CE Categories Explained
In 1998 the European Union created a Recreational Craft Directive that established design standards for most recreational boats from 2.5 to 24 meters (8 to 79 feet).
New and used boats sold in Europe, including boats built in the US – or anywhere else – for export to Europe, must be certified as complying with one of four design categories.
The following four design categories help to quantify a boat’s degree of seaworthiness, based on the wave height and wind speed the boat is designed to encounter and handle. The further offshore the vessel is expected to venture, the higher are the expectations for construction strength, stability, freeboard, reserve buoyancy, resistance to downflooding, deck drainage and other seaworthiness criteria.

Category A: OCEAN
This rating covers largely self-sufficient boats designed for extended voyages with winds of over Beaufort Force 8 (over 40 knots), and significant wave heights above 13 feet, but excluding abnormal conditions such as hurricanes.
Category B: OFFSHORE
This rating includes boats operating offshore with winds to 40 knots and significant seas to 13 feet.
Category C – Inshore
This rating is for boats operating in coastal waters and large bays and lakes with winds to Force 6, up to 27 knots, and significant seas 7 feet high.
Category D – Inland or sheltered coastal waters
This rating is for boats in small lakes and rivers with winds to Force 4 and significant wave heights to 18 inches.
The number of people onboard can alter the seaworthiness of a boat which can change the CE rated category. The more people there are aboard, the more weight on the boat and potentially less stability which would put the boat into the next lower rating category.
While the European standards are no guarantee that a boat will be suitable in all respects for the conditions in its designated category, they help to separate the purely inshore craft from those capable of operating safely in more demanding conditions.
additional info
Boats sold in the U.S. do not have to be CE rated, but rather, must only meet a few US Coast Guard regulations which address required safety items such as PFDs and flares, carrying capacity for boats under 26’ and level flotation if swamped for boats 20’ and under. America’s version of CE Standards and Recommendations have been promulgated by the American Boat and Yacht Council — but they are strictly voluntary. Most critically, there are no ABYC design categories to differentiate between boats of different capabilities, a crucial distinction CE ratings and American NMMA certification, which itself only requires about 70% of the ABYC recommended standards. While most quality U.S. builders follow the ABYC standards and many exceed those required by the NMMA, they are not mandatory as the CE standards are in Europe.
When you’re picking out your next boat, be sure to ask what its CE classification is – or would be if it is sold in Europe.

CE CERTIFICATION

DISCLAIMER: The text, places and opinions expressed in the text above are offered in good faith. Any action taken upon from the information on this website is strictly at your own risk; and Bates Wharf Marine Sales Ltd will not be liable for any losses or damage in connection to the use of our website.
Chertsey Head Office: 01932 571141
Eastbourne: 01323 470066
Poole: 01202 679421
Southampton: 01489 576888
Receive updates on news and boats for sale
© Copyright 2024 Bates Wharf. All rights reserved. Bridge Wharf, Chertsey, Surrey, KT16 8LG. For more details about the cookies we use, visit Privacy & Cookies .
Website by Drip Fed Design
Ita Yachts Canada
Brokerage / Courtage
Understanding the Classification of Yachts A, B, C and D
Understanding the Classification of Yachts A, B, C and D:
Since 1998, Europe (EEC) classifies yachts according to 4 categories A or B or C or D and this is a law. In order to sell a boat in the large territory of the EEC, it must be classified with a plate that mentions its classification and it must be clearly visible inside the boat, usually near the helm.

At first glance, it sounds very good when you hear class A, but what is it really, what are the differences, is it necessary to acquire a class A…
The brokers at ItaYachtsCanada have written an article on this subject in the past ( click here ), but here are the important characteristics to know about the subject.
The classification allows you to know in which kind of sea intensity you can safely venture, that is to say, taking into account the wind and the wave height in reference to the Beaufort index.
(At the end of this text, there is an explanation of the classes according to the Beaufort index).
Let’s say we focus on class A and B, on the major differences.
First of all, the differences are not very visible to the naked eye or it takes a trained eye to see them.
Depending on the type of water you plan to sail and if the weather guides you on each trip, a B class is also a very good choice.
Of course, you must have all the required safety equipment on board.
Ideally, a boater should always sail in rather peaceful conditions, taking into account the weather first. We always say that boating is fun, so stay away from difficult sailing situations. (Ideally, always with a Beaufort index of 6 and less, ideally a Beaufort index of 4 and less).
Many manufacturers have retained the parameters of the B class to build their boats, mainly for reasons of production costs and that boaters in general do not care much about these characteristics.
The problem is how to differentiate between the vast range of B class boats, how to distinguish those that are closer to an A class (B +) from those that are built as (B -).
How to find your way around, especially for a layman…

It is important to know that some manufacturers build their boats with an A approach, but without respecting all the mandatory specifications to be classified A.
Here are some guidelines to quickly see if the manufacturer has done things right.
– Inspect the portholes and closing mechanisms (Plastic or Metal)
– The presence of numerous drains to evacuate water (at the fly and cockpit), it is essential to be able to evacuate any water accumulation quickly.
– Height of the freeboard.
– Engine access hatch, well insulated and secured for water leaks.
– Bilge pumps (number, size and capacity)
– Mechanism to pump water from the engine room massively (e.g. possibility to use the engine water pumps with a joystick)
– The center of gravity of the boat is well balanced (rather low).
Hull joints, a very low center of gravity, excellent weight distribution, electrical system (24 V), are also part of the certification criteria especially for A boats, but difficult to assess for a yachtsman. It is possible, but in a summary way.
The CE classification allows to differentiate yachts according to certain criteria present, we are talking mainly about structural strength, integrity of essential parts of the hull, reliability of propulsion, steering systems, power generation and all other features installed on board to help ensure the essential services of the yacht.
Therefore, it is important to understand that a Class A yacht is built to a much higher standard than a Class B. This is not reflected in the luxurious appearance of the boat.
What you have to remember is that the major enemy for a boat, besides a fire, is water infiltration on board which can destabilize the behavior of the boat, cause a stop of the engines, major electrical problems, in short which can quickly put the boat out of use and/or out of control.
A classification body such as RINA (see list at the end of this text) has been checking the activities of builders and classifying yachts for over 20 years.
If the boat is sold in the European Community, the classification is mandatory and must be visible near the cockpit. This same classification is not present when the boat is intended for North America or very rarely.
Do not hesitate to contact a professional broker, he will be able to guide you according to your needs, your criteria and especially the places of navigation.

As the CE classification is not always displayed when the boat is destined for the North American market, here are some references on this subject based on the most recent data available (subject to change without notice):
P.S. Let’s mention that as a general rule yachts over 80 ft are Class A, but according to the rules in place, the classification is no longer mandatory or mentioned beyond 79 ft.
Class A (yachts over 50 ft):
BEST KNOWN MODELS :
Ferretti 500, 550, 670 and up
Pershing : 7X and up
Azimut 62, 64, 66, 68 Fly and up
Azimut S8 and up
Azimut Magellano : the whole range
Sunseeker Sport yacht 65, Yacht 88 and up
Princess yacht 80 and up (TBC)
Marquis Yachts (no longer in production)
Montecarlo MCY 66 and up
Searay L650
Class B (yachts over 50 ft):
Sunnseeker 52 fly, 55 fly , 66 fly, 68 fly, Sport Yacht 74, 76 Yacht
Azimut 50 fly, 55 fly, 60 fly, S6 and all Atlantis
Princess : all yachts under 70 ft
Princess Y72, Y78 and less
Ferretti 580 fly
All Absolute
All Fairline
All Beneteau & Jeanneau & Monte Carlo 52
All Searay except L650.
All Cruisers Yachts
For more information, here is an article published by the brokers at ItaYachtsCanada, click here .
There is also the dry weight which can help determine a quality yacht.
Don’t hesitate to compare yachts of the same size based on dry weight, you may be surprised.
For example, a 52′ yacht that weighs 30,000 lbs empty compared to another one that weighs 60,000 lbs empty, ask yourself some questions.
But be careful, it is more and more difficult to get the manufacturers’ empty weights. They have understood the importance of being rather vague on the subject or of making comparisons more difficult. Indeed, we are talking about LIGHT WEIGHT, which is difficult to measure.
The manufacturer who has confidence in thier boat will have no difficulty in giving a total warranty of at least 12 months, 24 and even 36 months. Please note the difference here between the manufacturer’s warranty and the dealer’s warranty .
Many European manufacturers sell their boats to dealers in America without a warranty. This means that the dealer assumes the full 12-month warranty out of his profit from the sale. The engine manufacturer, on the other hand, honors its own warranty such as Volvo, Cummins, Caterpillar, MAN, MTU, Yanmar. For other major components, it will be up to you to take the necessary steps to have the warranty honored, such as for the generator, the air conditioning, the thrusters, etc…

Therefore, acquiring a boat requires a much more specialized expertise than that of a car! Contact ITA Yachts Canada Inc. to speak with a professional and independent broker with experience in the following markets (Canada, United States and Europe whether the boat is new or used).
MORE INFORMATION.
Here is some more information about the classification, what the law in Europe says about it.

Here are some links to help you understand the Beaufort index in direct relation with the classification of yachts sold on the territory of the EEC:
Click here for the TRANSPORT CANADA website
Click here for an article on Wikipedia (more descriptive with photo).
According to the EEC rules, here is the description:
The classification of vessels marked “CE
CE marked vessels are classified into four design categories according to their ability to cope with sea conditions characterized by wind speed and significant wave height. Depending on the type of navigation practiced, the boater must choose a vessel whose design category authorizes such practice.
– Design Category A: Recreational vessels designed for winds that can exceed force 8 (on the Beaufort scale) and for waves that can exceed a significant height of 4 meters, excluding exceptional conditions such as storms, severe storms, tornadoes and extreme sea conditions or huge waves (these conditions exclude force 10 and following).
– Design Category B: Pleasure craft designed for winds up to and including force 8 and for waves up to and including 4 meters in significant height.
– Design Category C: Pleasure craft designed for winds up to and including force 6 and for waves up to and including two meters in significant height.
– Design Category D: Pleasure craft designed for winds up to and including force 4 and for waves up to and including 0.30 meters, with occasional waves up to and including 0.50 meters.

Vessels in each of these design categories shall be designed and constructed to withstand the parameters of each of these categories, with respect to buoyancy, stability and other relevant requirements, and to have good maneuverability characteristics.
The known classification bodies for the EEC:
RINA (Registro Italiano Navale),
BV (Bureau Veritas),
DNV (Det Norske Veritas),
Germanischer Lloyd,
LR (Lloyd’s Register).

Ita Yachts Canada provides the information in this article in good faith but cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information or the status of the data. It is the responsibility of the reader to instruct their agents or experts to verify and validate the information in this article.
Share this:
Published by Guy Bolduc
View all posts by Guy Bolduc
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from ita yachts canada.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- CATAMARAN MOTEUR
- CATAMARAN VOILE
- CENTER CONSOLE
- FISHING BOAT
- SPORT BRIDGE
- ABSOLUTE YACHTS
- CRUISERS YACHTS
- FOUNTAINE PAJOT
- GRAND BANKS
- KADEY-KROGEN
- MOCHI CRAFT
- MINIGHT EXPRESS
- MONTE CARLO
- NORTHERN MARINE
- OCEAN ALEXANDER
- OUTBACK YATCHS
- PARDO YACHTS
- PRESTIGE YACHTS
- SILENT YACHTS
- $1,5 M to $2,9 M
- $3,0 M to $4,9 M
- $5,0 M to $6,9 M
- $7,0 M to $9,9 M
- $10,0 M and more
- UNDER 49 FEET
- 50 to 59 FEET
- 60 to 69 FEET
- 70 to 79 FEET
- 80 to 89 FEET
- 90 to 99 FEET
- MORE THAN 100 FEET
- CENTRAL AMERICA
- PERSIAN GULF
- UNITED-STATES OF AMERICA
- YACHTS REGISTERED UPDATED
- VIRTUAL TOUR 3D
- YACHTS FOR SALE
- IMPORT-EXPORT
- BLOGUES, NOUVELLES ET CONSEILS
- PODCAST VIDEO
Insights, Advice, News
Ce categories: a brief explanation for boat owners (including 2023 update).

