reference manual. Let's kick off with a quick general overview of the different sailboat parts.

General Overview
The different segments
You can divide up a sailboat in four general segments. These segments are arbitrary (I made them up) but it will help us to understand the parts more quickly. Some are super straightforward and some have a bit more ninja names.
Something like that. You can see the different segments highlighted in this diagram below:
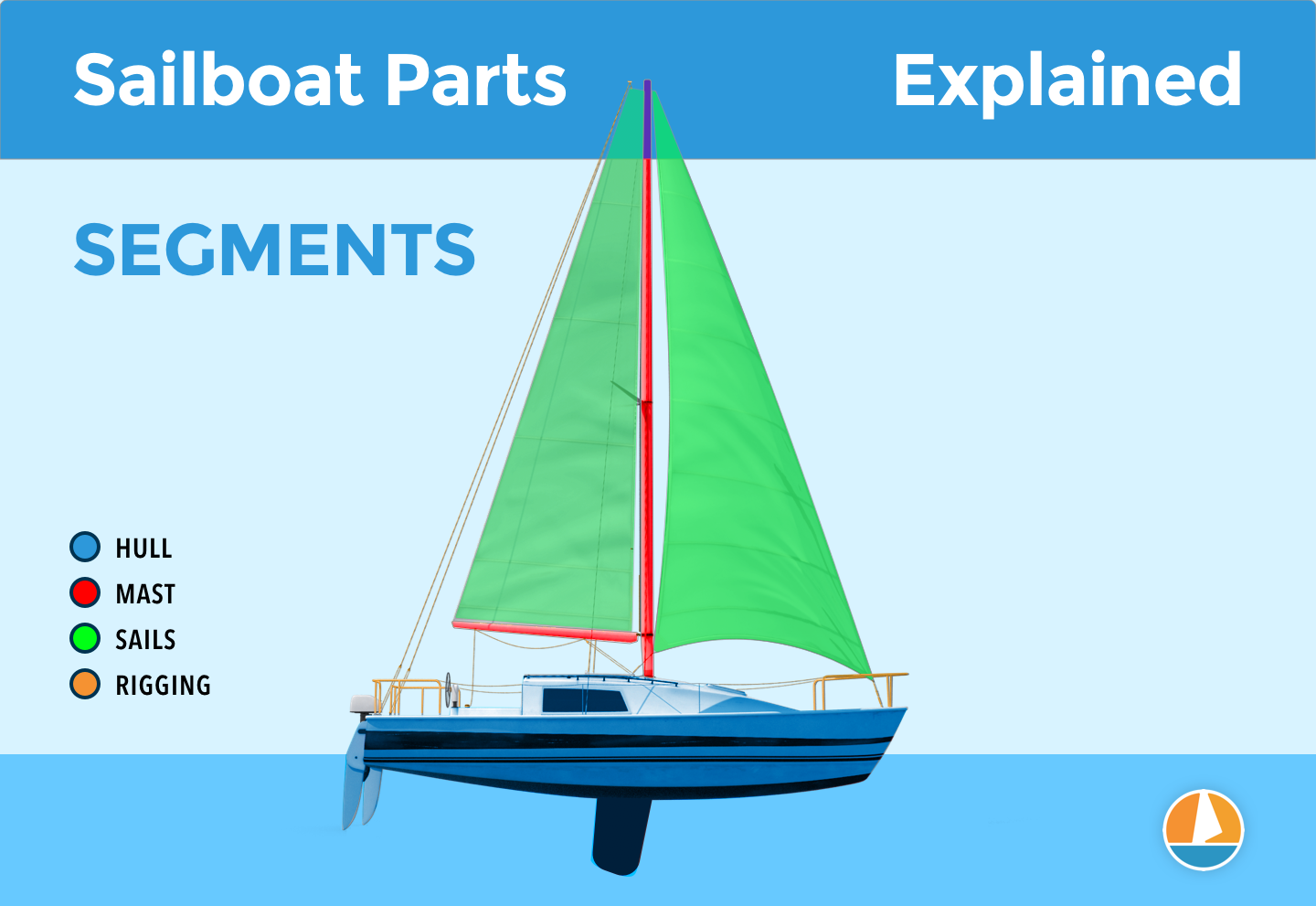
The hull is what most people would consider 'the boat'. It's the part that provides buoyancy and carries everything else: sails, masts, rigging, and so on. Without the hull, there would be no boat. The hull can be divided into different parts: deck, keel, cabin, waterline, bilge, bow, stern, rudder, and many more.
I'll show you those specific parts later on. First, let's move on to the mast.

Sailboats Explained
The mast is the long, standing pole holding the sails. It is typically placed just off-center of a sailboat (a little bit to the front) and gives the sailboat its characteristic shape. The mast is crucial for any sailboat: without a mast, any sailboat would become just a regular boat.
I think this segment speaks mostly for itself. Most modern sailboats you see will have two sails up, but they can carry a variety of other specialty sails. And there are all kinds of sail plans out there, which determine the amount and shape of sails that are used.
The Rigging
This is probably the most complex category of all of them.
Rigging is the means with which the sails are attached to the mast. The rigging consists of all kinds of lines, cables, spars, and hardware. It's the segment with the most different parts.
The most important parts
If you learn anything from this article, here are the most important parts of any sailboat. You will find all of these parts in some shape or form on almost any sailboat.

Okay, we now have a good starting point and a good basic understanding of the different sailboat parts. It's time for the good stuff. We're going to dive into each segment in detail.
Below, I'll go over them one by one, pointing out its different parts on a diagram, listing them with a brief explanation, and showing you examples as well.
After reading this article, you'll recognize every single sailboat part and know them by name. And if you forget one, you're free to look it up in this guide.
On this page:
The hull is the heart of the boat. It's what carries everything: the mast, the sails, the rigging, the passengers. The hull is what provides the sailboat with its buoyancy, allowing it to stay afloat.
Sailboats mostly use displacement hulls, which is a shape that displaces water when moving through it. They are generally very round and use buoyancy to support its own weight. These two characteristics make sure it is a smooth ride.
There are different hull shapes that work and handle differently. If you want to learn more about them, here's the Illustrated Guide to Boat Hull Types (with 11 Examples ). But for now, all we need to know is that the hull is the rounded, floating part of any sailboat.
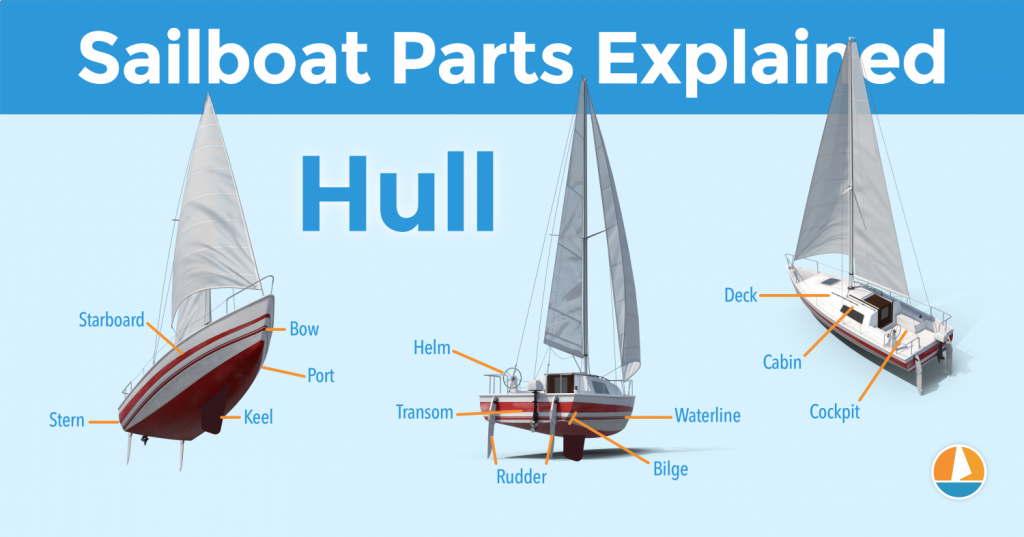
Instead of simply calling the different sides of a hull front, back, left and right , we use different names in sailing. Let's take a look at them.
The bow is the front part of the hull. It's simply the nautical word for 'front'. It's the pointy bit that cuts through the water. The shape of the bow determines partially how the boat handles.
The stern is the back part of the hull. It's simply the nautical word for 'back'. The shape of the stern partially determines the stability and speed of the boat. With motorboats, the stern lies deep inside the water, and the hull is flatter aft. Aft also means back. This allows it to plane, increasing the hull speed. For sailboats, stability is much more important, so the hull is rounded throughout, increasing its buoyancy and hydrodynamic properties.
The transom is the backplate of the boat's hull. It's the most aft (rear) part of the boat.
Port is the left side of a sailboat.
Starboard is the right side of a sailboat
The bilges are the part where the bottom and the sides of the hull meet. On sailboats, these are typically very round, which helps with hydrodynamics. On powerboats, they tend to have an angle.
The waterline is the point where the boat's hull meets the water. Generally, boat owners paint the waterline and use antifouling paint below it, to protect it from marine growth.
The deck is the top part of the boat's hull. In a way, it's the cap of the boat, and it holds the deck hardware and rigging.
Displacement hulls are very round and smooth, which makes them very efficient and comfortable. But it also makes them very easy to capsize: think of a canoe, for example.
The keel is a large fin that offsets the tendency to capsize by providing counterbalance. Typically, the keel carries ballast in the tip, creating a counterweight to the wind's force on the sails.
The rudder is the horizontal plate at the back of the boat that is used to steer by setting a course and maintaining it. It is connected to the helm or tiller.
Tiller or Helm
- The helm is simply the nautical term for the wheel.
- The tiller is simply the nautical term for the steering stick.
The tiller or helm is attached to the rudder and is used to steer the boat. Most smaller sailboats (below 30') have a tiller, most larger sailboats use a helm. Large ocean-going vessels tend to have two helms.
The cockpit is the recessed part in the deck where the helmsman sits or stands. It tends to have some benches. It houses the outside navigation and systems interfaces, like the compass, chartplotter, and so on. It also houses the mainsheet traveler and winches for the jib. Most boats are set up so that the entire vessel can be operated from the cockpit (hence the name). More on those different parts later.
Most larger boats have some sort of roofed part, which is called the cabin. The cabin is used as a shelter, and on cruising sailboats you'll find the galley for cooking, a bed, bath room, and so on.
The mast is the pole on a sailboat that holds the sails. Sailboats can have one or multiple masts, depending on the mast configuration. Most sailboats have only one or two masts. Three masts or more is less common.
The boom is the horizontal pole on the mast, that holds the mainsail in place.
The sails seem simple, but actually consist of many moving parts. The parts I list below work for most modern sailboats - I mean 90% of them. However, there are all sorts of specialty sails that are not included here, to keep things concise.

The mainsail is the largest sail on the largest mast. Most sailboats use a sloop rigging (just one mast with one bermuda mainsail). In that case, the main is easy to recognize. With other rig types, it gets more difficult, since there can be multiple tall masts and large sails.
If you want to take a look at the different sail plans and rig types that are out there, I suggest reading my previous guide on how to recognize any sailboat here (opens in new tab).
Sail sides:
- Leech - Leech is the name for the back side of the sail, running from the top to the bottom.
- Luff - Luff is the name for the front side of the sail, running from the top to the bottom.
- Foot - Foot is the name for the lower side of the sail, where it meets the boom.
Sail corners:
- Clew - The clew is the lower aft (back) corner of the mainsail, where the leech is connected to the foot. The clew is attached to the boom.
- Tack - The tack is the lower front corner of the mainsail
- Head - The head is the top corner of the mainsail
Battens are horizontal sail reinforcers that flatten and stiffen the sail.
Telltales are small strings that show you whether your sail trim is correct. You'll find telltales on both your jib and mainsail.
The jib is the standard sized headsail on a Bermuda Sloop rig (which is the sail plan most modern sailboats use).
As I mentioned: there are all kinds, types, and shapes of sails. For an overview of the most common sail types, check out my Guide on Sail Types here (with photos).
The rigging is what is used to attach your sails and mast to your boat. Rigging, in other words, mostly consists of all kinds of lines. Lines are just another word for ropes. Come to think of it, sailors really find all kinds of ways to complicate the word rope ...
Two types of rigging
There are two types of rigging: running and standing rigging. The difference between the two is very simple.
- The running rigging is the rigging on a sailboat that's used to operate the sails. For example, the halyard, which is used to lower and heave the mainsail.
- The standing rigging is the rigging that is used to support the mast and sail plan.
Standing Rigging
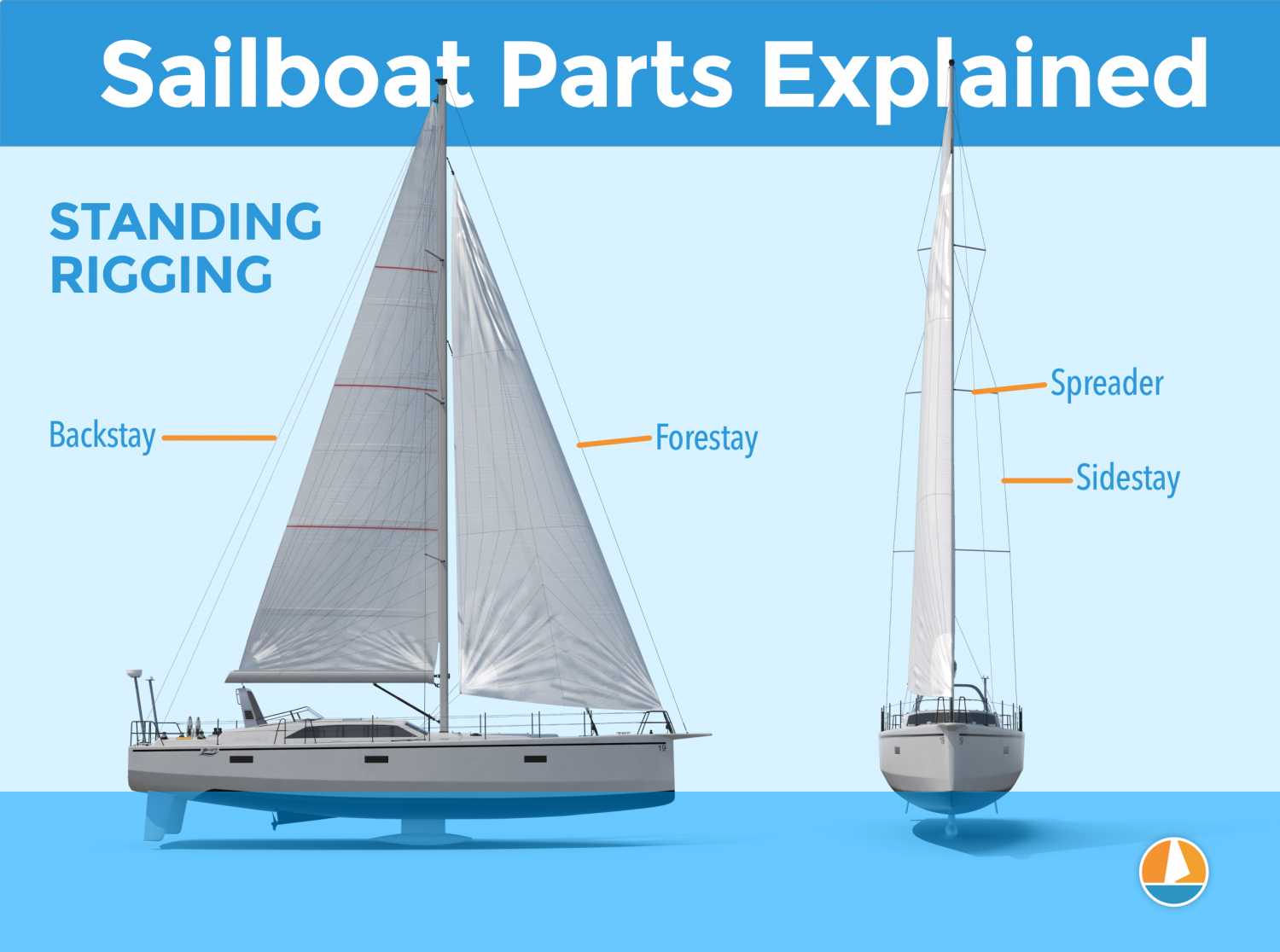
Here are the different parts that belong to the standing rigging:
- Forestay or Headstay - Line or cable that supports the mast and is attached to the bow of the boat. This is often a steel cable.
- Backstay - Line or cable that supports the mast and is attached to the stern of the boat. This is often a steel cable.
- Sidestay or Shroud - Line or cable that supports the mast from the sides of the boat. Most sailboats use at least two sidestays (one on each side).
- Spreader - The sidestays are spaced to steer clear from the mast using spreaders.
Running Rigging: different words for rope
Ropes play a big part in sailing, and especially in control over the sails. In sailboat jargon, we call ropes 'lines'. But there are some lines with a specific function that have a different name. I think this makes it easier to communicate with your crew: you don't have to define which line you mean. Instead, you simply shout 'mainsheet!'. Yeah, that works.
Running rigging consists of the lines, sheets, and hardware that are used to control, raise, lower, shape and manipulate the sails on a sailboat. Rigging varies for different rig types, but since most sailboats are use a sloop rig, nearly all sailboats use the following running rigging:
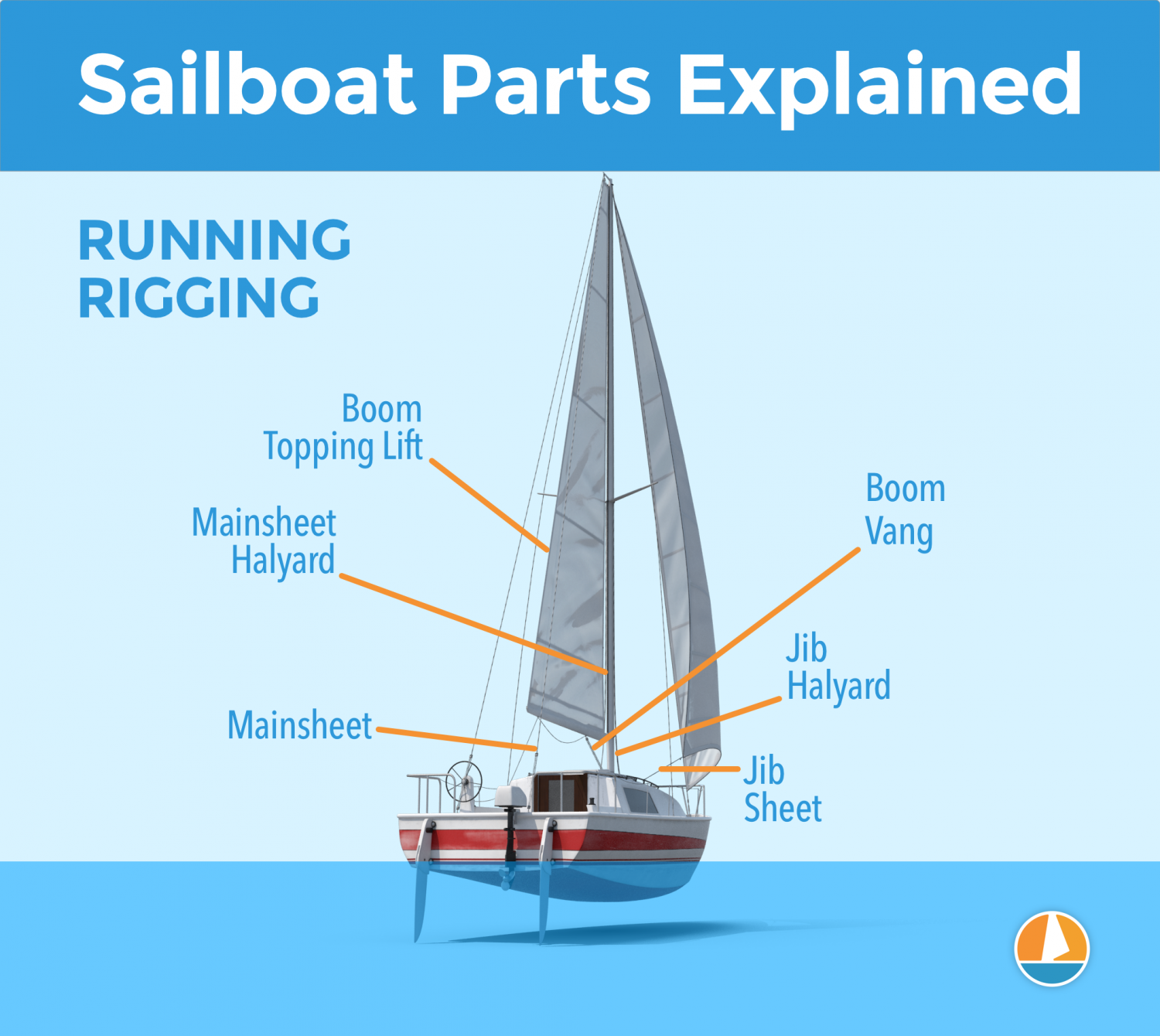
- Halyards -'Halyard' is simply the nautical name for lines or ropes that are used to raise and lower the mainsail. The halyard is attached to the top of the mainsail sheet, or the gaffer, which is a top spar that attaches to the mainsail. You'll find halyards on both the mainsail and jib.
- Sheets - 'Sheet' is simply the nautical term for lines or ropes that are used to set the angle of the sail.
- Mainsheet - The line, or sheet, that is used to set the angle of the mainsail. The mainsheet is attached to the Mainsheet traveler. More on that under hardware.
- Jib Sheet - The jib mostly comes with two sheets: one on each side of the mast. This prevents you from having to loosen your sheet, throwing it around the other side of the mast, and tightening it. The jib sheets are often controlled using winches (more on that under hardware).
- Cleats are small on-deck hooks that can be used to tie down sheets and lines after trimming them.
- Reefing lines - Lines that run through the mainsail, used to put a reef in the main.
- The Boom Topping Lift is a line that is attached to the aft (back) end of the boom and runs to the top of the mast. It supports the boom whenever you take down the mainsail.
- The Boom Vang is a line that places downward tension on the boom.
There are some more tensioning lines, but I'll leave them for now. I could probably do an entire guide on the different sheets on a sailboat. Who knows, perhaps I'll write it.
This is a new segment, that I didn't mention before. It's a bit of an odd duck, so I threw all sorts of stuff into this category. But they are just as important as all the other parts. Your hardware consists of cleats, winches, traveler and so on. If you don't know what all of this means, no worries: neither did I. Below, you'll find a complete overview of the different parts.
Deck Hardware
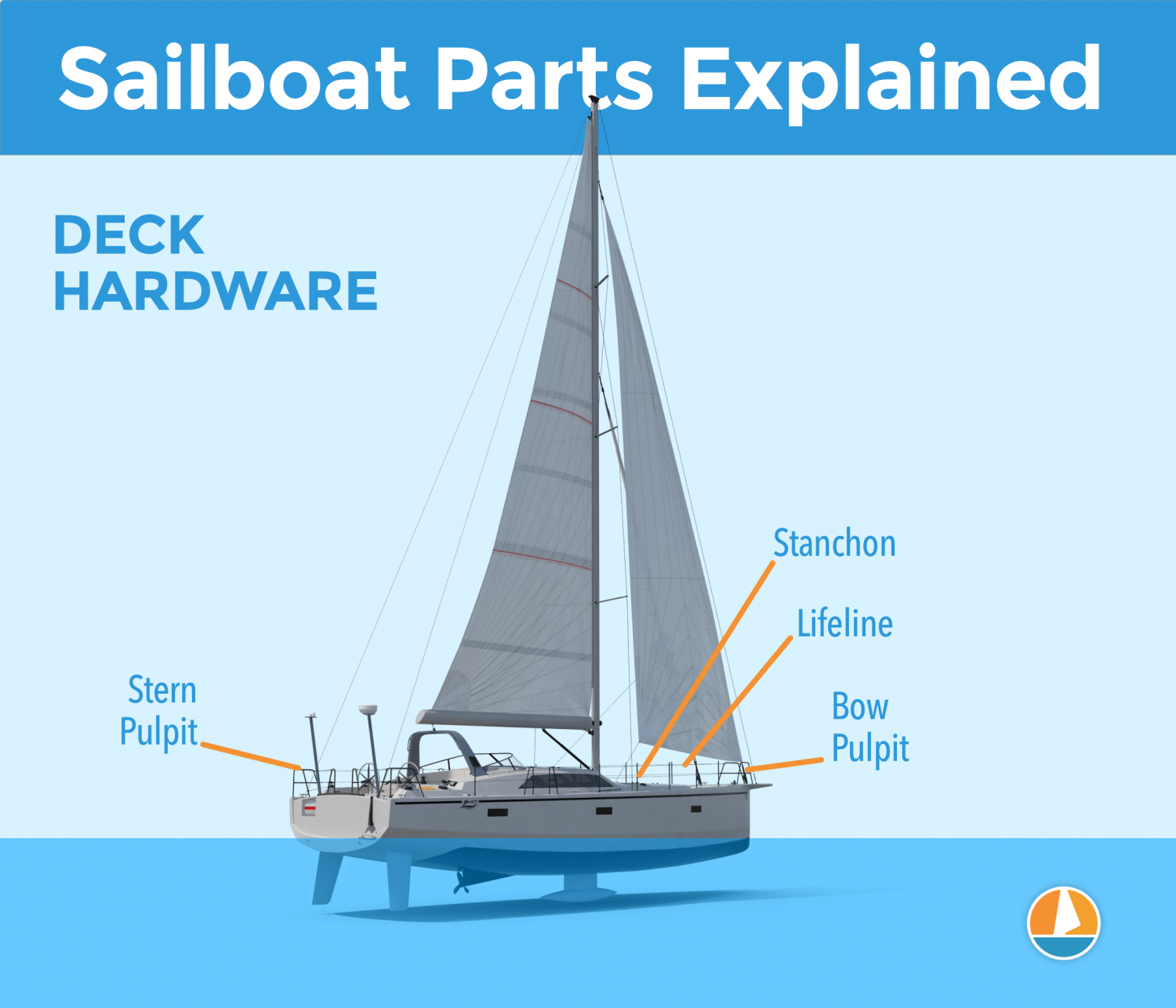
Just a brief mention of the different deck hardware parts:
- Pulpits are fenced platforms on the sailboat's stern and bow, which is why they are called the bow pulpit and stern pulpit here. They typically have a solid steel framing for safety.
- Stanchons are the standing poles supporting the lifeline , which combined for a sort of fencing around the sailboat's deck. On most sailboats, steel and steel cables are used for the stanchons and lifelines.
Mainsheet Traveler
The mainsheet traveler is a rail in the cockpit that is used to control the mainsheet. It helps to lock the mainsheet in place, fixing the mainsails angle to the wind.
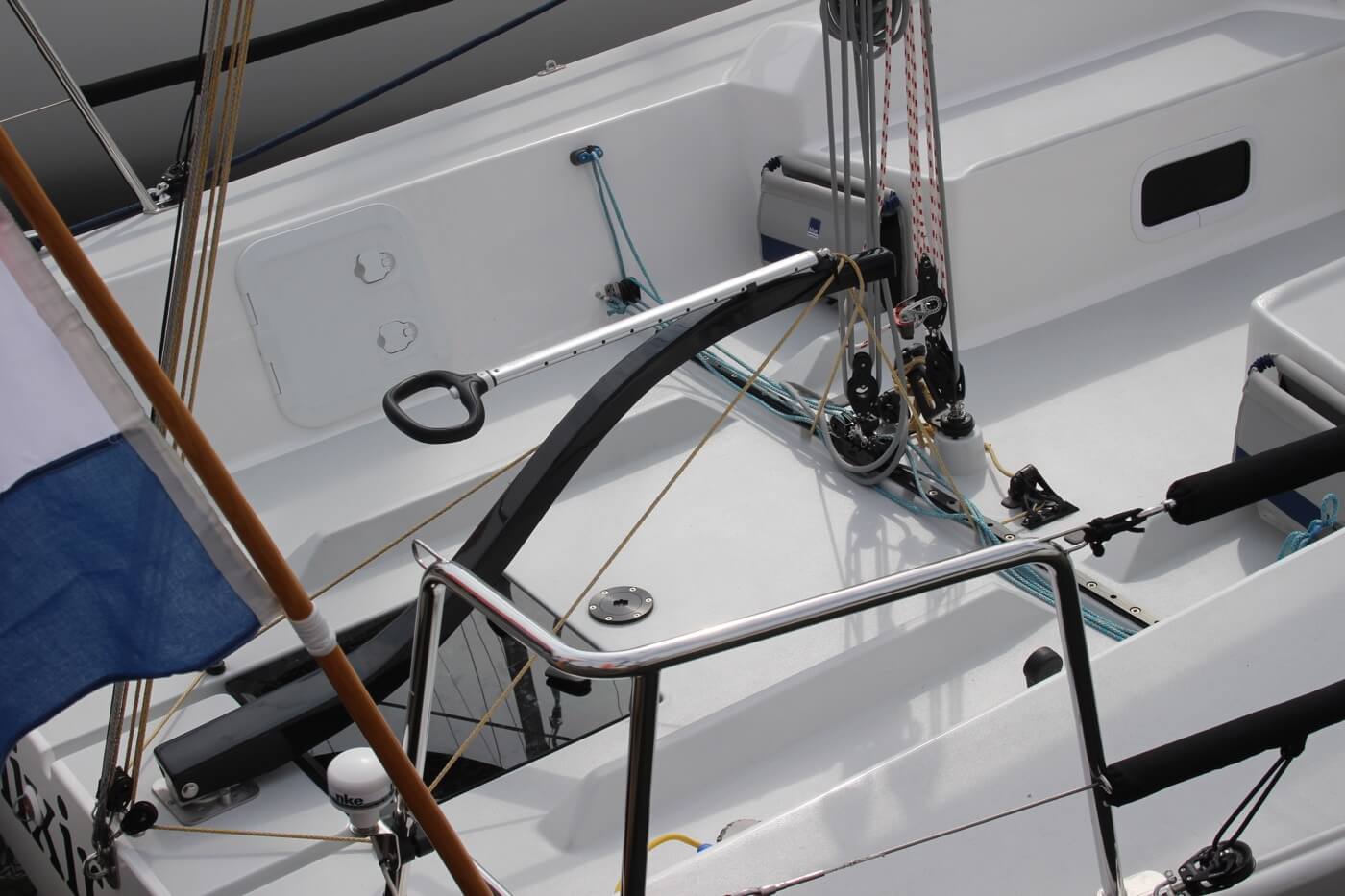