*This article was originally published in June 2021, before being updated in February 2022, and then again in November 2022, to reflect timeframe changes made by the UK government. The latest update was in August 2023, following the announcement that the CE mark will be recognised indefinitely.
Whether you are a seasoned boat owner or in the market for the very first time, the decision-making process when purchasing a boat can certainly be an overwhelming experience. There is so much to consider – from available budgets and financing, to licencing , insurance , storage and more.
However, your first decision will typically be focused on what type of boat you should buy. When researching the marketplace, you’re likely to come across various “categories”, so we felt it was important to explain what type of vessels fall under what category, and, of course, the implications…
Table of Contents
— A brief explanation of CE categories in Europe
— Brexit, boating, and the transition to UKCA categories
— CE & UKCA category A (Ocean)
— CE & UKCA category B (Offshore)
— CE & UKCA category C (Coastal & Estuary)
— CE & UKCA category D (Inland or Sheltered waters)
— The need for CE and UKCA certification
— Recognising a CE or UKCA certified boat
— What boats do not require UKCA or CE certification?
— Advice on type of boats
A brief explanation of CE categories in Europe
In 1998, a Recreational Craft Directive (EU RCD) was introduced by the EU to satisfy its demand to establish design standards for recreational boats – specifically those vessels measuring 2.5 to 24 metres. As a result, all new and used boats being sold in Europe must be certified as conforming to one of four CE (Conformité Européenne, meaning European Conformity) categories: A, B, C and D. This obligation applies to newly built and imported boats and yachts.
These categories have been put in place to determine the seaworthiness of any vessel, based upon the wind force and typical wave height a boat would be expected to encounter and navigate when sailing in different environments.
Brexit, boating, and the transition to UKCA categories
The Brexit vote and the UK’s subsequent withdrawal from the EU has had a profound effect on multiple industries across the country, especially how we interact and collaborate with our cousins on the continent – and the UK’s boat sector is no different. After 24 years of working to the CE standards set out in the EU’s RCD, the industry now adheres to the UK’s Recreational Craft Regulations (UK RCR) and will need a UKCA mark.
The UKCA marking came into effect on the 1st of January 2021. However, many British manufacturers had already taken the opportunity to sufficiently prepare by using the new marking in the lead-up to the switchover. A further announcement from the UK government in August 2021 confirmed an extension to the date ending recognition of the CE mark in Great Britain. As a result, CE marked goods may now continue to be placed on the GB market until 31st December 2024.
In a statement, UKAS (United Kingdom Accreditation Service) said (in August 2021) that whilst the extension is in place, the government is encouraging businesses to start using the UKCA mark as soon as possible.
Currently, the two sets of standards (EU RCD and UKCA) have the same requirements, which will initially make the transition somewhat seamless, however, we are aware things could change in the future. For more information, we recommend you take a look at this comprehensive article from trade magazine Boating Business .
CE & UKCA category A (Ocean)
Designed to undertake long voyages, these vessels should be expected to withstand winds in excess of Beaufort Force 8, as well as substantial waves above 4 metres. This would include those superyachts you’d commonly see in Puerto Banus (or even the Solent , which welcomed Superyacht Zen in June), plus some larger yachts.
CE & UKCA category B (Offshore)
Falling within category B will be smaller yachts and cabin cruisers with offshore capabilities. These boats can withstand winds up to and including Beaufort Force 8, plus waves up to 4 metres high. Our category B boats include:
- Intercruiser 29
- Intercruiser 32
- Intercruiser 34
CE & UKCA category C (Coastal & Estuary)
This group contains most tenders, open day-boats, smaller cruisers, bowriders and narrow boats. These vessels must be able to withstand winds of up to Beaufort Force 6 and waves up to and including 2 metres high. You’ll find that many of our customers – including those mooring at our marina – will be owners of category C vessels.
Our portfolio consists of:
- Haines 32 Sedan
- Haines 36 Sedan
- Intercruiser 27
- Intercruiser 28
- Our entire Interboat range
- Our entire Coaster range
- Our Corsiva range (apart from the 475)
CE & UKCA category D (Inland or Sheltered waters)
Finally, category D covers those vessels most suitable for sheltered waters, typically small lakes, canals, and rivers. The boats have been built to comfortably handle Beaufort Force 4 winds, and waves of up to and including 0.3 metres – most likely caused by other passing vessels. The majority of our boats are Cat C and above, but there is an option to have a Cat D version of some models which allows for more passengers, such as the Corsiva 650 .
The need for CE and UKCA certification
The four categories above have been largely put in place to provide a clear understanding of the capabilities of any individual boat, as well as a reflection of the structural strength and the overall integrity of the vessel – including the hull, the power system (if there is one), and other parts of the boat (we have a useful guide to boat parts if you’re not entirely used to boating language!)
As you can imagine, you would be a lot safer and more comfortable on a Class A boat when experiencing rough weather and stormy waters. If you are taking a trip on a boat, don’t be afraid to ask for confirmation of the CE/UKCA Marking and subsequent class, as well as information on what safety equipment they have on-board.
Recognising a CE or UKCA certified boat
To comply with the relevant inspection (either CE or UKCA), a boat must have the following:
- A Hull Identification Number (HIN), also known as a Craft Identification Number (CIN)
- Identification plate, including maximum allowed load and UKCA/CE category
- An owner’s manual featuring key information about the boat
- A declaration of conformity from the boat builder, shipyard, or importer
What boats do not require UKCA or CE certification?
Not all boats need a UKCA or CE marking. For instance, those vessels that have operated in EU/EEA countries prior to June 1998, plus boats built for personal use only, are exempt. Other types of vessels include hydrofoils, traditional canoes, pedalos, kayaks, sailing surfboards, historical boats, racing boats and gondolas.
Advice on type of boats
Looking for further guidance on different types of boats before making an investment? Get in touch with our experienced and friendly team. We are an independent business that prides itself on offering impartial advice. You can get in touch via our website , over the phone (01189 403211), or by visiting our beautiful marina ( map here ).
Announcement by the UK government on 1 August 2023
On 1 st August 2023, the Department for Business and Trade (DBT) announced its intention to recognise the CE mark indefinitely, in what the BBC called a “post-Brexit climbdown”.
As a result of this latest decision, British companies now have the option to either adopt the new UKCA symbol or keep the CE mark by seeking certification for their products from an accredited European body. In a statement , Business Minister Kevin Hollinrake explained the government had “listened to industry”, and the move will allow firms to “focus their time and money on creating jobs and growing the economy”.
The decision to recognise the CE mark indefinitely in the UK will simplify matters considerably, particularly for the boating industry. Bearing in mind that RCR (UK regulations) and RCD (EU regulations) were already mirroring each other, the reduction of an additional certification process is certainly welcome.
This latest change will streamline the sale of CE certified boats in the UK, allowing businesses like ours to focus more on quality, innovation and customer service. While we are ever adaptable to changes in regulations, this move aligns with the practical needs of the market. It’s a common-sense approach that is likely to be well-received across the sector.
The change in regulations was also welcomed by the Federation of Small Businesses who said the continued recognition of CE marked products would enable their members to concentrate on expanding their business both at home and internationally.
© 2024 Val Wyatt. All rights reserved.
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Filtering...

The global authority in superyachting
- NEWSLETTERS
- Yachts Home
- The Superyacht Directory
- Yacht Reports
- Brokerage News
- The largest yachts in the world
- The Register
- Yacht Advice
- Yacht Design
- 12m to 24m yachts
- Monaco Yacht Show
- Builder Directory
- Designer Directory
- Interior Design Directory
- Naval Architect Directory
- Yachts for sale home
- Motor yachts
- Sailing yachts
- Explorer yachts
- Classic yachts
- Sale Broker Directory
- Charter Home
- Yachts for Charter
- Charter Destinations
- Charter Broker Directory
- Destinations Home
- Mediterranean
- South Pacific
- Rest of the World
- Boat Life Home
- Owners' Experiences
- Interiors Suppliers
- Owners' Club
- Captains' Club
- BOAT Showcase
- Boat Presents
- Events Home
- World Superyacht Awards
- Superyacht Design Festival
- Design and Innovation Awards
- Young Designer of the Year Award
- Artistry and Craft Awards
- Explorer Yachts Summit
- Ocean Talks
- The Ocean Awards
- BOAT Connect
- Between the bays
- Golf Invitational
- Boat Pro Home
- Pricing Plan
- Superyacht Insight
- Product Features
- Premium Content
- Testimonials
- Global Order Book
- Tenders & Equipment
Classification: Statutory certification explained
Is certification an unnecessary complication, the costs and hassle of which far outweigh the benefits, or a helpful and reassuring framework which sets the highest standards for structural and operational safety and safeguards life, property and the sea environment?
No one could possibly deny that the large yacht industry is, and has been for some time, in the throes of a boom in spite of a recent downturn since 2008. Some observers would suggest that this is in spite of all the new rules and regulations that seem set to dog the yacht owner’s every move. Others would suggest that it is through the introduction of rules and regulations such as the MCA’s Code of Practice for Safety of Large Commercial Sailing and Motor Vessels that the industry has been given the confidence to expand with such vigour, knowing that their investments are safer – both financially and physically – because of regulation.
Classification societies are non-governmental organisations or groups of professionals, ship surveyors and representatives that develop, publish and certify standards and technical rules to ensure an acceptable degree of stability, safety and environmental impact, among other things. They are authorised to certify yachts and vessels flagged virtually anywhere.
A classification certificate attests that the yacht complies with the standards developed and published by the issuing society
New construction and refit surveys carried out by a surveyor from the classification society under which the yacht is built are important inspections that take place at intervals throughout the duration of the project. They ensure that any and every installation, repair, upgrade or modification is carried out to the standards of that society. Classification surveyors are interested in the structural integrity of the hull, installation of equipment, stability, structural, engine and machinery surveys, electrical, electronic and ancillary equipment, rigging inspections, safety recommendations and ultrasonic thickness gauging.
Every owner has his own vision of what he wants his yacht to be and designers strive to deliver just that. The fulfillment of this vision in turn becomes paramount in the eyes of the building yard and others who represent the owner, so it is often the policies imposed in the form of building regulations and classification rules that act as the voice of reason. This ultimately allows a balance to be struck between the attainment of that vision and the safety and reliability embodied in the construction of a yacht built to class.
A classification certificate attests that the yacht complies with the standards developed and published by the issuing society. Periodic surveying of a yacht in service by the appropriate class surveyor, at intervals dictated by the appropriate classification society, is also required to ensure the vessel continues to meet the rules and thus maintain her in-class status. Should any defects that may affect class become apparent, or if damage is sustained between surveys, the owner or operators are required to inform the society concerned without delay.
Almost every yacht that is launched is bigger or in some way better than the last and, quite often, more complex than its predecessor
As independent, self-regulating bodies, classification societies have no commercial interest in design, building, ownership, operation, management, maintenance, repairs, insurance or chartering. Classification rules are not intended as a design code and, in fact, cannot be used as such. These are more generally covered by the flag state, which lays down standards, or codes of practice that dictate construction good practice.
Almost every yacht that is launched is bigger or in some way better than the last and, quite often, more complex than its predecessor. As this trend continues, so too is the involvement and role of classification societies increasing and evolving. But what exactly does classification entail, and how is it linked to the statutory requirements of the various flag states? These matters are often misunderstood, which can potentially result in a conflict of responsibility.
Classification
The classification process The classification of yachts may be regarded as the development and worldwide implementation of published rules and regulations which – in conjunction with proper care and conduct on the part of the builder, owner and operator – provides for the structural strength and, where necessary, the watertight integrity of the hull. The same rules cover any appendages to the hull itself.
Classification rules lay down regulations that govern the effectiveness, safety and reliability of the propulsion and steering systems and other features, as well as the auxiliary systems which establish and maintain basic conditions on board and ensure that guests and crew can be safely carried while the yacht is at sea, at anchor, or moored inside a harbour.
Owners sometimes see classification as an unnecessary complication offering no real advantage for the cost. Some even suggest that the classification societies exist simply to make a profit out of a yacht builder’s desire to build a saleable product.
‘This is a misconception and one that needs to be addressed,’ Paul Martin, a principal engineer at DNV, points out: ‘Classification societies are independent bodies without a commercial stake in the build, and are therefore in a unique position to make sure that the yacht meets requirements without considering commercial impact. This enables yachts to be built with safety of the yacht, her crew, other vessels and the environment given maximum priority, irrespective of cost.’
Owners sometimes see classification as an unnecessary complication offering no real advantage for the cost
‘Because most classification societies have enormous experience,’ he continues, ‘as well as a lot of data on the failure of various types of vessels, machinery and other connected disciplines, they can bring these to bear on new projects ensuring fees are justified, and at the same time enhancing safety against the most up-to-date maritime knowledge and good safe practice.’
Yachts are said to be ‘in class’ when the classification society believes that its rules and regulations have been complied with, unless it has granted a special dispensation from compliance for a particular aspect. In order to decide whether a vessel should achieve in-class status surveyors appraise design, surveys and reports on the vessel’s construction, machinery, apparatus, materials, components, equipment, production methods and processes of all kinds for the purpose of verifying their compliance with plans, specifications and rules, codes of practice, or their fitness for particular requirements.
Class surveyors can also provide other technical inspection and advisory services relating to yachts and maintain these provisions during periodical visits to ascertain that the vessel is complying with classification society regulations at all times. Any modification which would affect class must always receive prior approval by the society.
When a yacht is going to be built to class, construction plans and all particulars relevant to the hull, equipment and machinery have to be submitted for the society’s approval before the work commences. Subsequent modifications or additions to the scantlings, arrangements or equipment shown on the approved plans must also be submitted for appraisal.
Implementation Statutory aspects deal with issues such as stability, life-saving appliances, pollution prevention and structural fire protection. Generally there are quite clear dividing lines between class and statutory requirements, although there are a few exceptions.
Flag states
The flag state, or nationality, of a yacht is important because it controls which country has the right to prescribe and enforce laws governing her operation. A ship must sail under the flag of a single state. The most common method by which a ship is granted the nationality of a state is by formal registration of the ship with that state.
Upon registration the ship acquires rights and duties as a result of registration which vary depending upon the state and the conventions and treaties to which it is party.
The rights will normally include action in an international court if there is a violation of international law against the vessel by another state, and representation at international conferences and organisations.
The duties include the upholding of the law of the flag state aboard the vessel, wherever she may be in the world.
Quality flags will also provide a recognised reputation for excellence, helping the vessel to avoid lengthy Port State Control inspections in foreign ports, and give worldwide support from embassies and consuls of that state and the protection of its navy.
International Maritime Organization
Statutory regulations are not only produced by the marine administrations of countries, but also the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
While some marine or flag administrations have the ability and knowledge to produce their own legislation, this is not true for the majority of countries. As shipping is an international business an international organisation is needed to regulate statutory issues. The United Nations established the IMO for the purpose of adopting the highest standards concerning matters of safety, navigation, and pollution prevention. The IMO held its first meeting in 1959 and now comprises 165 flag state members.
The United Nations established the IMO for the purpose of adopting the highest standards concerning matters of safety, navigation, and pollution prevention
The IMO’s purpose is to facilitate the general adoption of the highest practical standards in matters concerning maritime safety, efficiency of navigation and the prevention of marine pollution from ships among governments. Since its inception the IMO has introduced 40 conventions and protocols, although it is the responsibility of member countries to put these regulations into effect.
Statutory Implementation
The process of statutory implementation begins with the development and adoption of regulations by working groups at the IMO. Before these regulations come into force they have to have been accepted by a certain percentage of the IMO’s member states. This can take some time as each country has to introduce these statutory regulations as part of their maritime law before they can actually become mandatory on the ships registered in those countries.
It is important to understand that the IMO can adopt international legislation but that it remains the prerogative of the flag state to implement and enforce it. If a yacht registers with a country that has accepted these regulations then the yacht and her operators have to comply with them.
Maintenance of compliance is verified by a regular survey regime, which is the responsibility of the flag administrations and normally carried out by flag surveyors.
Not all flag administrations have the expertise or manpower to carry out the survey regime themselves, and they often delegate this work to classification societies
This arrangement means that the same class surveyor can issue certification on behalf of a flag state for compliance with, amongst other things, the MCA Large Yacht Code and Load Line Conventions. The class surveyor can also handle issues covered by the various annexes contained within the MARPOL Regulations, such as the prevention of oil, sewage and air pollution.
Class surveyors are often empowered by the state to inspect and certify crew accommodation, safety equipment, safety radio requirements, safety of navigation requirements, international tonnage, Suez and Panama Canal Tonnage Certification, and United States Coast Guard compliance. They are also frequently called on to service the requirements of SOLAS whenever a yacht becomes liable to comply with it.
Clearly, classification and statutory certification often go hand-in-hand where statutory certification requires classification of the yacht, and where a classification society requires valid statutory certification for the class to be valid.
In the preparation of this article the authors gratefully acknowledge the help they received from:
Engel JW de Boer – Service delivery manager, Lloyd’s Register, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Mario Dogliani – Corporate affairs and communication, RINA, Genoa, Italy
Jean-Jacques Juenet – Commercial manager, Bureau Veritas (BV), Paris, France
Paul Martin – Det Norske Veritas (DNV), Houston, USA
John Guy – Merlin Corporate Communications, London, UK
Nick Gladwell – Regs4yachts, Southampton, UK
Originally published: May 2008.
More stories
Most popular, from our partners, sponsored listings.
- No results were found.
What is CE Certification and why is It important to you?
CE Certification means more than safety.
Since 1998, CE Certification is required for all recreational boats entering or being sold in the European Union. Manufacturers must test and document to ensure conformity.
Aquila Power Catamarans doesn’t just build boats that offer comfort, innovation, and performance. We also build to these very demanding CE Certification standards. View a sample Aquila 54 Yacht CE Certificate. .
The following four design categories help quantify a boat’s degree of seaworthiness, based on the wave height and wind speed the boat is designed to encounter and handle. The further offshore the vessel is expected to venture, the higher the expectations for construction strength, stability, freeboard, reserve buoyancy, resistance to down flooding, deck drainage, and other seaworthiness criteria. All boats built by Aquila Power Catamarans are rated in one of these four categories.
- Category A – Ocean: covers largely self-sufficient boats designed for extended voyages with winds of over Beaufort Force 8 (over 40 knots), and significant wave heights above 13 feet, but excluding abnormal conditions such as hurricanes.
- Category B – Offshore: includes boats operating offshore with winds to 40 knots and significant seas to 13 feet.
- Category C – Inshore: is for boats operating in coastal waters and large bays and lakes with winds to Force 6, up to 27 knots, and significant seas 7 feet high.
- Category D – Inland or sheltered coastal waters: is for boats in small lakes and rivers with winds to Force 4, up to 16 knots, and significant wave heights to 18 inches.
While CE Certification is mandatory for new and used boats sold in Europe, it is not a requirement for the United States. CE standards clearly identify what each Aquila model design category is met, based on sea and wind conditions. However, with ABYC standards there aren’t any design categories that differentiate between boats of different capabilities based on sea and wind conditions. While you may never experience rough weather conditions, your mind can be at ease knowing that, if you do, you will be on one of the safest power catamarans in the world.
Want to Learn More About CE Certification?
Request information.
.jpg?h=177&w=365&la=en&hash=B07DF7F09EB63C4F8B6789082FD43405)
The Aquila Story

Discover the Aquila for You

Find Your Aquila Dealer
CE marking for pleasure craft
Meet the highest safety standards.
Directive 2013/53/EU states that new build boats up to 24 m hull length must bear the CE Marking to be allowed to be freely marketed anywhere in the European Economic Area (EEA). As established by Decision No. 768/2008/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, the process is based on eight evaluation procedures (modules) that are applied to the design and manufacturing phases: from internal production control (module A) to product verification (module F), through to full quality assurance (module H).
Service Details
The CE Mark is issued on the basis of construction and fitting out criteria laid down by the Directive, and related to fundamental aspects, such as:
- the health and safety of passengers
- product quality
- environmental impact
- protection of the consumer.
The CE Marking process for recreational craft ensures both owners and manufacturers that their yachts meet the highest safety standards, enhancing their market and quality value for the entire lifespan of the boat.
Deliverables
Application for certification by the customer
Checking activities, in relation to the audit module chosen:
- examination of the documentation and construction drawings
- on-site visits to verify compliance of the product with the drawings submitted and quality of the construction process visits on board to check that all essential CE marking requirements have in fact been met.
Depending on the evaluation module chosen, the process runs parallel to designing and building the product. Our team of highly qualified technicians and surveyors monitors the boat from the preliminary design phase through to the finished product being launched.
RINA is a Notified Body according to European Directive 2013/53/EU and offers a range of instruments to support designers and manufacturers as well as offering new services in application of the Recreational Craft Directive's essential requirements. The strong point of RINA is the service offered, fast and qualified, throughout the yacht's life cycle: from design to construction, testing of materials and components, sea trials and periodic surveys.
Is CE marking of a boat obligatory? Yes, for putting it onto the market in the European Community, CE Marking is obligatory. The philosophy behind the new community directive approach is based on the free circulation of goods, as well as people and services. For this reason, no Country on the European Union may now prevent a CE marked product from entering its territory, not may it refuse to allow it to be marketed.
Does the CE Marking have an expiry date? No, provided no modifications are made to the unit in question, the Marking has no expiry date. However, it may be necessary to have the Marking updated, if the Reference Standards change.
Click here to see the List of Certified Pleasure Craft
Alberto Carmagnani Pleasure Craft EC Marking and safety certification Scheme Leader
You may also like
Hybrid and electrical propulsion.
Comfort class for yachts
Green plus for yachts, small commercial yachts.
- Seller Market Analysis
- Trade Your Yacht
- Vessel Donation
- Sold Yachts
- We Buy Boats
- Exclusive Listings
- Yachts for Sale
- New Yacht Builds
- Nautor Swan Yachts
- Sichterman Yachts
- Luxury Yacht Charters
- Search Charter Yachts
- Charter Management
- Luxury Events
- Team Members
- Boat Show Events
- North Report Magazine
- Testimonials
- +1.954.900.9988
Blog | Owner’s Guide to Yacht Classification
Yacht classification is a system used to categorize yachts based on various factors such as size, construction, and intended use. The specific classification categories and requirements can vary between different yacht classification societies, but some common classifications include:
- Pleasure Yacht: A yacht intended for leisure use, typically not engaged in commerce.
- Charter Yacht: A yacht that is available for hire for pleasure use, also known as commercial yacht.
- Large Yacht: A yacht that exceeds a certain size or gross tonnage.
- Small Commercial Yacht: A yacht that is used for commercial purposes but does not exceed a certain size or gross tonnage.
- Passenger Yacht: A yacht that is used to carry passengers for hire.
- Workboat: A yacht or vessel intended for work-related use, such as a survey vessel, cable layer, or other specialty use.
- Ocean Going: Yachts that are able to make ocean passages and are built and equipped to meet the requirement of such voyages
- Coastal: Yachts that are intended to operate in coastal and sheltered waters and meeting less stringent requirement than ocean going yachts.
The main differences between yacht classification societies are their specific rules, regulations, and requirements for yacht classification. While many societies have similar overall goals of ensuring that yachts meet certain standards of design, construction, and maintenance, they may have slightly different interpretations of these standards and how they should be applied.
Some societies may have stricter or more detailed rules and regulations than others. For example, one society may have more stringent requirements for fire protection, while another society may place more emphasis on stability calculations.
Another difference is the type of yachts they cover and the services they offer. Some societies focus primarily on pleasure yachts, while others also cover commercial yachts and workboats. Societies may also offer different levels of classification, such as “unrestricted” or “restricted” class, and this might vary depending on the intended use of the yacht.
Lastly, some societies have a more global presence than others, or have more experience or expertise in certain types of yachts or regions. This can be important for yacht owners who plan to take their vessel to different parts of the world and may need to comply with different regulations in different countries.
In short, yacht classification societies are similar in their overall goals, but they can have different rules, regulations, and requirements for yacht classification, different services and different areas of focus. Yacht owners should research and compare different societies to determine which one is the best fit for their specific needs and intended use of the yacht.
There are several yacht classification societies that provide certification and inspection services for yachts and other small vessels. Some of the most well-known include:
- American Bureau of Shipping (ABS)
- Bureau Veritas (BV)
- Germanischer Lloyd (GL)
- Lloyd’s Register (LR)
- RINA (Registro Italiano Navale)
- Det Norske Veritas (DNV) now known as DNV GL
These organizations are responsible for ensuring that yachts and other vessels meet certain standards of design, construction, and maintenance, and they issue certificates of compliance to vessels that meet these standards. They also conduct periodic inspections to ensure that vessels continue to meet these standards over time. Some of them also provide additional services such as collision avoidance, navigation and stability calculations and other specialized services.
Recent Stories
Navigating luxury: chartering a yacht in the british virgin islands, embark on luxury: yachting in newport, ri with 26 north yachts.