If you're interested in learning more about how to use the mainsheet traveler, Matej has written a great list of tips for using your mainsheet traveler the right way . It's a good starting point for beginners.
Winches are mechanical or electronic spools that are used to easily trim lines and sheets. Most sailboats use winches to control the jib sheets. Modern large sailing yachts use electronic winches for nearly all lines. This makes it incredibly easy to trim your lines.

You'll find the compass typically in the cockpit. It's the most old-skool navigation tool out there, but I'm convinced it's also one of the most reliable. In any way, it definitely is the most solid backup navigator you can get for the money.

Want to learn how to use a compass quickly and reliably? It's easy. Just read my step-by-step beginner guide on How To Use a Compass (opens in new tab .
Chartplotter
Most sailboats nowadays use, besides a compass and a map, a chartplotter. Chartplotters are GPS devices that show a map and a course. It's very similar to your normal car navigation.

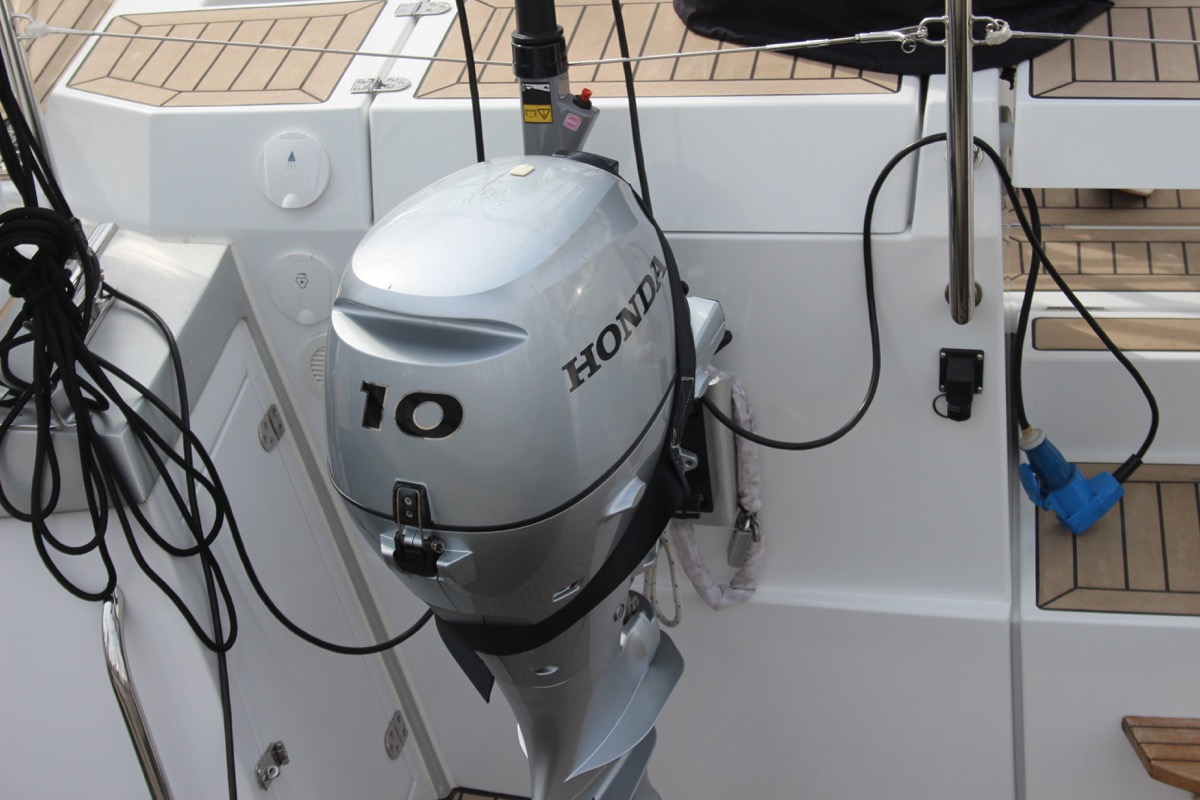
Outboard motor
Most sailboats have some sort of motor to help out when there's just the slightest breeze. These engines aren't very big or powerful, and most sailboats up to 32' use an outboard motor. You'll find these at the back of the boat.