Talk to us Contact Our Team
I understand that by signing up I agree with 26 North’s Privacy Policy .
Welcome aboard!
We have added you to the newsletter.
We have received your information and an agent will get back to you ASAP
Sign up for Yoga On the Docks Tuesdays at 8 AM
We have received your registration. See you on the docks!

Class Notations on Yachts – Classification Guide
9 December 2016
INTRODUCTION TO YACHTS CLASSES
Classification.
Rules are developed to establish standards for the structural strength of the large yacht’s hull and its appendages, and the suitability of the propulsion and steering systems, power generation and those other features and auxiliary systems which have been built into the ship to assist in its operation, and even pollution protection systems. A yacht may be maintained in class provided that, in the opinion of the Society concerned, it remains in compliance with the relevant Rules, as ascertained by a periodic or non-periodic survey(s). Today a vessel either meets the relevant Class Society’s Rules or it does not. As a consequence, it is either “in” or “out” of “Class”.
In summary, Class Notations on Yachts will tell you a lot about the building quality and condition of each vessel and its components on an annual basis, according to the excellence of its construction and its adjudged continuing soundness. A yacht that has been designed and built to the appropriate Rules of a Society may apply for a Certificate of Class from that Society or for a periodical survey (generally required every 5 years) meant for the Renewal of Class Certificate . Class Societies have often developed two separate sets of Rules for Commercial and Private Yachts . They can be applied to New Construction as well as Existing Yachts .
Classification Societies
Classification Societies play a fundamental role in today’s marine industry. A Society will act on behalf of ship-owners and builders to ensure high build quality and the safety of a ship’s main structural parts . Classification also provides a point of reference with regard to those who were involved in the supply chain including builders, charterers and insurers.
As an independent, self-regulating, externally audited, body, a Classification Society has no commercial interests related to ship design, shipbuilding, ship ownership, ship operation, ship management, ship maintenance or repairs, insurance, or chartering.
The process begins with the design and construction phases, focussing on the implementation and manufacture of key components as well as technical specifications. The standards which must be adhered to are dictated by the regulations of the chosen society and are published as rules, evolving continuously to incorporate new technologies and client requests via the advice of highly competent engineers and architects.
All Classification Societies waive liability for future faults as a surveyor can only record a vessel’s quality at the time of inspection; it is then the responsibility of the yacht owner to maintain the vessel and inform the society in the event of damage or structural alteration. Although the surveys are thorough, they do not cover all aspects of a ship’s build and operating service. This can include crew qualifications, navigational aids and manoeuvrability.
Classification Societies are often simply referred to as “Class Societies” or just “Class”. There are currently 13 members of the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS) , each with a unique set of rules, classification layouts and notations. Five of the biggest Classification Societies are listed below, along with their identifying signature, to denote a ship constructed under special survey in compliance with the Society’s rules, suitable for unrestricted sea-going service:
The marks following the Society’s standard signature are not interchangeable between organizations, meaning each letter or number will represent a different characteristic for each society. Each mark can be broken down to highlight a yacht’s capabilities, equipment or restrictions.
Each of the Classification Societies has developed a series of notations that may be granted to a vessel to indicate that it is in compliance with some additional voluntary criteria that may be either specific to that vessel type or that are in excess of the standard classification requirements.
The Classification of a yacht does not absolve the Interested Party from compliance with any requirements issued by Administrations and any other applicable international and national regulations for the safety of life at sea and protection of the marine environment such as SOLAS, ILLC, MARPOL, ILO or IMO.
Smaller vessels are categorized differently, adhering to different requirements and statutory regulations. With a heavier focus on passenger numbers and distance of operation from shore, the Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA) outlines guidance for UK vessels (up to 24 meters in length) which are used for charter or commercial use.
As RINA is today the most reputed Classification Society in the Mediterranean and a leader in the yachting certification business, developing and offering services of ships classification, certification, verification of conformity, inspection, and testing, we will hereby provide you with a summary of their more common Class Notations on Yachts , this will be helpful to identify these most peculiar symbols :
CLASS NOTATIONS – RINA
Main class symbol.
The main class symbol C is assigned to ships built in accordance with the requirements of the Rules or other rules recognized as equivalent and maintained in a condition considered satisfactory by the Society. The period of class (or interval between class renewal surveys) assigned to a ship is a maximum of 5 years.
Except for special cases, a class is assigned to a ship only when the hull, propulsion and auxiliary machinery installations, and equipment providing essential services have all been reviewed in relation to the requirements of RINA’s Rules.
With the 5 year class period is to be understood as being the highest class granted by the Society.
Construction Marks
The construction mark identifies the procedure under which the yacht and its main equipment or arrangements have been surveyed for the initial assignment of the Class.
Construction marks defined below are assigned separately to the hull of the yacht and its appendages, to the machinery installation.
The construction mark is placed before the symbol HULL for the hull, before the symbol MACH for the machinery installations, and before the additional Class Notation granted, when such a notation is eligible for a construction mark.
When the same construction mark is assigned to both hull and machinery, the construction mark is assigned globally to the ship without indication HULL and MACH after the main class symbol.
Hull Construction Mark (HULL)
- Construction mark ✠ is assigned to the hull when it has been surveyed by RINA during its construction in compliance with the new building procedure.
- Construction mark ✠ is assigned to the hull when it was built under the survey of another Society.
- Construction mark ● is assigned to the hull in all cases other than those listed above.
Machinery Construction Mark (MACH)
- The construction mark ✠ is assigned when the propelling and auxiliary machinery has been designed, constructed, certified, installed and tested in accordance with RINA Rules.
- The construction mark ✠ is assigned when the propelling and auxiliary machinery has been designed, constructed and certified in accordance with the rules of another society and installed and tested under the survey of RINA.
- Construction mark ● is assigned in all cases other than those listed above.
Navigation and Operating Notations
The navigation notation UNRESTRICTED NAVIGATION is assigned to a ship intended to operate in any area and any period of the year.
Restricted operating area notations are optional and will be marked accordingly like, for example, on a specified operating area or operation service within “x” miles from shore.
Additional Class Notations
An additional Class Notation expresses the classification of additional equipment or specific arrangement, which has been requested by the Interested Party. The assignment of such an additional Class Notation is subject to the compliance with additional rule requirements.
Some additional Class Notations, due to the importance of relevant equipment or arrangements, are assigned a construction mark. This is indicated in the definition of the relevant additional Class Notations. Class Notations which may be assigned to a ship are listed according to the category to which they belong:
Automated Machinery Systems (AUT)
AUT notations are relevant to automated machinery systems installed onboard ships.
Automated machinery systems (AUT – UMS (Y))
The additional Class Notation AUT-UMS (Y) may be assigned to yachts that are fitted with automated installations enabling machinery spaces to remain periodically unattended in all sailing conditions including manoeuvring.
Integrated Ship Systems (SYS)
SYS notations are relevant to the operation of integrated systems regarding navigation, machinery, communication and specific cargo, as applicable.
Centralised Navigation Equipment (SYS-NEQ)
The additional Class Notation SYS-NEQ is assigned to yachts which are fitted with a centralized navigation control system so laid out and arranged that it enables normal navigation and manoeuvring operation of the ship by two persons in cooperation.
Centralised Navigation Equipment (SYS-NEQ-1)
The additional Class Notation SYS-NEQ-1 is assigned when, in addition to the above, the installation is so arranged that the navigation and manoeuvring of the yacht can be operated under normal conditions by one person, for a periodical one-man watch. This notation includes specific requirements for the prevention of accidents caused by the operator’s unfitness.
Integrated Bridge System (SYS-IBS)
The additional Class Notation SYS-IBS is assigned to yachts which are fitted with an integrated bridge system which allows simplified and centralized bridge operation of all main functions of navigation manoeuvring and communication, as well as monitoring from the bridge of other functions related to specific cargoes and pollution; for passenger ships, heating, ventilation and air conditioning are also included in the monitored functions
Communication System (SYS-COM)
The additional Class Notation SYS-COM is assigned to yachts which are fitted with a local area network including the alarm, monitoring and control systems and computers used for management operations and external communication devices for reporting ashore navigation, maintenance and operational information.
Damage Stability (DMS)
The additional Class Notation DMS may be assigned to yachts complying with the damage stability requirements.
STAR Notation
General STAR is a System of Trace and Analysis of Records integrating rational analysis with data and records from ship-in-service concerning planned inspection and ship maintenance.
The additional Class Notation STAR-HULL is assigned to ships on which an Inspection and Maintenance Plan (IMP) for the hull is implemented.
The notation may be completed by the suffix NB when a structural tridimensional analysis has been performed for the hull structures, at the new building stage. The suffix NB is removed when the ship enters the STAR-HULL survey program through the implementation of the Inspection and Maintenance Plan (IMP).
The additional Class Notation STAR-MACH is assigned to yachts on which an Inspection and Maintenance Plan (IMP) for the machinery is implemented. This plan is based on a risk analysis review of the installation.
STAR Notation (STAR)
When yachts are granted both STAR-HULL and STAR-MACH, the two separate notations are superseded by the cumulative additional Class Notation STAR.
Crew Accommodation and Recreational Facilities (MLCDESIGN)
According to the Maritime Labour Convention 2006 Notation:
The additional Class Notation MLCDESIGN is assigned to yachts having crew accommodation and recreational facilities complying with the Maritime Labour Convention 2006 (MLC).
GREEN PLUS Notation (Eco-Friendly Yachts)
Issued in 2008 and updated yearly, the GREEN PLUS additional Class Notation has been revised in 2012 to cover new issues for seagoing ships and ships operated at a fixed location. The additional Class Notation GREEN PLUS is assigned to Eco-Friendly yachts compliant with the Society’s environmental protection framework of airborne gases, spillage/leakage of substances, oil, sewage, greywater, garbage disposal and noise mitigation systems to prevent pollution.
Safety Class Notation EFP (Bureau Veritas)
The following additional Class Notations are assigned to yachts complying with the requirements of this Section:
- EFP-A : for yachts having Enhanced Fire Safety Protection in accommodation spaces,
- EFP-M : for yachts having Enhanced Fire Safety Protection in machinery spaces,
- EFP-C : for yachts having Enhanced Fire Safety Protection in cargo areas,
- EFP-AMC : for yachts complying with all the requirements of this Section.
For more information on Class Notations on Yachts – Classification of Yachts , please feel free to contact Allied Yachting .
OUR YACHT LISTINGS:
- New Yachts for Sale
- Pre-owned Yachts for Sale
- Yachts for Charter
You might also like