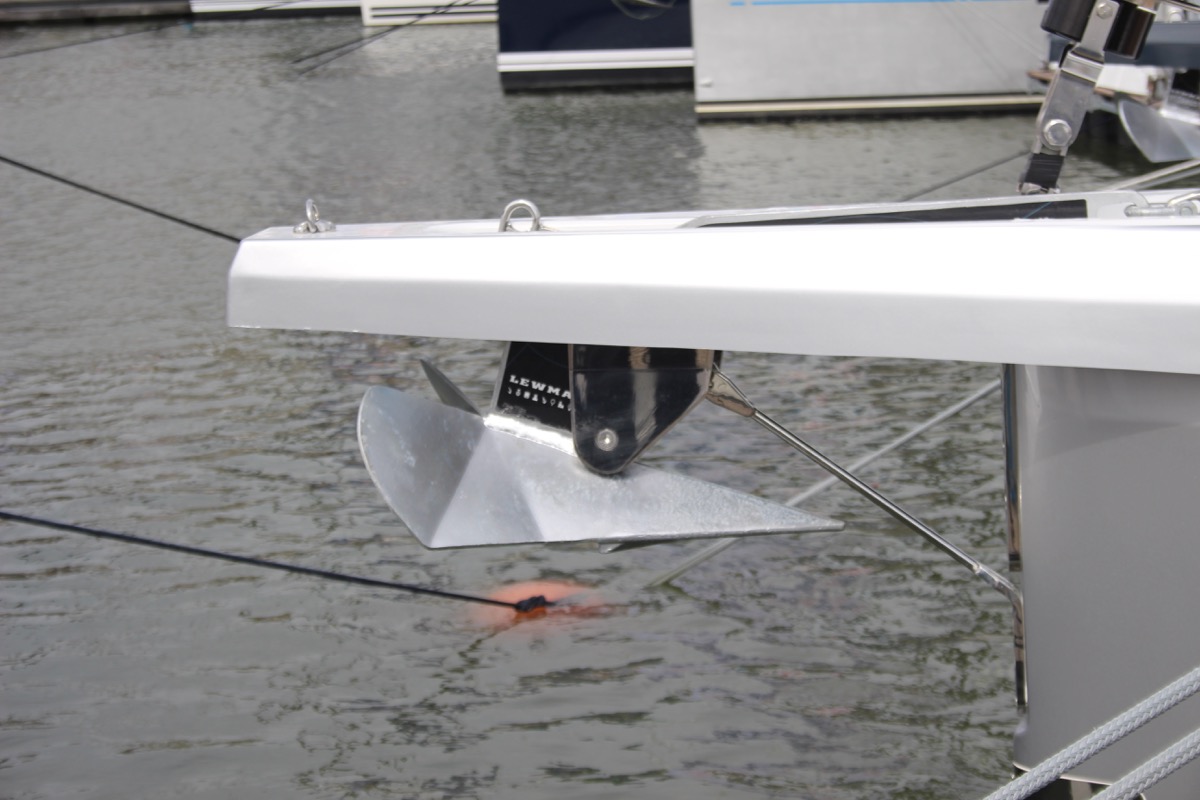
Most sailboats carry 1 - 3 anchors: one bow anchor (the main one) and two stern anchors. The last two are optional and are mostly used by bluewater cruisers.

I hope this was helpful, and that you've gained a good understanding of the different parts involved in sailing. I wanted to write a good walk-through instead of overwhelming you with lists and lists of nautical terms. I hope I've succeeded. If so, I appreciate any comments and tips below.
I've tried to be as comprehensive as possible, without getting into the real nitty gritty. That would make for a gigantic article. However, if you feel I've left something out that really should be in here, please let me know in the comments below, so I can update the article.
I own a small 20 foot yacht called a Red witch made locally back in the 70s here in Western Australia i found your article great and enjoyed reading it i know it will be a great help for me in my future leaning to sail regards John.
David Gardner
İ think this is a good explanation of the difference between a ”rope” and a ”line”:
Rope is unemployed cordage. In other words, when it is in a coil and has not been assigned a job, it is just a rope.
On the other hand, when you prepare a rope for a specific task, it becomes employed and is a line. The line is labeled by the job it performs; for example, anchor line, dock line, fender line, etc.
Hey Mr. Buckles
I am taking on new crew to race with me on my Flying Scot (19ft dingy). I find your Sailboat Parts Explained to be clear and concise. I believe it will help my new crew learn the language that we use on the boat quickly without being overwhelmed.
PS: my grandparents were from Friesland and emigrated to America.
Thank you Shawn for the well written, clear and easy to digest introductory article. Just after reading this first article I feel excited and ready to set sails and go!! LOL!! Cheers! Daniel.
steve Balog
well done, chap
Great intro. However, the overview diagram misidentifies the cockpit location. The cockpit is located aft of the helm. Your diagram points to a location to the fore of the helm.
William Thompson-Ambrose
An excellent introduction to the basic anatomy and function of the sailboat. Anyone who wants to start sailing should consider the above article before stepping aboard! Thank-you
James Huskisson
Thanks for you efforts mate. We’ve all got to start somewhere. Thanks for sharing. Hoping to my first yacht. 25ft Holland. Would love to cross the Bass Strait one day to Tasmania. 👌 Cheers mate
Alan Alexander Percy
thankyou ijust aquired my first sailboat at 66yrs of age its down at pelican point a beautifull place in virginia usa my sailboat is a redwing 30 if you are ever in the area i wouldnt mind your guidance and superior knowledge of how to sail but iam sure your fantastic article will help my sailboat is wings 30 ft
Thanks for quick refresher course. Having sailed in California for 20+ years I now live in Spain where I have to take a spanish exam for a sailboat license. Problem is, it’s only in spanish. So a lot to learn for an old guy like me.
Very comprehensive, thank you
Your article really brought all the pieces together for me today. I have been adventuring my first sailing voyage for 2 months from the Carolinas and am now in Eleuthera waiting on weather to make the Exumas!!! Great job and thanks
Helen Ballard
I’ve at last found something of an adventure to have in sailing, so I’m starting at the basics, I have done a little sailing but need more despite being over 60 life in the old dog etc, thanks for your information 😊
Barbara Scott
I don’t have a sailboat, neither do l plan to literally take to the waters. But for mental exercise, l have decided to take to sailing in my Bermuda sloop, learning what it takes to become a good sailor and run a tight ship, even if it’s just imaginary. Thank you for helping me on my journey to countless adventures and misadventures, just to keep it out of the doldrums! (I’m a 69 year old African American female who have rediscovered why l enjoyed reading The Adventures of Robert Louis Stevenson as well as his captivating description of sea, wind, sailboat,and sailor).
Great article and very good information source for a beginner like me. But I didn’t find out what I had hoped to, which is, what are all those noisy bits of kit on top of the mast? I know the one with the arrow is a weather vane, but the rest? Many thanks, Jay.
Louis Cohen
The main halyard is attached to the head of the mainsail, not the to the mainsheet. In the USA, we say gaff, not gaffer. The gaff often has its own halyard separate from the main halyard.
Other than that it’s a nice article with good diagrams.
A Girl Who Has an Open Sail Dream
Wow! That was a lot of great detail! Thank you, this is going to help me a lot on my project!
Hi, good info, do u know a book that explains all the systems on a candc 27,
Leave a comment
You may also like, guide to understanding sail rig types (with pictures).
There are a lot of different sail rig types and it can be difficult to remember what's what. So I've come up with a system. Let me explain it in this article.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

The Illustrated Guide To Boat Hull Types (11 Examples)

How To Live On a Boat For Free: How I'd Do It

How To Live on a Sailboat: Consider These 5 Things
A Guide to the Different Parts of a Sailboat

Table of Contents
Last Updated on November 29, 2023 by Boatsetter Team
When you use Boatsetter, you have the opportunity to choose from a myriad of different sailboat rentals from all over the United States and beyond . A sailboat is a perfect way to relax on the water, either on a solo adventure or on an excursion with friends and family.
When you rent a sailboat with Boatsetter, you will have the option to book a captained sailboat to enjoy your day out on the water or book bareboat to hone your sailing skills. Either way, you may be interested in the intricacies of a sailboat and its different parts. If this sounds like you, you have come to the right place. In this article, we go in-depth about the different parts of a sailboat so that you can be more knowledgeable about whatever boat you may choose and come away from reading this feeling more confident about the whole sailing experience.
A basic sailboat is composed of at least 12 parts: the hull , the keel , the rudder , the mast, the mainsail, the boom, the kicking strap (boom vang), the topping lift, the jib, the spinnaker, the genoa, the backstay, and the forestay. Read all the way through for the definition of each sailboat part and to know how they work.
Explore sailboats for rent near you or wherever you want to go

In short, the hull is the watertight body of the ship or boat. There are different types of hulls that a sailboat may have, and these different hulls will often affect the speed and stability of the boat.
Displacement Hulls
Most sailboats have displacement hulls , like round bottom hulls, which move through the water by pushing water aside and are designed to cut through the water with very little propulsion. The reason these are called displacement hulls is that if you lower the boat into the water, some of the water moves out of the way to adjust for the boat, and if you could weigh the displayed water, you would find that it equals the weight of the boat, and that weight is the boat’s displacement. One thing to know about displacement hulls is that boats with these hulls are usually limited to slower speeds.
Planing Hull
Another type of hull is a planing hull. These hulls are designed to rise and glide on top of the water when enough power is supplied. When there is not enough power behind the boat, these boats often act as displacement hulls, such as when a boat is at rest. However, they climb to the surface of the water as they begin to move faster. Unlike the round bottom displacement hulls, these planing hulls will often have flat or v-shaped bottoms. These are very common with motor-driven water vessels, such as pontoon boats, but they can also be found on smaller sailboats which allow them to glide quickly over the water.
Finally, sailboats can differ depending on the number of hulls that they have. There are three options: monohulls (one hull), catamarans (two hulls), and trimarans (three hulls).
Monohulls , which have only a single hull, will usually be the typical round bottom displacement hull or occasionally the flat bottomed or v-shaped planning hull. Catamarans have two hulls with a deck or a trampoline in between, with the extra hulls providing increased stability. Finally, trimarans have three hulls — a main hull in the middle and two side hulls used for stability. These trimarans have gained popularity because of their excellent stability and ability to go at high speeds.
When evaluating a sailboat , it is important to pay attention to the type of hull that the boat has because the type of hull a sailboat has can drastically change the sailing experience, especially when it comes to stability and speed.
All sailboats have a keel, a flat blade sticking down into the water from the sailboat’s hull bottom. It has several functions: it provides counterbalance, life, controls sideways movement, holds the boat’s ballast , and helps prevent the boat from capsizing. When a boat leans from one side to the other, the keel and its ballast counteract the movement and prevent the boat from completely tipping over.
As with hulls, there are a number of different types of keels, though the two most common types of keels on recreational sailboats are the full keel or the fin keel. A full keel is larger than a fin keel and is much more stable. The full keel is generally half or more of the length of the sailboat. However, it is much slower than the fin keel. A fin keel, which is smaller than the full keel, offers less water resistance and therefore affords higher speeds.
A more recent feature on sailboats is the “winged keel,” which is short and shallow but carries a lot of weight in two “wings” that run sideways from the keel’s main part. Another more recent invention in sailing is the concept of the canting keels, which are designed to move the weight at the bottom of the sailboat to the upwind side. This invention allows the boat to carry more sails.
The Rudder
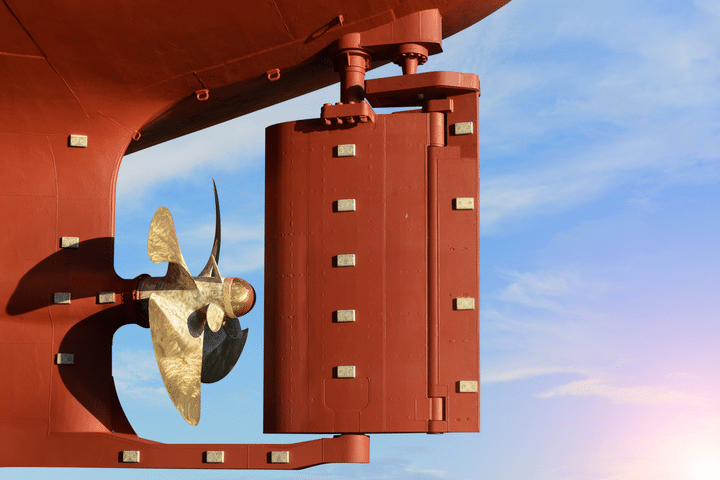
A rudder is the primary control surface used to steer a sailboat. A rudder is a vertical blade that is either attached to the flat surface of the boat’s stern (the back of the boat) or under the boat. The rudder works by deflecting water flow. When the person steering the boat turns the rudder, the water strikes it with increased force on one side and decreased force on the other, turning the boat in the direction of lower pressure.
On most smaller sailboats, the helmsman — the person steering the boat — uses a “ tiller ” to turn the rudder. The “tiller” is a stick made of wood or some type of metal attached to the top of the rudder. However, larger boats will generally use a wheel to steer the rudder since it provides greater leverage for turning the rudder, necessary for larger boats’ weight and water resistance.
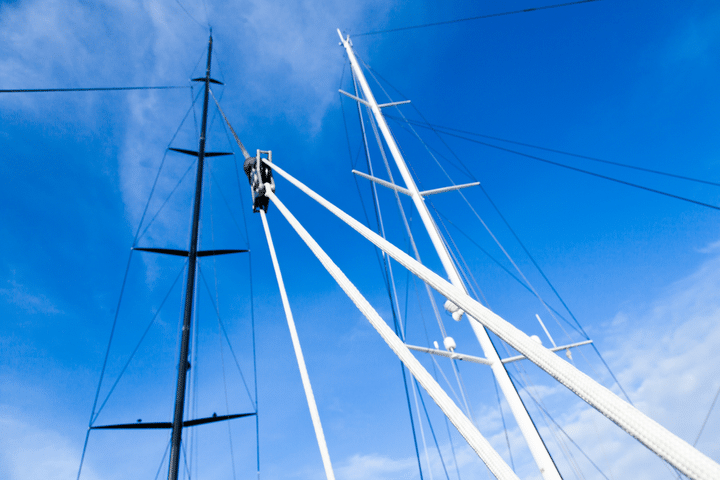

The mast of a sailboat is a tall vertical pole that supports the sails. Larger ships often have multiple masts. The different types of masts are as follows:
(1) The Foremast — This is the first mast near the bow (front) of the boat, and it is the mast that is before the mainmast.
(2) The Mainmast — This is the tallest mast, usually located near the ship’s center.
(3) The Mizzen mast — This is the third mast closest to the stern (back), immediately in the back of the mainmast. It is always shorter than the mainmast and is typically shorter than the foremast.
The Main Sail
The mainsail is the principal sail on a sailboat, and it is set on the backside of the mainmast. It is the main source that propels the boat windward.
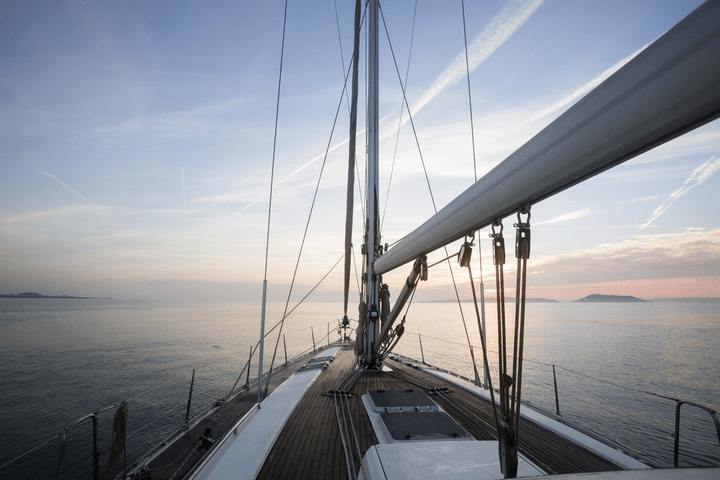

A boom is a spar (a pole made of wood or some other type of lightweight metal) along the bottom of a fore-and-aft rigged sail, which greatly improves the control of the angle and the shape of the sail, making it an indispensable tool for the navigation of the boat by controlling the sailes. The boom’s primary action is to keep the foot (bottom) of the sail flatter when the sail angle is away from the centerline of the sailboat.
The Kicking Strap (Boom Vang)
The boom vang is the line or piston system on a sailboat used to exert a downward force on the boom, enabling one to control the sail’s shape. The vang typically runs from the base of the mast to a point about a third of the way out the boom. It holds the boom down, enabling it to flatten the mainsail.
The Topping Lift
The topping lift is a line that is a part of the rigging on a sailboat, which applies an upward force on a spar (a pole) or a boom. Topping lifts are also used to hold a boom up when it’s sail is lowered. This line runs from the free end of the boom forward to the top of the mast. The line may run over a block at the top of the mast and down the deck to allow it to be adjusted.

A jib is a triangular staysail set ahead of the foremost mast of a sailboat. Its tack is fixed to the bowsprit, the bow, or the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsails on modern boats.
The Spinnaker

A spinnaker is a type of sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind from a reaching downwind course. The spinnaker fills up with wind and balloons out in front of the sailboat when it is deployed. This maneuver is called “flying.” The spinnaker is constructed of very lightweight material, such a nylon fabric and on many sailing vessels, it is very brightly colored.
Another name for the spinnaker is the “chute” because it often resembles a parachute, both in the material it is constructed from and its appearance when it is full of wind.
People often use the term genoa and jib as if they were the same thing, but there is a marked difference between these two types of sails. A job is no larger than a foretriangle, the triangular area formed by the mast, the deck or bowsprit, and the forestay. On the other hand, a genoa is larger than the jib, with part of the sail going past the mast and overlapping the mainsail. These two sails, however, serve very similar purposes.
The Backstay

The backstay is a standing rigging that runs from the mast to the transom (the vertical section at the back of the boat), counteracting the forestay and the jib. The backstay is an important sail trip, control and directly affects the mainsail’s shape and the headsail.
There are two general categories of backstays:
1) A permanent backstay is attached to the top of the mast and may or may not be readily adjustable.
2) A running backstay is attached about two-thirds up the mast and sometimes at multiple locations along the mast. Most modern sailboats will have a permanent backstay, and some will have permanent backstays combined with a running backstay.
The Forestay

A forestay is a piece of standing rigging that keeps the mast from falling backward. It is attached at the very top of the mast, or at certain points near the top of the mast, with the other end of the forestay being attached to the bow (the front of the boat). Often a sail, such as a jib or a genoa, is attached to the forestay.
A forestay might be made from stainless steel wire, stainless steel rod or carbon rod, or galvanized wire or natural fibers.
Parts of a sail
Sails are vital for sailboats, made up of complex parts that improve performance and maneuverability. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the different parts of that make up the sails.
Luff – The luff is a vertical sail part that maintains its shape and generates lift by interacting with the wind. It attaches securely with a bolt rope or luff tape for easy hoisting.
Leech – The leech controls air flow and reduces turbulence. Battens or leech lines are used to maintain shape and prevent fluttering.
Foot – The foot of a sail connects the luff and leech at the bottom edge. It helps define the sail’s shape and area. The outhaul is used to adjust its tension and shape.
Head – The sail’s head is where the luff and leech meet. It has a reinforced section for attaching the halyard to raise the sail.
Battens -The b attens are placed horizontally in sail pockets to maintain shape and optimize performance in varying wind conditions. They provide structural support from luff to leech.
Telltales – Sailors use telltales to adjust sail trim and ensure optimal performance.
Clew – The clew is important for shaping the sail and connecting the sheet, which regulates the angle and tension, producing energy. It’s located at the lower back corner of the sail.
Sailing is a favorite pastime for millions of Americans across the country. For some, there is nothing better than gliding across the water propelled by nothing more than the natural force of the wind alone. For both experienced and non-experienced sailors alike, Boatsetter is the perfect place to get your ideal sailboat rental from the mouthwatering Florida keys to the crystal blue waters of the Caribbean .
Smaller sailing boats are perfect for a single day out on the water, either by yourself or with friends and family. In comparison, larger sailing boats and sailing yachts can allow you days of luxury on longer excursions full of adventure and luxury.
Whatever your sailing dreams are, it is always good to know, for both the experienced sailor and the novice, all about the sailboat’s different parts. In this article, we learned all about the boat’s hull, the keel, the rudder, the mast, the mainsail, the boom, the kicking strap (boom vang), the topping lift, the jib, the spinnaker, the genoa, the backstay, and the forestay, which make up the basic parts of any sailboat you might find yourself on.
About us
Boatsetter is the go-to app for boat rentals and on-water experiences. Whatever the adventure, we’ve got a boat for that—Set sail , start the party , go yachting , make your trophy catch , and hone your watersports skills! Download the Boatsetter app ( App Store | Google Play ). Make sure to follow @boatsetter on Instagram, and tag us in all your boat day pictures for the chance to be featured.
Rent. List. Share—Only at Boatsetter

Boatsetter empowers people to explore with confidence by showing them a world of possibility on the water. Rent a boat, list your boat, or become a Boatsetter captain today.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

Boatsetter, Rec Boat Holdings Form Strategic Partnership

How to Plan a Boat Trip

Honolulu, Hawaii Fishing Guide


Fishing Report from St. Petersburg – Late October Afternoon // Inshore Action Charters
Parts of a Sailboat