Yachting Consultants
Sale-Charter-Brokerage-Management
Headquarters:
34 Rue Caffarelli 06000 Nice, France
Front Office:
Boulevard de La Croisette – Port Canto 06400 Cannes, France
T.: +33 493 43 82 83 Email: [email protected] Website: www.alliedyachting.com

- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
Sailboat Design Categories, STIX and Dynamic Stability
Just what are these design categories? In the UK and other EC countries, all pleasure boats must be marked as complying with one of four design categories as set out by the Recreational Craft Directive (RCD).
Similarly all boats built in the US – or anywhere else – for export to Europe, must be certified as complying with one of these design categories.
These four categories A, B, C and D
- B ~ Offshore;
- C ~ Inshore;
- D ~ Sheltered Waters.
are described primarily by the wave and wind conditions likely to be encountered and the circumstances under which such a boat might be used.
Design Category A ~ 'OCEAN'
Designed for extended voyages where conditions may exceed winds of Beaufort F8 and significant wave heights of 4m and above, and for which vessels must be largely self-sufficient.
Design Category B ~ 'OFFSHORE'
Designed for offshore voyages where conditions up to, and including winds of wind force 8 and significant wave heights up to, and including 4m may be experienced.
Design Category C ~ 'INSHORE'
Designed for sailing in coastal waters, large bays, estuaries, lakes and rivers where conditions up to and wind force 6 and significant wave heights up to, and including 2m may be experienced.

Design Category D ~ 'SHELTERED WATERS'
Designed for sailing on small lakes, rivers and canals where conditions up to and wind F4 and significant wave heights up to, and including 0.5m may be experienced.

In allocating a boat to one of the four categories, the boat's displacement and the Angle of Vanishing Stability (AVS) as indicated on its Gz Curve , play a major part.

Category A boat limits are a minimum mass of 3.0 tonnes and an AVS greater than [130 - (2 x mass)]º but always equal to or greater than 100º. Category B boat limits are a minimum mass of 1.5 tonnes and an AVS greater than [130 - (5 x mass)]º but always equal to or greater than 95º.
A Category A boat needs to be to the right of and above the blue line and a Category B boat to the right and above the red line. But it's not just static stability considerations alone that are taken into account when establishing a sailboat's category - which is where STIX comes in...
ISO 12217, STIX and Dynamic Stability
The International Standards Organisation (ISO) address Small Craft Stability and Buoyancy Assessment and Categorisation under ISO 12217 , and similarly use both AVS and mass in dealing with the static stability of monohull ballasted sailing yachts, but take into account a number of other issues in addressing the dynamic issue.
STIX ( ST ability I nde X ), a numerical index which scores a boats stability on a scale of 1 to 100, is a function of a number of safety and stability related features, ie:
- length on deck;
- ability to withstand a capsize by considering the area under the Gz curve;
- recovery from inversion by considering AVS and mass;
- recovery from knockdown by overcoming water in the sails;
- displacement/length ratio giving credit for a heavy displacement for a given length;
- beam/displacement factor recognizing problems associated with topside flare and excessive beam;
- wind moment representing the risk of flooding due to a gust the risk of down-flooding in a broach or knockdown.
STIX scores generally fall in the range 5 to 50 and are applied in addition to the above limits on mass and AVS, ie:
- Category A boats: equal to or greater than 32, and
- Category B boats: equal to or greater than 23.
Since June 1998 all new recreational boats sold in the European Community have been required by law to have undergone a stability assessment with the preferred method being the application of ISO 12217.
This means that all but a very few new monohull ballasted sailing boats sold in the EU will have had a GZ/RM curve generated, their displacement and AVS determined and a STIX calculated.
You might like to take a look at these...

The Righting Moment Is a Key Factor to a Sailboat's Stability
Whilst it's the righting moment that influences a sailboat's static stability, it's the dynamic stability that has the larger affect on seaworthiness. And here's what it means to us

Importance of the Prismatic Coefficient in Sailboat Hull Design
The prismatic coefficient is associated with the fullness of fineness of the ends of a boat's hull, but why is this important and how does it affect performance?

How Boat Displacement and Sail Area Affect Performance
Sail area and boat displacement clearly have a major impact on a sailboat's performance. After all, it's akin to the power-to-weight ratio we apply to a car's performance
Understanding Sailboat Design Ratios
The formulae for sailboat design ratios are quite complex, but with this tool the calculations are done for you in an instant!
How Gz Curves Reveal the Truth about A Sailboat's Stability
Gz curves are a graphic representation as to how a sailboat's righting moment changes with heel angle, identifying the heel angle at which the boat will capsize rather than come back upright
You Are Here: Sailboat Cruising > Sailboat Design > Design Categories
Recent Articles
'Natalya', a Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 54DS for Sale
Mar 17, 24 04:07 PM
'Wahoo', a Hunter Passage 42 for Sale
Mar 17, 24 08:13 AM
Used Sailing Equipment For Sale
Feb 28, 24 05:58 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
- Sign-up for our newsletter, 'The Sailboat Cruiser' ...
- Identify this month's Mystery Boat...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com
- Construction
- Optimisations
- Performance
- Equipment care
- Provisioning
- Keeping afloat
- Precautions

Understanding the seagoing capabilities of a vessel
What is the issue, why address this, how to address this.
- Category A : Designed for extended voyages where conditions may exceed wind force 8 (Beaufort scale) and significant wave heights of 4 metres and above but excluding abnormal conditions, and vessels are largely self-sufficient.
- Category B : Designed for offshore voyages where conditions up to, and including, wind force 8 and significant wave heights up to, and including, 4 metres may be experienced.
- Category C : Designed for voyages in coastal waters, large bays, estuaries, lakes and rivers where conditions up to, and including, wind force 6 and significant wave heights up to, and including, 2 metres may be experienced.
- Category D : Designed for voyages on sheltered coastal waters, small bays, small lakes, rivers and canals where conditions up to, and including, wind force 4 and significant wave heights up to, and including, 0.3 metres may be experienced, with occasional waves of 0.5 metres maximum height, for example from passing vessels.

- • Manufacturer’s name, registered trade name or registered trademark, contact address
- • CE marking
- • Watercraft design category
- • Manufacturer’s maximum recommended load (fuel, water, provisions, miscellaneous equipment and people), excluding the weight of the contents of the fixed tanks when full, this should appear in kilograms.
- • Number of persons recommended by the manufacturer for which the watercraft was designed to carry when underway.
With thanks to:
Add your review or comment:.
Please log in to leave a review of this tip.
eOceanic makes no guarantee of the validity of this information, you must read our legal page . However, we ask you to help us increase accuracy. If you spot an inaccuracy or an omission on this page please contact us and we will be delighted to rectify it. Don't forget to help us by sharing your own experience .

Can Yachts Cross The Pacific & Atlantic Oceans?
Both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans can be crossed in a yacht. You can cross the Pacific and Atlantic oceans on a sailing yacht or a motor yacht. It would be best to have a big enough tank to hold the amount of fuel you expect to burn.
This being said, not all yachts are capable of making these trips. If you decide to cross either of these oceans, you’ll want to make sure you have an ocean-faring yacht as well as the equipment and skills needed to make the trip.
Some yachts will not hold enough fuel to complete the trip and will typically be shipped on freighters designed for this.
In this post, I’ll go over some of the important facts you should know about yachts before you decide to make your voyage:
Table of Contents
Category “A” Yachts Are Ideal For Open Oceans
Yachts are categorized into four main categories.
These categories range from A to D, and they determine what type of waters the yacht was built to navigate.
Category “D” Yachts

A category D yacht is only rated for inland or sheltered coastal waters.
You can use them on lakes and rivers and even protected harbors.
They’ll do well as long as the waves don’t reach heights of over 4 feet.
Category “C” Yachts

A category C yacht is rated to be used inshore.
This means that it can head away from the protected harbors, but it shouldn’t go very far. Large bays and lakes can be navigated, and the boat can take on waves up to 8 feet high.
Category “B” Yachts

A category B yacht is designed to go offshore.
It can handle strong winds and waves of up to 13 feet.
While you probably wouldn’t want to do an ocean crossing in this vessel, it might be able to handle one of the weather stayed calm for an extended period of time.
One of the issues a category B would have is that it might not be built to be self-sustaining for the length of time needed to cross an ocean.
Also, it wouldn’t be able to hold up in the event of an extreme foul-weather event.
Category “A” Yachts

On the other hand, Category A boats are designed to sustain themselves for long voyages like a crossing of the world’s oceans.
They are made to withstand rough weather and storms so you won’t get lost in the middle of the Atlantic or Pacific.
They are longer than 40 feet and can take on waves of up to 23 feet. These boats can also take on strong winds of at least 47 knots.
They have weather systems and advanced computers that help you calculate and master the long trip of crossing the biggest seas.
Who Determines How A Yacht Is Categorized?
The manufacturer or boat builder will initially determine which category the boat should fall under.
However, this shouldn’t be the only determining factor.
To ensure that the yacht is actually built correctly for trips over the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, it should be certified by the International Marine Certification Institute.
When you’re looking to buy a yacht, make sure it has been rated by this institute. You can do this by looking for a certification plaque that will be mounted on the bulkhead.
Your Motor Yacht Should Be Able to Carry 1.5 Times The Amount of Fuel You’ll Need
Sailing yachts are often better suited for longer ocean crossings. One of the main reasons for this is that they can sail themselves for an indefinite amount of time.
This being said, you don’t have to own a sailing yacht to cross the Atlantic or the Pacific. A large motor yacht can potentially make the trip as well if it is designed for it.
How Much Fuel Is Needed To Cross The Atlantic & Pacific ocean?
For a medium-sized yacht, you should expect to have at least 500 gallons of fuel (2000 liters), unless you have sails.
If you are motoring in a big yacht, you will need more than that. You should bring 1.5 times the amount you expect to burn.
The motor yacht will need to be able to hold more than enough fuel for the trip, though.
This is because strong winds and currents can drastically increase the amount of fuel needed to complete a voyage. For this reason, many veteran sailors say that you should bring about 1.5 times the amount of fuel you think you’ll actually need to complete the voyage.
Remember, running out of fuel in the middle of the ocean is a whole lot different than running out of fuel while cruising up the coastline.
You may not see anyone for days in the ocean, and even if you do, they probably won’t be able to tow you back to shore.
Remember the boating flag rules if you travel abroad .
How Long Time Does It Take To Cross The Atlantic & Pacific Seas?