Sailboats share many parts with other boats, such as keels, decks, and sometimes engines. But parts like halyards, sheets, and blocks are unique to sailboats.
Sailboats require four main parts to operate: a hull, mast, sail, and rudder. The hull is the body of the boat, and all other parts are directly or indirectly connected to it. The mast is a long pole that serves as a guide and mounting point for the sail. The sail catches the wind and propels the boat, and the rudder directs the boat and acts as its steering.
Here are all the main parts of a typical cruising sailboat , including hardware, lines, controls, cabin items, and a rundown of common sailing terminology.
Table of contents
Port, Starboard, Bow, Stem, and Stern
Before we get into the parts of a sailboat, let’s get a handle on sailboat direction. The bow of the boat is the front (forward), and the stern is the rear (aft). The stem is the forward-most part of the bow and determines its shape. These words describe the general area of front and back.
When determining port and starboard, picture looking down on the boat with the bow oriented forward. The port side is the left side of the boat, and the starboard is the right side. Now picture yourself at the controls of your boat.
If your lookout sees an obstacle off the port bow, which direction should you look? That’s right—the obstacle is forward and to the left of you. Now, we’ll go over the basic parts of a sailboat.
Basic Parts of a Sailboat
What are the basic parts of a sailboat? These are items that are essential to the operation of the boat and universal across most sailing craft. Every sailor should know where these parts are and what they do. Here are nine fundamental sailboat parts, their function, and why they’re important.
The hull is the ‘boat’ itself. It comprises the frame of the boat, the skin that keeps the water out and serves as the mounting point for everything else on the boat (both directly and indirectly). Simply put, if you punch a hole in the hull, water will come into the boat. Sailboat hulls are constructed most commonly out of fiberglass or hardwood (such as white oak), but some boat hulls are made out of aluminum, steel, and even a material called ferrocement.
The deck is the platform that covers the hull. It’s the place where you walk when you’re not inside the boat. Most people would consider the deck as any place ‘on top’ of the hull. The deck serves as a mounting point for essential boat hardware such as the mast and winches. We’ll get into those later; just think of the deck as the visible top area of the vessel. Decks are often made of fiberglass as well, but traditional boats use teak wood planking in this area. You’ll often find abrasive anti-slip material on the deck, as sailors often walk across it in wet conditions.
The keel is the structural backbone of the boat. It’s located in the bottom of the hull and serves as a sort of ‘spine’ to which all frame members are mounted during construction. The keel is an essential part of the boat and cannot be broken or damaged. You’ll often hear the term ‘keelboat’ in the sailing community. This word describes a sailboat with a long and deep keel, which is like a thin fin that runs the length of the hull. Keelboats are seaworthy vessels, as the elongated hull adds stability and keeps the boat on a straight track.
Centerboard
Many sailboats don’t have a long, deep keel, but they still need some sort of fin to keep the boat tracking straight. To substitute a long keel, many boats utilize a dagger-like board called a centerboard . This plate protrudes underneath the center of the boat, usually between one and three feet below the bottom of the hull. Centerboards are often retractable, which is great for towing and beaching. Centerboards are most common on small sailboats designed for inland or coastal cruising.
The cockpit is usually located in the rear of the boat. It features seating for the crew and controls for the steering, sails, and engine. The cockpit is the command center of the sailboat and often features storage lockers under the seats. Many cockpits are self-draining, which means they’re located above the water line and clear themselves of water accumulation. Some sailboats have enclosed cockpits for off-shore sailing. In a typical cruising sailboat , the cockpit usually takes up ⅓ of the total length of the boat or less.
The mast is the big pole extending from the deck of the sailboat. It connects the sail to the boat and serves as a frame for all sails carried by the vessel. The mast is a key part of the sail plan and helps determine what kind of boat you’re looking at. Most sailboats have just one mast, but others have numerous masts. A schooner, for example, has two masts and a specific sail plan. A yawl also has two, but each mast serves a separate function.
The rudder steers the boat and is located on or under the stern of the vessel. Rudders are an essential part of the boat, and they’re particularly sensitive to impact or misalignment. On some boats, the rudder is completely invisible when in the water. Other boats have retractable rudders for beaching or towing. Fundamentally, a rudder is just a plate that’s hinged to move side to side. It’s connected to the tiller or the helm, which we’ll cover in a bit.
The sail is what propels the boat, and most boats have more than one. The aft (rear) sail on a single-masted boat is called the mainsail , and it’s the largest of the two primary sails. The triangular forward (front) sail is called the jib, and it’s generally smaller than the mainsail. Other sails include the spinnaker, which is like a loosely-mounted parachute that flies in front of the boat during conditions of low wind.
The boom is a hinged rod that extends perpendicular to the mast. It’s mounted on the lower part of the mast, and it controls the side-to-side position of the mainsail. The best way to remember the boom is to consider what happens when it swings side to side. If you’re not paying attention, a swinging boom could give you a nice crack on the head. Think of the boom as the throttle of the boat. If you’re properly pointed relative to the wind, pulling in the boom will increase the speed of the boat. This is where the bottom of the sail connects to the mast. The boom is also connected to the deck and adjustable using a winch and a crank.
Here is some of the hardware you’ll find on a typical sailboat. These items are usually mounted to the hull, on the deck, or to the mast. Boat hardware consists of control systems and other items that are essential to the operation or integrity of the boat.
Cleats are the universal mounting points for ropes on the deck. Cleats are used for tying up to the dock, securing lines, and tethering important items that can’t fall overboard. There’s a special kind of knot called a ‘cleat knot,’ which is essential to learn before sailing. A properly tied cleat will stay secure in almost all conditions, and it’ll be easy to untie if the need arises. An important distinction must be made for clam cleats, which are spring-loaded sets of jaws that secure rigging lines that need to be adjusted frequently.
Block is a nautical word for a pulley. Blocks (pulleys) are everywhere on a sailboat, and they’re an essential part of the rigging system. Blocks distribute and regulate force. For example, a deck-mounted block can change the direction of a line from vertical to horizontal, allowing you to apply a horizontal force to lift something vertically. Blocks also reduce the force required to lift heavy loads and help make adjustments more precise.
Winches are cylindrical mechanical devices that transmit force. Winches are often located on either side of the boat. They’re multi-directional like a socket wrench and feature one-way locking mechanisms for raising, lowering, tightening, and loosening lines. Winches have a hole in the top for a crank, which makes it easy to wind rope in and out. Winches are present on almost every medium to large sailboat. They’re either manual or electrically-powered.
A hatch is a watertight or water-resistant door used to enter the cabin or storage compartment of a boat. Hatches can be flush with the deck and hinged, threaded like a large screw, or they can slide back and forth. The purpose of a hatch is to keep water out when closed and allow easy access to the interior parts of the boat.
Tiller and Helm
The tiller and helm are used to control the direction of the rudder and steer the boat. Usually, a boat has either a tiller or a helm. The tiller is the most basic steering control and consists of a simple rod connected to the rudder or rudder shaft. Tillers move side to side and point in the opposite direction that the boat steers. The helm is essentially a steering wheel, and it operates the same way that a car steering wheel does. The helm is connected to the rudder by complex mechanical or hydraulic linkage.
Mast and Sail Components
Mast and sail components are referred to as ‘rigging’ in most cases. These items are part of the wind-powered propulsion system of the boat. You’ll operate these systems to control the speed of the boat. Here are three common sail components that you’ll need to understand before hitting the water.
Stays are the lines that secure the mast to the boat. Usually, the mast is bolted or tied to the deck of the boat; but much of the load and pressure created by the wind is transferred to the stays. Stays are usually made of strong stainless steel cable. Losing a stay at sea is a serious problem, as these small cables keep the mast from collapsing.
Halyards are the ropes used to hoist and lower the sail on the mast. They also hoist flags, spars, and other components that need to be raised and lowered. Halyards are usually found on the mast and are fixed to cleats or winches around the boat.
Sheets and halyards are often confused, but they serve a very different function. Sheets are the control lines of the sail. These ropes control how far in or out the sail is, and they’re usually found connected to the jib (jib sheet) and the mainsail (mainsheet). Sheets are controlled by winches and blocks and secured onto cleats or clam cleats on the deck. Sheets can be controlled from the cockpit of the boat.
Navigation components are the parts of the sailboat used to find direction and alert other boats of your position. These four items aren’t the only navigation items found on sailboats, but they’re the most common.
This item should be self-explanatory, but it’s essential nonetheless. A compass is arguably the most basic and important marine navigation item. It shows you what direction you’re heading. Sailboat compasses are precise instruments designed to display an accurate heading no matter how much the boat rolls up and down or side to side. Compasses are usually mounted in the cockpit, in clear view of the captain.
Charts are old-fashioned navigational tools and indicate important information such as water depth and the location of ship channels. Learning to read and purchasing charts is essential, even in the age of modern GPS navigation. When all else fails, a chart can help guide you and your vessel to safety and away from hazardous areas. No electricity is required.
Navigation Lights
Navigation lights are mandatory beacons located around the boat. These lights help other boats figure out where you are and where you’re going. Sailboats are required to have red and green bow lights. Red indicates port, and green indicates starboard. This is how boats determine if they’re looking at your bow or stern. Other lights, such as a white stern light, a mast light, are also necessary during specific circumstances. Check your state requirements for lighting.
VHF radios are the standard marine over-the-air communication system. You can use a VHF radio to communicate with the coast guard, other boats, harbors, towing services, and drawbridges. It’s important to learn and write down the specific channels and call signs for each situation, as you need to be able to properly communicate on the radio.
The cabin is the ‘below decks’ area of the sailboat and usually contains living quarters for the captain and crew. Not all boats have cabins, and cabin size varies widely. Some sailboats have rudimentary cabins with basic sleeping accommodations and sitting headroom. Other boats have full standing headroom, shower and wash facilities, full-size kitchens, and separate staterooms for sleeping and sitting. The cabin is usually located forward of the cockpit. Here are some common sailboat parts located within the cabin.
The berth is the sleeping area of a boat. Berths are often convertible, which means they fold or rearrange into a table and seating area. There are numerous kinds of berths. The ‘V’ or ‘vee’ berth is a triangle-shaped sleeping area located in the bow of the boat. Side berths typically convert into couches or settees, and pole berths are essentially cots that roll up and stow away easily.
The bilge is the bottommost interior part of the boat. It’s usually located under the floor in the cabin. When water finds its way into the boat, it drains down to the bilge and gets pumped out by bilge pumps. Bilge pumps are an essential piece of hardware, as they keep the boat dry and prevent sinking. Some boats have a wet bilge, which means it’s always full of water (and supposed to be). Most boats have a dry bilge.
Portlights are watertight windows located in the upper part of the cabin. They can usually be opened or secured using threaded latches. Portlights are generally smaller than traditional portholes and offer a watertight barrier between the inside and outside of the cabin. They’re also useful for ventilation.
Gimballed Utilities
A gimbal is a special type of hinge that keeps an item vertical when the boat rolls. Oil lamps are commonly fitted to gimbals, so they stay upright when the boat bobs around. Stoves are also gimballed, which is extremely useful for cooking or boiling water when the weather gets rough.
Head is the nautical term for a toilet. Most medium-sized sailboats have compact wash facilities that sailors refer to as the ‘head,’ or a porta-potty at the bare minimum. A sailboat’s bathroom usually consists of a marine toilet, a sink, and often a shower with a drain in the floor.
Related Articles
Daniel Wade
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Sailboat Parts
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

Dufour Sailboats Guide & Common Problems
October 16, 2024

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 24, 2024

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat

No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
The Different Parts Of A Sailboat Explained
A sailboat consists of hundreds of parts, each with its specific term and function. From stern to bow, keel to mast, each part and its equipment plays a vital role in making the vessel seaworthy and able to sail.
In this guide, I’ll show you most of the components so you can better understand what they are and their function. We’ll begin with the main components, move to the basic features, and finish with our interior and equipment.
The main parts of a sailboat

The main parts of a sailboat are the key components that make it a vessel able to sail. You’ll notice that the structure has several distinct differences from powerboats.
We can categorize the main parts into the following:
- Hull: The main structure, or “body” part of a boat.
- Keel: The heavy fin at the bottom allows stability under sail.
- Rudder: The fin sticking down at the stern, allowing us to steer the vessel.
- Mast: The “spars” or “poles” holding the sails.
- Rigging: The standing rig is the wires that supports the mast. The running rigging is all the lines that control the sails.
- Boom: The horizontal spar supporting the bottom of the mainsail.
- Sails: The canvas used to harness the energy of the wind.
Let’s dig a bit deeper into each of the components.
Hull – The main structure
A sailboat’s hull is the vessel’s main body or structure. The shape is vital to the boat’s performance and stability, and you have probably seen boats in many different forms. Older vessels are typically narrow, with a rounded underbody and a small stern. Modern designs have a flatter belly and broad stern supporting dual helm stations.
One of the hull’s primary functions is to displace water and provide buoyancy to keep the boat afloat. The hull is also the structure that holds the vessel’s living compartments and all its equipment. The main structure must be strong enough to withstand the forces of the water and any rough weather conditions that Mother Nature might throw at it.
Fiberglass (GRP), steel, aluminum, and wood are the most commonly used hull materials, each with pros and cons.
You can learn more about hull materials and their strengths in this article .
A monohull is a type of sailboat that has a single hull. Monohulls are classified into two categories based on weight and shape: planing and displacement hulls.
Sailboats with more than one hull are called multihulls. There are two types of multihulls: catamarans, which have two, and trimarans, which have three. These boats are typically designed with planing hulls.
Keel – The fin under the boat
The keel of a sailboat is a structural fin that extends downward from the bottom of the hull. There are several types of keels, each with unique characteristics and advantages. They all serve the same fundamental purpose of stabilizing the boat when we sail by adding lateral resistance in the water and weight at the vessel’s bottom.
Standard keel designs include:
- Lifting Keel
Some sailboats have a retractable centerboard functioning as their keel, allowing them to take the boat into shallower areas.
Rudder – To steer the boat
The rudder is a flat surface that sits perpendicular to the waterline. It is connected to the boat by a pivot point, allowing it to swivel left and right. When the steering wheel or tiller is turned, the rudder moves, creating drag in the water causing the boat to turn. The size and shape of the rudder can vary depending on the size and type of boat.
The most commonly seen rudder designs:
- Full skeg-supported
- Semi skeg-supported
Skeg-supported rudders are structurally one of the most reliable and robust constructions, but they are less efficient than a balanced rudder performance-wise. Balanced rudders pivot around their vertical center, giving less drag in the water and higher maneuverability at the cost of being a more vulnerable construction.
Twin rudders are often seen on modern performance sailboats with a wide stern. When the sailboat heel over , the leeward rudder gets better track through the water than a single rudder placed at the vessel’s center line. Contrary to some misconceptions, they can’t be controlled individually, even if the boat has two steering wheels.
Mast and Rigging – Supporting the sails

The mast is the long vertical spar that extends upward from the deck of a sailboat and holds the sails. It is the tallest part of the boat and is typically made of wood, aluminum, or carbon fiber. The mast is held in place by stays and shrouds, which form the sailboat’s standing rigging.
Depending on the rig the boat is manufactured with, there are several different types of masts. For example, a sloop-rigged sailboat will have only one main mast, while a ketch-rigged vessel will have a smaller additional mizzen mast placed further aft from the main mast.
There are two types of rigging:
- The Standing rigging consists of the stays and shrouds that keep the mast or masts in place.
- The Running rigging is the lines we use to hoist, lower, and control the sails.
Pro Tip: “S par” is a general term for a pole made of a solid material like wood, metal, or composite and is used to support a boat’s sail. The mast, boom, spreaders, and poles are defined as spars.
Boom – Supporting the mainsail
The boom is a horizontal beam extending from the mast and supporting the mainsail’s tack and clew (bottom two corners). It is attached to the mast by a hinge called a Gooseneck .
We use the boom to control the shape and angle of the mainsail to optimize its efficiency and power. Some booms also have a Vang or Rod-Kicker installed to assist in trimming the mainsail.
Sails – The canvas used to harness the energy of the wind
Most vessels have at least two sails, depending on the rig type and boat setup.
The Mainsail flies behind the mast, on top of the boom. Although it may not always be the largest sail on the vessel, we commonly refer to it as “the main.”
The Headsail(s ), located in front of the mast, are often of different sizes and shapes, and many sailboats have more than one. The Jib and Genoa are two of the most common types.
Different types of sails are used for various sail plans and situations, and you can learn more about them in this guide .
Now that we had a look at the main parts of the boat, let us dive deeper and look at the rest of the vessel.
The starboard and port side of the boat
Learning about the boat’s components is very important, but we must also know how to orient ourselves on the vessel. Using the words “left and right” on onboard often leads to confusion.
If you refer to something on the left side of the boat, the person facing you will be confused. He won’t know if you are referring to his or your left. This is where the terms “Port” and “ Starboard ” make better sense.

When facing the front of the boat or the bow , your left side of the boat is the port side, and the right-hand side is the starboard . If you turn around and face the back of the boat or the stern , your right-hand side will be the port side.
- A red light identifies the port side of a vessel.
- A green light identifies the starboard side of a vessel.
Windward and Leeward
- The windward side of the boat is the side facing the wind. If the wind comes from your right-hand side while facing forward, the starboard side is windward. This will be the boat’s high side as the wind heels the boat over.
- The leeward side of the boat is the side opposite to the wind. This will be the lower side of the ship while sailing as the wind heels the boat over.
Windward and leeward are two of the most important aspects to understand when sailing and navigating. Not only to identify equipment and gear on each side of the boat but to avoid collisions when sailing close to other vessels. There are rules on the water dictating which boat is “Stand On” and which has to “Give Way” depending on whether you are the windward or the leeward vessel in the situation.
Read this article to access a free course on navigation rules .
Basic parts of a sailboat

The boat’s bow is the front part, typically shaped like a “V” to cut through the waves. Larger vessels often have a locker for their anchor chain in this section, holding the anchor at the front.
The midship section is the center of the boat. Some refer to this part as amidships.
The stern is the rear or back part of the boat. It is also referred to as the aft . I’ve had French crew calling the stern the butt of the vessel, which is funny but also correct!
The beam is the widest part of the boat. Also referred to as the sides on the middle.
The transom is a flat surface across the stern of the boat.
The waterline is the part where the hull (body) of the boat meets the water. Many vessels have a painted stripe to mark the waterline, indicating how loaded the ship is. If you have too much stuff on board, the waterline goes underwater, and it is time to do some housekeeping!
The freeboard is the vertical part of the ship side between the water and the deck. When you see a blue boat like Ellidah, the freeboard is the blue part.
The deck is the “floor” of the boat when you are outside. You have probably heard the term “All hands on deck!” The front deck is the deck space in front of the mast. Side decks are the decks on the boat’s sides.
The mid-deck is between the cockpit and the mast. The aft deck is the deck behind the cockpit. Sailboats with aft cockpits often don’t have any aft decks, but some have a swimming platform instead.
The cockpit is the boat’s steering position and where you will find the helm.
The helm is the position the helmsman uses to steer the boat. Smaller sailboats often use a tiller to navigate, while most bigger yachts have one or two steering wheels.
Main parts below deck (inside the boat)
Let us look at the interior to highlight and learn about the parts we have below the deck.

The Companionway
The companionway is the “front door” of the boat. This is where the steps lead from the cockpit or deck down below. It is usually opened and closed using a hatch, two doors, or a plate.
The Galley
The galley is the boat’s kitchen. This is where sailors prepare their delicious meals.
The Saloon
The saloon is basically the boat’s living room, usually where you find the settee and dinette. This is where delicious meals from the galley are served together with refreshing beverages in good company.
The settee is the sofa or couch in a boat. It is also used as a sea berth to sleep in when sailing.
The dinette is the area where you can sit down at a table and eat your dinner. It’s also perfect for consuming rum and a game of cards in good company.
A cabin is often used as a bedroom in a boat but is not necessarily where you sleep. Many boats have more than one cabin.
A berth is a place in the boat where you can sleep. This doesn’t necessarily have to be a bed and can often include the sleeping space in the saloon. Sea-berth usually refers to a sleeping position where you are tucked well in and can sleep when the boat is heeling over and moving around.
The head is the toilet on a boat. If your skipper tells you to go and clean the head, getting out the shampoo won’t do you any good!
Nav station
The navigation station is usually a chart table and a console with mysterious instruments like radios, switchboards, and complicated electronics. This is where adventures are planned and the skipper’s favorite seat onboard.

The bilge is a space in the bottom of the hull where water collects and sometimes a storage space for all sorts of things. It usually contains a bilge pump to pump out water that finds its way into the boat in various places.
A v-berth is a bed in the front cabin shaped like a V.
A bulkhead is a wall inside the boat, usually supporting the structure.
Hardware and Equipment
Sailboats come equipped with a variety of different hardware and equipment. While the specific items may vary from boat to boat, there are some essentials that nearly every sailboat has.

A winch is a metal drum that gives you a mechanical advantage and is used to control and tighten lines. These can be operated by turning a line around it and pulling manually or by a winch handle to get more force.
Most modern winches are so-called “self-tailing,” which means they lock the line on so you can winch the line without holding on to it. Some boats even have electrical winches operated by a button.
A cleat is a fitting used to fasten a rope. Most boats have at least 6 of these. One on each side on the bow, midship and stern. These are used to secure the boat to a mooring buoy or key. Many ships have more cleats than this for various lines and ropes, and they can be used for anything as they are strong points fitted to the hull.
The sprayhood is the boat’s windshield that protects the people in the cockpit from sea spray. Some vessels have a canvas sprayhood that can be folded down or removed. Others have solid sprayhoods, often called a hard dodger or a doghouse .
The bimini is the cockpit’s “roof.” It protects you from the elements and shelters you from spray, rain, and burning sun rays! A bimini can be made of canvas or hard material. A hard bimini can also be called a hardtop .
Dinghy

A dinghy is a little boat you use to get from the mothership to shore when you are at anchor, also called a tender or annex . It can be everything from a small inflatable rubber kayak to a RIB or even a solid boat.
An essential and valuable piece of kit as it is the daily driver for most cruisers. It is like the car of a land crab, used for all commuting on the water and hauling important stuff like beer, rum, and food onboard. Dinghies often have electric or petrol engines, which we call outboards.
Dinghies are also great to use for watersports, such as wakeboarding!
Like Captain Ron said in the movie, fenders are the rubber bumper things you hang off your boat to prevent it from scratching against something like the pontoon or another ship. It is conveniently also used to sit on or as a backrest while relaxing on deck.
A boat hook is a long stick with a hook at the end. Used to grab lines, items, and stuff that is too far to reach by hand, like cushions flying overboard. It is also convenient as a tool to push the boat away from another craft or the key. Most vessels have them on board.
The guard rail can be a flexible wire or a solid metal rail surrounding the boat to prevent us from falling overboard. Some also use a net as an addition for increased safety.
The pushpit is a metal guard rail around the stern of the boat. This is where the guard rail is secured on the stern: a common place to mount the BBQ, life raft, and the outboard for the dinghy.
The pulpit is the metal guardrail on the bow. This is where the guard rail is secured onto the bow.
The stanchions are the metal bars that keep the guard rail in place around the boat between the pushpit and the pulpit.
An arch is a typical structure made of stainless steel on the back of a boat and is often used to mount a variety of items like antennas, radars, solar panels, wind generators, etc. It is also convenient to use for lifting the dinghy and its outboard.

Ground Tackle
The ground tackle consists of several things:
- Your anchor
- Your anchor chain
- The link between the two
- The connection between the chain and your boat
It includes all equipment holding your boat to the ground. Larger boats sometimes have two anchors on the bow.
A windlass is a winch that hoists and lowers the anchor and chain. Most boats have one on the bow and some on the stern. These incredible things can be electrical or manual (some are both) and are essential to anchor your boat when not in a port or marina.
VHF stands for “Very High-Frequency Radio.” It broadcasts on the VHF network and allows you to communicate with others around you. Sadly, you won’t be able to tune in to your favorite radio show on these.
Still, they are essential for contacting other boats and port authorities. It is also the radio you will transmit an emergency mayday over in case of emergency. VHF radios sometimes require a license, depending on the country you are in.
Chartplotter
A Chartplotter is a navigation computer that shows various information on a screen, like charts, routes, radar images, etc. It is another vital piece of equipment that helps you navigate and maneuver the boat.
Final words
I hope this guide has been helpful and not too overwhelming for you. We’ve covered many of the parts of a sailboat and its terms and functions, but this article only touches on the basics. If you want to keep learning about sailing, I have written several other guides to help you get started.
Now that you have a basic understanding of sailboats, it’s time to take the next step and dive into a sailboat’s standing rigging .
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Parts of a sailboat | Boating Test Guide to Sailboat Parts