It will take around 20 days or more to cross the Atlantic ocean and potentially much more if you are using your sails instead of the motor.
Depending on the weather conditions, it can take significantly longer to cross the Pacific ocean with a large yacht with a strong motor.
These are very general numbers.
They will vary a lot according to how much fuel you are willing to burn. The faster your motor, the more fuel you will burn. You can also cross the oceans with a yacht with sails.
This will save fuel but be slower because of the boat’s characteristics and since you are much more dependent on the weather conditions.
You May Need to Upgrade Some of Your Systems
It takes a significant amount of time to make an ocean crossing.
During this time, you’ll need to meet your food, water, and energy requirements. You’ll also need to navigate the boat continuously.
Modern technology makes meeting these needs much easier.
In addition to having good navigation equipment, here are some systems you may want to consider upgrading to make life easier on the ocean.
- Your water maker.
- Your power generation systems.
- Your freezer.
- Your autopilot.
Water Makers
A watermaker will give you the ability to make your own potable water throughout your journey.
This cuts down on how much freshwater you need to pack and makes your yacht more self-sufficient.
This is important for a trip as long as crossing the Atlantic or Pacific sea.
Remember, your freshwater needs aren’t just restricted to drinking water. You’ll need fresh water for bathing, cooking, and for washing your yacht off as well. Most yachts will need daily cleanings as saltwater can quickly take its toll on a yacht’s decks and make the windows difficult to see through.
Power Generation Systems
A yacht can generate its own power using the sun, the wind, and the water.
They do this through the use of wind turbines, solar panels, and hydro-generators.
Wind turbines can create an impressive amount of energy in high winds. However, most people will want to travel downwind, which reduces the amount of power that the wind turbine can generate.
Solar panels work great on sunny days while the panels are angled towards the sun.
The drawback is that they do not work nearly as well when they’re shaded, and every day is not a sunny day while out on the water or land for that matter.
Hydro-generators, on the other hand, can generate power 24 hours a day. This is because the water’s movement powers them, and since you’ll be traveling day and night, you’ll always be generating energy.
The only drawback is that a hydro-generator does not produce a lot of energy at one time, and on sailboats, they will slow you down.
What Is The Best System to Use?
The best power generation system is a system that makes use of all of the technologies available.
Your energy requirements during an ocean crossing can be extremely high. Not only this but yachts, in general, tend to need more power than other vessels.
Add a hydro-generator, a wind turbine, and some solar panels to your system, and you’ll have power day and night whether your crossing wide-open expanses or anchor at one of the islands along the way. Larger sailing and power yachts also will typically have a diesel-powered generator or gen-set.
This one might be obvious, but you’ll need to pack a lot of food for your voyage.
Increasing the size and number of freezers you bring with you will increase the amount of meat and fruit you can bring.
Of course, you could skip this step and go with mostly dry foods instead. But honestly, what yacht owner wants to subsist on a daily diet of rice and beans?
Autopilot Systems

Your yacht will be moving at all times, and someone or something will need to be navigating it.
Autopilot systems make navigation easy and make an ocean crossing much less taxing.
Bring a backup autopilot system or spare parts for your existing system so that you can make any repairs necessary to keep it working throughout the entire trip.
Fail to do this, and you’ll find that the crew has to spend a lot more time navigating and a lot less time enjoying the journey.
Remember, it takes more than 20 days, at least, to cross the Atlantic ocean.
Your Crew Should Have Ocean Crossing Experience
It is possible to make an ocean crossing by yourself, but it isn’t recommended.
This is especially true if you’re making the crossing on a yacht.
The reason being, a yacht is going to be larger and more difficult to manage alone than a small sailing craft would be to manage alone.
For this reason, you’ll probably want to hire a crew or bring along plenty of friends or family members that can help you make the trip. At least one person on the crew should have some experience making an ocean crossing.
This person’s knowledge could prove invaluable both before and during the long trip. You and your other passengers should also have some experience with long passages so that you all know what to expect.
Trade Winds Will Dictate Your Voyage
You might think that you can easily shorten the time it takes to cross the Atlantic or Pacific oceans by making it a more direct one.
Unfortunately, this isn’t true, and your route will largely be dependent on trade winds.
What I mean by this is that you’ll end up traveling in a direction that follows the prevailing winds, so you are mostly traveling downwind. This reduces the stress on your boat, makes the ride more enjoyable, and even makes it quicker.
Final Thoughts
Many people have crossed the Atlantic and the Pacific oceans in yachts and many other types of watercraft.
Some experience and adequate preparations are important for a safe adventure.
If you’re planning on making the trip on your yacht, make sure you have the right boat for the job, the right crew for the journey, and the right technology to make everything simple and easy.
Click to share...
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Maritime and shipping
- Vessel surveys and inspection
Vessel classification and certification
Class and permitted use of passenger ships, cargo ships, tankers, tugs, tenders, fishing boats, yachts, commercial vessels, and the required certificates.
Introduction
All seagoing vessels registered in the UK are assigned to a specific class, which defines their type of permitted use, determines which certification they must hold and specifies the inspection and survey regime required to comply with this certification. These classes are established and assigned by the Recognised Classification Societies, who also approve surveys and inspections.
This guide explains the main classes of UK-registered seagoing vessels, and gives outline details of the statutory certificates they must carry.
Certification requirements for UK vessels
The certificates that you must carry for UK-registered vessels vary according to their type, gross tonnage (gt), type of cargo and whether they are on a domestic or international voyage.
The following is an outline of the main certification requirements:
- passenger ship safety certificate - for all passenger ships
- cargo ship safety radio certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 300gt on international voyages only
- cargo ship safety equipment certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 500gt on international voyages only
- cargo ship safety construction certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 500gt on international voyages only
- cargo ship safety certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 300gt
- load line certificate - for passenger ships in non-UK waters, cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 24 metres in length (if built on or after 21 July 1968) or of more than 150gt and for passenger ships in UK waters over 80 net tonnes
- oil pollution prevention certificate - for fishing vessels, passenger ships, cargo ships, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 400gt and oil tankers over 150gt
- minimum safe manning document certificate - for passenger ships, cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 500gt
- safety management certificate - for all passenger ships and for cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 500gt
- ship security certificate - for passenger ships, cargo ships oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts on international voyages only
- sewage pollution certificate - for fishing vessels, passenger ships, cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts of 400gt or more, or carrying 15 persons or more on international voyages only
- air pollution certificate - for fishing vessels, passenger ships, cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts of 400gt or more
- anti-fouling declaration - for fishing vessels under 24 metres in length or of less than 400gt
- anti-fouling certificate - for fishing vessels, passenger ships, cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts of 400gt or more
- certificate of fitness (chemical or gas) certificate - for all chemical tankers or gas carriers
- dangerous goods certificate - for passenger ships built after 1 September 1984, and for cargo ships after a certain date of build on international voyages only
- certificate of compliance for a large charter yacht - for all large passenger yachts
- UK fishing vessel certificate - for fishing vessels between 15 and 24 metres in length
- international fishing vessel certificate - for fishing vessels over 24 metres in length
- small commercial vessel certificate - for pilot boats and small commercial vessels under 24 metres in length
- certificate of registry - mandatory for all fishing vessels, optional for pilot boats and small commercial vessels
- international tonnage - for fishing vessels under 24 metres in length
Merchant ships: classification and certification
Merchant ships are classified by the type of cargo that they carry (general cargo, oil, chemicals, gas etc), their gt and the voyages they undertake, which can be:
- inshore, in the sea areas around the UK - for details of these, download Marine Shipping Notice (MSN) 1747 The Merchant Shipping ( Domestic Voyages) Regulations 2000
- short international - when the ship is never more than 200 nautical miles (nm) from a port or place of safety, and on which there is no more than 600nm between the final departure port and the first destination port
- long international - all other voyages between ports in two countries to which the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) applies
The classes of merchant vessels are as follows:
- Class VII - ships (other than those in Classes VII(A), VII(T), XI and XII) engaged on voyages, any of which are long international voyages
- Class VII(A) - ships employed as fish processing or canning factory ships and ships engaged in the carriage of persons employed in the fish processing or canning industries
- Class VII(T) - tankers engaged on voyages, any of which are long international voyages
- Class VIII - ships (other than ships of Classes VIII(T), IX, XI and XII) engaged only on short international voyages
- Class VIII(T) - tankers engaged on voyages, any of which are short international voyages
- Class VIII(A) - ships (other than ships of VIII(A)(T), IX, IX(A), IX(A)(T), XI and XII) engaged only on voyages which are not international voyages - this class includes small commercial vessels
- Class VIII(A)(T) - tankers engaged only on voyages which are not international voyages
- Class IX - tugs and tenders which go to sea but not on long international voyages
Certification for merchant ships
The certificates that merchant ships must carry vary according to class, type of cargo and size. The following is an outline of the main certification requirements for UK ships:
- cargo ship safety radio certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers over 300gt on international voyages only
- cargo ship safety equipment certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers over 500gt on international voyages only
- cargo ship safety construction certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers over 500gt on international voyages only
- cargo ship safety certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers over 300gt
- load line certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers over 24 metres in length (if built on or after 21 July 1968) or of more than 150gt
- oil pollution prevention certificate - for cargo ships and chemical tankers or gas carriers over 400gt and oil tankers over 150gt
- minimum safe manning document certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers over 500gt
- safety management certificate - for all passenger ships, and for cargo ships, oil tankers, chemical tankers or gas carriers and large commercial yachts over 500gt
- ship security certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers on international voyages only
- sewage pollution certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers of 400gt or more, or carrying 15 persons or more, on international voyages only
- air pollution certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers of 400gt or more
- anti -fouling certificate - for cargo ships, oil tankers and chemical tankers or gas carriers of 400gt or more
- dangerous goods certificate - for cargo ships after a certain date of build, on international voyages only
For information about requirements for the certification, see the guidance to legislation
Passenger ships: classification and certification
Passenger-carrying ships are classified primarily on whether they operate inshore or on short or long international voyages.
The classes of passenger ships are as follows:
- Class I - ships engaged on voyages any of which are long international voyages.
- Class II - ships engaged only on voyages any of which are short international voyages.
- Class II(A) - ships engaged on voyages of any kind other than international voyages, which are not ships of Classes III to VI(A).
- Class III - ships engaged only on voyages in the course of which they are at no time more than 70 miles by sea from their point of departure and not more than 18 miles from the coast of the UK and which are at sea only in favourable weather and during restricted periods.
- Class VI - ships engaged only on voyages with not more than 250 passengers on board. In favourable weather and during restricted periods, in the course of which the ships are at no time more than 15 miles from their point of departure, nor more than 3 miles from land.
- Class VI (A) - ships carrying not more than 50 passengers for a distance of not more than 6 miles. Voyages to or from isolated communities on the islands or coast of the UK and which do not proceed for a distance of more than 3 miles from land - this is subject to any conditions which the Secretary of State may impose.
Additional classifications for inshore ships are:
- Class A - passenger ships engaged on domestic voyages other than voyages covered by Classes B, C and D
- Class B - a passenger ship engaged on domestic voyages in the course of which it is at no time more than 20 miles from the line of the coast
- Class C - a passenger ship engaged on domestic voyages in sea areas where the probability of exceeding 2.5 metres significant wave height is less than 10% over a one-year period for all-year round operation; or operating over a specific restricted period (eg summer) in the course of which it is at no time more than 15 miles from a place of refuge, nor more than 5 miles from the line of the coast
- Class D - a passenger ship engaged on domestic voyages in sea areas where the probability of exceeding 1.5 metres significant wave height is less than 10% over a one-year period for all-year round operation; or operating over a specific restricted period (eg summer) in the course of which it is at no time more than 15 miles from a place of refuge, nor more than 5 miles from the line of the coast
Certification for passenger ships
The certificates that passenger ships must carry vary according to their gt. The following is an outline of the main certification requirements for UK ships:
- passenger ship safety certificate
- load line certificate required for passenger ships either operating in UK waters and of more than 80 gross tonnes (gt) or operating in non-UK waters and of 24 metres length (if keel was laid on or after 21 July 1968) or of more than 150gt
- oil pollution prevention certificate - ships of 400gt or more
- minimum safe manning document - ships of 500gt or more
- safety management certificate
- ship security certificate - ships on international voyages
- sewage pollution certificate - ships of 400gt or more, or carrying 15 persons and on international voyages
- air pollution certificate - ships of 400gt or more - application to ships other than on international voyages not yet confirmed
- anti-fouling certificate - ships of 400gt or more
- dangerous goods certificate - ships built after 1 September 1984 on international voyages only
Small commercial vessels and pilot boats certification
The operation of small commercial vessels in the UK is covered by the Small Commercial Vessel Codes of Practice. The Codes define small commercial vessels as those of less than 24 metres load line length (or under 150 tonnes if built before 21 July 1968) which are engaged at sea and are not pleasure vessels..
These vessels are classed as Class VIII (A).
The Codes regulations and classifications apply to UK registered vessels and all other vessels which are registered or owned in another country but operate from a UK port while in UK waters.
Pleasure vessels are not covered by the Codes.
To view the Yellow, Blue, Brown and Red Codes please click here .
Download Marine Guidance Note (MGN) 280 (M) Small Vessels in Commercial Use for Sport or Pleasure, Workboats and Pilot Boats standards from the MCA website (PDF, 921K) .
Certification for small vessels
The specific type of certificate issued depends on operational activities of the vessel - different certificates are issued for vessels used commercially for sport or pleasure, workboats and pilot boats. Commercial vessels that are 24 metres load-line length or over are treated as cargo ships.
Large commercial yachts classification and certification
Large commercial yachts are defined as those vessels which are:
- in commercial use for sport or pleasure
- 24 metres load line length or more or over 150 gross tonnes if built before 21 July 1968
- carry no cargo and no more than 12 passengers
- are in commercial use for sport or pleasure
Certification for large commercial yachts
The certificates that large commercial yachts must carry vary according to their gt. Further information on this can be found in Section 28 of the Large Commercial Yacht Code. You can download MSN 1792 (M) Large Commercial Yacht Code (LY2) .
Fishing vessels: classification and certification
Fishing vessels are classified by length. In general, operation of fishing vessels of less than 24 metres registered length are covered by The Code of Practice for the Safety of Small Fishing Vessels of less than 15m Length Overall and The Code of Safe Working Practice for the Construction and Use of Fishing Vessels of 15m Length Overall to less than 24m Registered Length Fishing Vessels.
Fishing Vessels of 24 metres in length and over are covered The Code of Practice for the Construction and Safe Operation of Fishing Vessels of 24m Registered Length and Over.
Download MSN 1871 (F) The Code of Safe Working Practice for the Construction and Use of Fishing Vessels of 15m Length Overall to less than 24m Registered Length.
Download MSN 1872 (F) The Code of Safe Working Practice for the Construction and Use of Fishing Vessels of 15m Length Overall to less than 24m Registered Length
Download MSN 1873 (F) The Code of Practice for the Construction and Safe Operation of Fishing Vessels of 24m Registered Length and Over
Certification of fishing vessels
Fishing vessels are exempt from some certification requirements, although other specialised certificates must be carried, as follows:
- Small fishing vessel certificate
- UK fishing vessel certificate - for vessels 15-24 metres
- international fishing vessel certificate - for vessels 24 metres or longer
- oil pollution prevention certificate
- air pollution certificate - vessels of 400 gross tonnes (gt) or more
- sewage pollution certificate - vessels of 400gt or more, or carrying 15 persons, and on international voyages
- anti-fouling declaration - vessels of less than 24 metres in length and less than 400gt
- anti-fouling certificate - vessels of 400gt or more
- international tonnage certificate - vessels of 400gt or more
Organisations that can help
As well as guidance on specific types of vessel, more general information on classification, certification and other issues related to the operation of commercial shipping is available from the MCA and the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
Read about the IMO’s work .
Full information on UK regulations and procedures, including details of the certificates that must be carried on UK-registered ships can be found in MCA’s Master’s guide to the UK flag .
Further information
Download the small craft codes from the MCA website
Download MSN 1792 (M) Large Commercial Yacht Code (LY2)
Fishing Vessel (Codes of Practice) Regulations 2017
Organisation information on the MCA website
Agency overview on the IMO website
Download the Master’s guide to the UK flag from the MCA website (PDF, 5.59MB)
Document information
Published: 9 October 2012
Updated: 23 October 2017
From: Maritime and Coastguard Agency
Part of: Ship registration Surveys and inspections
Links updated
Updated text and links
First published.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- Pontoon Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- nauticalknowhow
- Nautical Knots
- Tools and Calculators
What are the Different Classes of Boats?
Classes of boats and types of boats are two different things. Every type of boat fits into one of four classes of boats. While a type of boat can vary significantly in appearance and function, class is easy to understand. Boat classes are all determined by the overall length of the vessel.
The class of a boat is significant for you as a boat owner. Boats classes are required to meet certain safety guidelines based on those classes. The size of your boat determines what you need to keep on board. Let’s take a look at the different classes of boats. We’ll also get into different types of boats and see where they fit in terms of class.
Class A Boats