Learn about the various parts of a sailboat in our ultimate boating test guide for sailboat parts
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the parts of a sailboat! Whether you’re preparing for your boating license or simply brushing up on your sailing knowledge, understanding the anatomy of a sailboat is crucial. At [Your Website Name], we provide the most current and detailed boating test content available, making us your go-to resource for mastering sailboat parts and terminology. Whether you’re a novice or seasoned sailor, this guide will equip you with essential knowledge for navigating the waters confidently.
Table of Contents
Parts of a sailboat, simple parts of a sailboat, parts of the sail, anatomy of a sailboat, parts of a sail ship, what are the sails on a sailboat called, parts of a small sailboat, what are the parts of a sailboat labeled.
A sailboat is composed of several essential parts that work harmoniously to navigate through water using wind power. At its core is the hull, the main body that provides buoyancy and stability. Rising from the hull is the mast, a tall vertical spar that supports the sails, which are fabric sheets designed to catch and utilize wind energy for propulsion. The rigging, consisting of ropes, wires, and chains, supports and controls the sails’ position and tension. The boom, a horizontal spar attached to the bottom edge of the mainsail, aids in adjusting the sail’s angle. Beneath the hull, either a keel or a centerboard provides stability and prevents sideways movement. At the stern, the rudder directs the boat’s course, while the deck and cockpit provide platforms for crew and passengers, with winches and cleats facilitating the handling of ropes and lines essential for sail control and safety.
Here is a list of the several parts of a sailboat that work together to navigate through wind and water:
- Hull : The main body of the boat, which provides buoyancy and stability.
- Mast : A tall vertical spar or pole that supports the sails.
- Sails : Fabric sheets that catch wind and propel the boat forward.
- Rigging : The system of ropes, wires, and chains that support and control the sails.
- Boom : A horizontal spar attached to the bottom edge of the mainsail, used to control the sail’s position.
- Keel or Centerboard : A fin-like structure beneath the hull that prevents the boat from sliding sideways (keel) or can be raised or lowered (centerboard).
- Rudder : A flat, movable piece typically located at the stern (back) of the boat that steers the boat.
- Deck : The horizontal surface of the boat where crew and passengers stand or sit.
- Cockpit : A sunken area in the deck where the helm (steering wheel or tiller) and controls are located.
- Winches and Cleats : Devices used to control and secure ropes and lines.
These parts vary in size and configuration depending on the type and size of the sailboat, its intended use, and design.
In a boat test guide related to parts of a sailboat, potential answers could include:
- Hull : The main body of the boat that provides buoyancy and stability.
- Mast : A vertical spar or pole that supports the sails.
- Sails : Fabric sheets that catch wind to propel the boat.
- Rigging : Ropes, wires, and chains that control the position and tension of the sails.
- Boom : A horizontal spar attached to the bottom edge of the mainsail.
- Keel or Centerboard : Provides stability and prevents sideways movement.
- Rudder : Controls the boat’s direction at the stern.
- Deck and Cockpit : Platforms for crew and passengers.
- Winches and Cleats : Devices used for handling ropes and lines.
- Bow and Stern : The front and rear ends of the boat respectively.
These answers cover the fundamental components of a sailboat that are typically tested in boating certification exams.
In addition to understanding the parts of a sailboat , you will be expected to answer the following questions on your boating test. Here’s a brief summary of each part of a sailboat and how they might be relevant on a boater exam:
- Hull : The main body of the boat, typically quizzed on buoyancy, construction materials, and types (e.g., monohull, catamaran).
- Mast : Vertical spar supporting sails, tested on its parts (like the head, halyards, and spreaders) and types (e.g., single mast, multiple masts).
- Sails : Fabric sheets catching wind, assessed on types (e.g., mainsail, jib), sail parts (like luff, leech, and foot), and trim adjustments.
- Rigging : Ropes, wires, and chains controlling sail position and tension, quizzed on types (standing vs. running rigging), parts (like shrouds and stays), and basic knots.
- Boom : Horizontal spar attaching to the mainsail’s bottom edge, tested on its parts (like gooseneck and outhaul) and safety considerations.
- Keel or Centerboard : Provides stability and prevents sideways movement, quizzed on types (fixed vs. retractable), maintenance, and effects on sailing performance.
- Rudder : Controls boat direction at the stern, assessed on types (like spade vs. skeg rudders), operation, and emergency steering techniques.
- Deck and Cockpit : Platforms for crew and passengers, quizzed on safety features, equipment storage, and navigation instruments.
- Winches and Cleats : Devices for handling ropes and lines, tested on types (self-tailing vs. standard winches), usage, and safety precautions.
- Bow and Stern : Front and rear ends of the boat respectively, quizzed on docking procedures, anchoring techniques, and emergency procedures involving these areas.
These summaries provide a foundational understanding of sailboat parts and how they might be tested in boater certification exams.
The simple parts of a sailboat include:
- Hull : The main body of the boat that provides buoyancy and houses the internal components.
- Mast : A vertical spar that supports the sails and may have additional features like spreaders and halyards.
- Sails : Fabric sheets that catch wind to propel the boat, including the mainsail and headsails like jibs.
- Keel or Centerboard : Provides stability and prevents the boat from drifting sideways.
- Rudder : A vertical blade at the stern that steers the boat by changing its direction in the water.
- Deck : The upper surface of the hull, where crew members walk and work.
- Cockpit : An open area in the aft of the boat where the helm (steering wheel) and crew often sit.
- Winches and Cleats : Devices used to handle lines and secure them in place.
- Bow and Stern : The front and rear ends of the boat, respectively, important for docking and anchoring.
Understanding these basic parts is fundamental for operating and maintaining a sailboat safely and effectively.

The main parts that make up a sail on a sailboat include:
- Mainsail : The largest and primary sail on a sailboat, typically attached to the mast and boom.
- Headsail (Jib or Genoa) : A smaller sail located forward of the mast, used to aid in steering and balance.
- Spinnaker : A large, lightweight sail used for downwind sailing, often brightly colored and flown from a pole.
- Boom : A horizontal spar attached to the bottom edge of the mainsail, used to control the angle and shape of the sail.
- Mast : The vertical spar to which the sails are attached, providing height and support for the sails.
- Sail Battens : Stiffeners inserted into the sail to maintain its shape and improve performance.
- Sail Tracks and Cars : Systems on the mast and boom that allow for adjustment and control of the sails’ position.
Understanding these parts of a sail is essential for managing and maneuvering a sailboat effectively in various wind conditions and points of sail.
The anatomy of a sailboat encompasses several key components essential for sailing. At its core is the hull, the boat’s main body that floats on water, supporting the deck where crew and equipment are stationed. Rising from the deck is the mast, a vertical spar that supports the sails and rigging. The sails, made of fabric panels, catch the wind to propel the boat forward, while the boom, a horizontal spar attached to the mast, helps control the mainsail. Rigging, consisting of both standing and running rigging, supports the mast and allows sailors to adjust the sails. Below the waterline, the keel provides stability and prevents sideways drift, while at the stern, the rudder, controlled by a tiller or wheel, directs the boat’s course. Additional components like winches assist in adjusting sail tension. Understanding this anatomy is fundamental for sailors, enabling them to effectively navigate, maneuver, and maintain their sailboat while on the water.
The anatomy of a sailboat refers to its structural components and features that enable sailing. Here are the main parts:
- Hull : The main body of the boat that floats on water.
- Deck : The upper surface of the hull that provides a platform for crew and gear.
- Mast : A vertical spar that holds the sails and rigging.
- Boom : A horizontal spar attached to the mast and used to control the mainsail.
- Sails : Fabric panels that catch the wind to propel the boat.
- Rigging : The system of wires and ropes (standing and running rigging) that support the mast and control the sails.
- Keel : A fin-like structure at the bottom of the hull that provides stability and prevents sideways drift.
- Rudder : A vertical blade at the stern (back) of the boat used for steering.
- Tiller or Wheel : Controls connected to the rudder for steering.
- Winches : Mechanical devices used to adjust the tension in the rigging and sails.
Understanding the anatomy of a sailboat is crucial for sailors to effectively navigate, control, and maintain their vessel while sailing.
A sail ship, also known as a sailing ship or sailboat, consists of several key parts that enable it to navigate using wind power. These parts include:
- Hull : The main body of the ship that floats on water.
- Mast : A tall vertical spar that supports the sails.
- Sails : Large fabric panels that capture wind energy to propel the ship.
- Boom : A horizontal spar attached to the bottom of the mainsail to control its position.
- Rigging : The system of ropes, wires, and chains that support the mast and control the sails.
- Keel : A heavy fin or plate attached to the hull’s bottom to prevent the ship from sliding sideways and provide stability.
- Rudder : A vertical blade at the ship’s stern (back) that steers the ship.
- Deck : The upper surface of the ship where crew and passengers stand or move about.
- Winches : Mechanical devices used to adjust the tension of the rigging and sails.
- Bow : The front of the ship.
- Stern : The rear of the ship.
Understanding these parts is essential for sailors to effectively navigate, maneuver, and maintain their sail ship during voyages. Each component plays a crucial role in harnessing wind power and ensuring safe and efficient sailing.
On a sailboat, the sails are named based on their position and function. The mainsail is the largest and most essential sail, positioned on the main mast. The jib, a smaller triangular sail, sits forward of the mast and often works in tandem with the mainsail. A genoa is a larger foresail that overlaps the mast and jib, providing extra propulsion in stronger winds. Additionally, a spinnaker is a large, colorful sail used for downwind sailing, typically flown from a spinnaker pole. Stay sails are smaller sails positioned between masts or between the mast and bowsprit, helping to optimize sail configuration for various wind conditions and maneuvers on the sailboat.
On a sailboat, the sails are generally referred to by their specific names based on their location and function. Here are the main types of sails found on a sailboat:
- Mainsail : The largest and most essential sail on a sailboat, typically located on the main mast.
- Jib : A smaller triangular sail that is forward of the mast, often used in conjunction with the mainsail.
- Genoa : A larger foresail that overlaps the mast and jib, providing additional propulsion in stronger winds.
- Spinnaker : A large, colorful sail used for downwind sailing, typically flown from a spinnaker pole.
- Stay sails : Smaller sails set between masts or between the mast and bowsprit.
These sails work together to harness wind power efficiently, allowing the sailboat to navigate and maneuver effectively in various wind conditions.

A small sailboat typically consists of several key parts:
- Mast : A vertical pole that supports the sails and rigging.
- Boom : A horizontal pole attached to the mast and used to control the bottom edge of the mainsail.
- Sails : Includes the mainsail and jib or genoa, which are the primary sails for propulsion.
- Rigging : The network of ropes, wires, and chains that support the mast and sails, including shrouds and stays.
- Tiller or Wheel : The steering mechanism used by the skipper to control the direction of the rudder.
- Keel or Centerboard : Provides stability and prevents the boat from sliding sideways through the water.
- Cockpit : The area where the skipper and crew sit or stand while sailing.
- Deck : The top surface of the boat, providing a stable platform for crew and equipment.
These parts work together to make up the basic structure and functionality of a small sailboat, enabling it to sail efficiently in various wind and water conditions.
Here are the labeled parts of a sailboat:
- Hull : The main body of the boat that floats on the water.
- Bow : The front of the boat.
- Stern : The rear of the boat.
- Keel : The fin-like structure underneath the hull that provides stability and prevents the boat from sliding sideways.
- Rudder : A vertical blade at the stern used for steering.
- Tiller or Wheel : The mechanism used to steer the rudder.
- Boom : A horizontal pole attached to the mast that controls the bottom edge of the mainsail.
- Sails : Includes the mainsail and jib or genoa, the primary sails for propulsion.
- Rigging : The network of ropes, wires, and chains that support the mast and control the sails.
- Deck : The top surface of the boat, providing a platform for crew and equipment.
These parts are essential for sailing and navigation, each serving a specific function to ensure the boat operates effectively in various conditions on the water.
The engine cutoff switch (kill switch) lanyard is a crucial safety device for PWC operators, ensuring that the engine shuts off in case of an emergency or operator ejection. By wearing the lanyard, boaters significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries, making watersports safer for everyone involved.
For the most comprehensive and up-to-date boat test guides, including essential information on safety equipment like the engine cutoff switch lanyard, look no further than Wavve Boating. We’re committed to providing the best resources to help boaters navigate the waters safely and confidently.
When you’re ready to hit the water, be sure to download the Wavve Boating App for easy-to-use navigation, directions to top boating destinations, and plenty of more tools to help you get the most out of your time on the water.
New to boating? Check out this article on how to drive a boat next!

Related Posts

Navionics Chart Viewer website “decommissioned” by Garmin. What happened? 2025 Update

how to read a barometer? learn how to use a barometer and how barometers work

what is a rudder on a boat? what is a boat rudder ultimate guide

types of fishing rods explained | 7 different types of fishing rods | Ultimate Guide


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Parts of a Sail and Their Functions. In this guide, we'll focus on the three main types of sails: Mainsail, Jib, and Spinnaker. Mainsail is the primary sail on your boat. The mainsail is the largest sail on a sailboat and is typically attached to the mast and boom. It is found aft (rear) of the mast.
When you first get into sailing, there are a lot of sailboat parts to learn. Scouting for a good guide to all the parts, I couldn't find any, so I wrote one myself. Below, I'll go over each different sailboat part. And I mean each and every one of them. I'll walk you through them one by one, and explain each part's function.
Mar 16, 2021 · Parts of a sail. Sails are vital for sailboats, made up of complex parts that improve performance and maneuverability. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the different parts of that make up the sails. Luff– The luff is a vertical sail part that maintains its shape and generates lift by interacting with the wind. It attaches ...
The sail catches the wind and propels the boat, and the rudder directs the boat and acts as its steering. Here are all the main parts of a typical cruising sailboat , including hardware, lines, controls, cabin items, and a rundown of common sailing terminology.
Jan 12, 2024 · The main parts of a sailboat Diagram explaining the main parts of the sailboat. The main parts of a sailboat are the key components that make it a vessel able to sail. You’ll notice that the structure has several distinct differences from powerboats. We can categorize the main parts into the following: Hull: The main structure, or “body ...
The main parts that make up a sail on a sailboat include: Mainsail: The largest and primary sail on a sailboat, typically attached to the mast and boom.; Headsail (Jib or Genoa): A smaller sail located forward of the mast, used to aid in steering and balance.