Any boat that clocks in at under 16 feet in length. That means it could be:
- a fishing boat
- A personal watercraft
- An inflatable boat
Recreational boats that are less than 16 feet in length are not required to carry any day signals on board. That said, there are safety requirements. These are regulated by the US Coast Guard. It’s also worth noting that these regulations are slightly different for canoes and kayaks.
Canoes/Kayaks Under 16 Feet

For these vessels, a Type I, II, III or V personal flotation device must be available for every person on board. These need to be US Coast Guard approved flotation devices. They need to be the right size and wearable by the person who plans to wear them as well. If the person is not wearing it, it needs to be someplace they can reach it easily. We recommend anyone on a boat of this size keep their flotation device on at all times. The minimum requirement is that one be available and easy to reach. In an emergency, you can save yourself precious time by having it on already. This is especially true for children on boats.
Visual distress signals are required on the vessel if it’s being operated at night. Your night signal has to be made within the last 42 months as well.
Sound devices are required as well. A whistle is recommended but a horn will work also.
Other Boats Under 16 Feet
All boats under 16 feet require the same personal flotation devices. The rules for a kayak or canoe apply here as well. One for everyone on board that is accessible and wearable. A distress signal is also required for these boats. Sound signals are the same as for kayaks and canoes as well.
There are additional requirements for these kinds of boats if they meet certain conditions.
A B-1 fire extinguisher of any type must be on board any vessel under 16 feet besides a canoe or kayak. That is, if it has an enclosed engine, enclosed living space, or a permanent fuel tank.
A type I, II, or III Marine Sanitation device is required if the vessel has an installed toilet.
A backfire flame arrestor is required if the vessel has a gasoline-powered engine. The exception is if it is an outboard motor.
Enclosed engines must also have ventilation that meets Coast Guard standards.
Class I Boats

Boats that are between 16 feet and 26 feet fall under this classification. Any number of boats could fall into this class.
- Smaller deck boats
- Cuddy cabin boats
- Pontoon boats
- Aluminum fishing boats
- Wakeboard boats
All Class I boats must have one personal flotation device of Type I, I, III or V per person on board. In addition, one throwable Type IV device is required to be on board. Often people overlook these on tow sports boats. They will only think of the person looking for a thrilling ride water skiing as the one who needs a PFD. The Coast Guard requires them for everyone, however.
A B-1 fire extinguisher of any type is also required to be on board. This is true, again, if the engine is enclosed. It’s not required for outboard motor boats. However, as before, if there is an enclosed living space or permanent fuel tank, then you do need a fire extinguisher.
This size of boat requires specific distress signals. You need a minimum of three day use and night use flares. You can also have a non-flare substitute for day use in the form of an orange distress flag. A Non-pyrotechnic substitute for night use is an electric SOS light. Flares must have been made within the last 42 months.
A horn or whistle is needed as a sound signal.
Class II Boats

Class II boats are any vessel that span 26 feet to 40 feet. This can include
- Cabin cruisers
- Bowrider boats
- Trawler boats
- Runabout boats
These boats meet the same requirements for PFDs as Class I boats. That means every single passenger on board needs to have access to their own life jacket or other PFD. The acceptable types are Type I, II, III and V. And again a throwable Type IV is also required. These recreational boats can easily hold over one dozen people. Even if you’re freshwater fishing in shallow waters, these requirements must be met.
At this size, either one B-II fire extinguisher or two B-Is are needed. Remember, marine plywood isn’t able to stand up to fire well at all. The extra extinguishers could be a lifesaver at this size of a boat. Nothing ruins some relaxed cruising faster than a boat fire.
Visual distress signals on this kind of boat are the same as those for Class I boats. That means three day use and three night use. Three combination day and night use signals are also acceptable. These are essential for any overnight trips on the boat. Even high performance boats can run into troubles in the dark. Make sure any signal flares have been manufactured within the last 42 months.
Sound devices must be present as with lower boat classes.
Enclosed engines must also have ventilation that meets Coast Guard standards
This class of boat is also required to have pollution regulation placards. Your boat will need a 5″ x 8″ Oil Discharge placard and 4″ x 9″ Waste Discharge placard.
Class III Boats

These boats range from 40 feet to no more than 65 feet in length. This can include
- Cigarette boats
- Sport fishers
These are the largest class of boat available to typical boat owners. For these, the same flotation device standards apply as they did for Class II. That means one PFD of Class I, II, III or V is required for every passenger on board. Since different types of boats can carry passengers in greater numbers, this needs to be respected. Make sure every single person knows where the PFD is and how to wear it. Each person must have one that fits properly.
In terms of fire extinguishers, the rules change again with Class III boats. You will need one B-II extinguisher and one B-I extinguisher on board. Alternatively, you could have three B-I extinguishers handy.
Visual distress signals and sound signals are the same as the requirements for smaller class boats. That means three day use and three night use signals. An orange signal flag may substitute one of the day use flares, and an electric SOS light can substitute for one of the night use. A horn or whistle is also required.
This class of boat is also required to have pollution regulation placards. Your boat will need a 5″ x 8″ Oil Discharge placard and 4″ x 9″ Waste Discharge placard. If the vessel has a galley then it must also have a waste management plan.
At this length, the boat must also have the Inland Navigation Rules on board. This is the “Rules of the Road” that govern boating.
Boats Over 65 Feet
Some yachts and things like a ferry boat can easily be over 65 feet. These no longer qualify as subject to small boat regulations. Typically no one is going to own a personal watercraft of this size. The Coast Guard does have regulations in place if you are on a large vessel such as this, however. These apply to vessels from 65 feet up to 165 feet. After that, vessels are typically considered research, commercial, or military.
The rules regarding flotation devices remain static here. One Type I, II, III or V PFD for every passenger on board. In addition, one Type IV throwable device. It’s worth noting there that the “Type” system will not be around forever. The Newton system is slowly being phased on. Newtons measure pounds of force and help indicate how much a PFD can keep afloat. This buoyancy rating in Newtons has been in place since 2019. The transfer is going slowly to allow people time to adjust. Most PFDs you purchase now will explain buoyancy in Newtons.
For instance, a Type II flotation device is equivalent to a current PFD that is rated for 70 Newtons. This device should be able to keep most people floating face up in the water. Type III devices will be replaced with 70 Newton rated PFDs that do not turn you face up. Each device has a Newton rating plus icons. These explain how much weight the PFD is meant to keep you afloat and how it floats you. In several years time, all PFDs will follow these guidelines. That said, old PFDs are still perfectly legal and usable.
For fire extinguishers, weight becomes a factor at this size. Vessels that weigh up to 50 gross tons need one B-II extinguisher. Over 50 gross tons requires two B-II extinguishers on board.
Visual and sound signals are the same for the previous class of vessels. This class does have a variation in sanitation requirements, however. A Type II or Type III marine sanitation device is required for this size of a vessel.
Additional requirements are the same as for the previous class. This includes sanitation and ventilation. The backfire flame arrestor must meet the same requirements as well. A copy of the inland navigation rules must also be on board the boat at all times, also.
What Class are Fishing Boats?

There are dozens and dozens of kinds of boats in the world. You have banana boats, log boats, bass boats and so many more. That’s why the class system is broken down by length. It makes it much easier to categorize a boat in these simple terms rather than trying to manage each type individually.
As a result, something like a fishing boat does not necessarily fit into one class. Your fishing boat could easily fit into literally any one of these classes. Remember, a fishing boat is not even technically a specific kind of boat. A fishing boat is just a boat from which you go fishing. A pontoon boat or some high performance boat could be a fishing boat. An inflatable dinghy could be a fishing boat. There is no standard for that particular description of a boat.
Does a Fishing Boat Need All The Same Safety Gear?
Some people question the application of safety standards. A Class I boat that only has one person on board seems different than one with ten people on board. But the rules are adaptable. If you are the only passenger on the boat then you only need one flotation device. You only need the fire extinguisher if your boat meets the requirements for it. That means something other than an outboard motor.
Man powered boats do not require the same level of safety and concern that power boats do. That’s why canoes and kayaks are exempt from requiring a fire extinguisher. After all, what would be the point? But just because your boat doesn’t have a swim platform or whatever doesn’t matter. Smaller boats or bigger boats all have the same potential to get into trouble. These rules are meant to help prevent that as much as possible. What About Pontoon Boats and Deck Boats?
No matter what kind of boat you’re on, the Coast Guard requirements apply evenly. Again, this can sometimes seem unnecessary. Something like a ski boat may seem more dangerous than cruising around on a deck boat. If you’re just relaxing on inland waters trying to catch largemouth bass, it can seem like overkill. But these measures are designed to ensure safety. In fact, these are the minimum requirements that the Coast Guard has implemented.
Some boaters prefer to have additional measures in place. For instance, as we said above, we recommend wearing a PFD at all times. This is not specifically required, only that the PFD be wearable and accessible. We feel that, the more people on board a boat, the more important it is to make sure everyone is wearing a PFD. This can cut down on wasted time and confusion if an accident happens later. If everyone scrambles for a PFD at the same time, a bad situation could easily become worse.
The Bottom Line
Boat classification has no effect on how you enjoy your boat. It also doesn’t change what you are allowed to do on your boat. The only purpose of classifications is to account for safety on board. Larger boats need to take more care in keeping the boat and passengers safe. Understanding the requirement is key to ensuring the safety of everyone on the water. Make sure you know the full dimensions of any boat you plan to take out onto the water. Once you are aware, you should always do a pre-departure check of the boat.
It’s important to know if you have all the safety gear every time you head out. Make sure the personal flotation devices are all in good working order. Check the date on all flares or visual signals to make sure they meet requirements. Also, check the date on your fire extinguishers before heading out as well. Old gear should be replaced immediately. It’s better to have it and not need it than to need it and not have it.
Keep yourself and your passengers safe and you’ll be having a great time on the water.
My grandfather first took me fishing when I was too young to actually hold up a rod on my own. As an avid camper, hiker, and nature enthusiast I'm always looking for a new adventure.
Categories : Boats
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More in Boats

What Is A Gunwale?

131 of the Best Hawaiian Boat Names

167 Patriotic Boat Names

The 138 Best Boat Names for Dog Lovers

The People’s Poncho Review and Ratings

Oru Lake Kayak Review

About Boatsafe
Established in 1998, BoatSafe is your independent guide into the world of boating, fishing, and watersports. We provide expert insights and detailed guides to help you find products tailored to your needs and budget.
Contact Boatsafe
- Address: 4021 West Walnut Street. Rogers, AR 72756
- Phone: (479)339-4795
- Email: [email protected]
Site Navigation
- How We Test
- Corrections Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Editorial Policy
- Affiliate Disclosure
Our Reviews

All content is © Copyright 2024. All rights reserved.

Category A “Ocean” Certification – What Does It Mean?
MJM made it a primary objective that all MJMs would be certified at the highest level of safety possible… which meant those models under 40 feet are ISO CE Certified Category B Offshore, while the 40z and 50z are Certified ISO CE Certified Category A Ocean. There are no other boats of their type, of any size, achieving this high level of offshore safety. In fact, in the worldwide database of the International Marine Certification Institute (IMCI), we have only identified two other models under 40-feet with this certification, both being heavy displacement trawlers. The former achieves this with a low vertical center of gravity and the latter with massive tonnage. What does ISO Certification mean and how should it affect one’s peace of mind on the water? Let’s take a look at the subject.
When the European Union started in 1998, a Recreational Craft Directive was developed to set design/building standards for recreational boats up to 24 meters (79 feet). New and used boats sold in Europe, including boats built in the U.S. or anywhere else being exported to Europe, had to be certified as complying with one of four design categories for seaworthiness. These categories are based on factors such as the wave height and wind speed a given design is capable of handling, plus hull scantlings/strength and stability.
In essence, the further offshore a vessel is expected to venture, the greater the requirements for the vessel’s construction strength, stability, reserve buoyancy, resistance to flooding, deck drainage, crew safety, and other seaworthiness criteria have to be. Let’s take a look at the four categories.
Category A — Ocean – This is the category with the toughest standards and covers vessels 40’ and over designed to be self-sufficient for extended voyages. It is defined as the “category of boats considered suitable for seas of up to 23 feet (7 meters) significant wave height and winds of Beaufort Force 9 (41-47 knots) or less, but excluding abnormal conditions such as hurricanes.”
Category B — Offshore – These boats are designed to go offshore with the ability to handle winds up to gale force 8 of 40 knots, and seas up to 13 feet (3.96 meters).
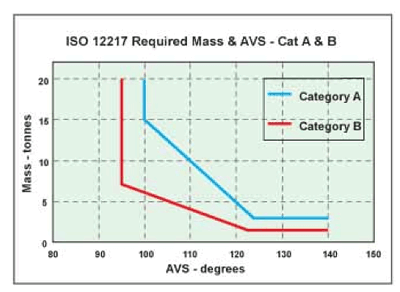
The difference between Category A & B is shown in the above graphic, where Mass is tons and AVS is the Angle of Vanishing Stability when the boat goes upside down. Category A boats need to be to the right of and above the blue line and a Category B boats to the right and above the red line.
Category C — Inshore – These boats may venture away from the protected harbors, but within striking distance of home… operating in coastal waters or large bays and lakes with winds up to 27 knots with and significant seas 8 feet (2.44 meters) high.
Category D — Inland or sheltered coastal waters – These are your typical day boats, operating in protected harbors, small lakes and rivers with winds to Force 4 (up to 16 knots) and significant wave heights to 4 feet (1.22 meters).
Now This Is Important
While a builder may claim that a boat is designed to a certain standard, it doesn’t necessarily mean that it ends up being built to it, unless inspected and certified by an IMCI (International Marine Certification Institute) surveyor, AND the builder can show you this plaque affixed to a bulkhead.

Because the number of people in the boat can reduce stability, the plaque shows the max number of people for Category A conditions, which on the 40z is 16. That’s not a USCG limit for liability purposes at all times. That’s just for Category A conditions.
Good story here. When Bob Johnstone was told that the 50z could carry only 2 more people under Category A than the 40z (18 versus 16), he was concerned about losing a 50z sale to a 40z owner who was moving up, because he wanted to be able to take 20 or so friends on the ICW to eat at Coconuts Restaurant near Bahia Mar… and might be concerned about the liability. “No worries,” said the IMCI surveyor, “We can provide the 50z with a ‘B’ rating as well as an ‘A’ rating, showing he can carry 30 people…and if he’s just going down the ICW or close to shore, you can post a ‘C’ rating, too, showing a capacity for 50 people.” Bob thought was going a bit too far and was happy to settle with the following plaque for the 50z.
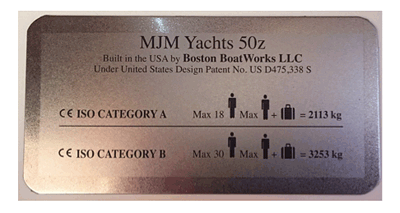
Impact on Design and Manufacturing?
MJM Yachts is dedicated to producing the safest, strongest and most durable yachts possible. For this reason, while those under 40 feet can only be rated “B,” each of our powerboats is designed and built to exceed small craft structural requirements for ISO Category A Ocean. ISO requirements for strength are based on a design’s top speed and the expected impact to be absorbed by hull bottom and sides, as well as decks, bulkheads, structural grid, and any part of the vessel’s structure. The laminate schedule and materials are then specified to meet such stringent requirements.

ISO standards for polyester or vinylester resin and the 50:50 glass-to-resin ratio are lower than those achieved on MJMs, built by Boston Boatworks. An MJM is built using a wet prepreg epoxy, Kevlar, Eglass and Corecell with a glass-to-resin ratio of 62:38. Epoxy is significantly more expensive, but 25% stronger, unlikely to crack with use, and is water-resistant… which is why epoxy is used to coat the bottom of boats suffering from osmotic blistering. The MJM is built right from the start!
That’s Not All…
ISO CE certification also takes into account engine emissions. In a world where greenhouse emissions are taking their toll on our environment, this is an important point. Meeting strict ISO CE emissions standards is comparable to meeting similar U.S. CARB requirements.
Additionally, sound levels will come into play. Boats are limited to 75 decibels for a single engine and 78 decibels for twin, triple or quad installations from a distance of 25 meters.
Highest Standards for MJM Yachts
MJM meets and exceeds all applicable standards, because ISO CE standards are more stringent than those of the United States Coast Guard (USCG), American Boat and Yacht Council (ABYC), or National Marine Manufacturers Association (NMMA) which mirror ABYC.

Boats sold in the U.S. do not have to be ISO CE certified… which costs upwards of $20,000 per model. USCG regulations require safety items such as PFDs and flares, carrying capacity for boats under 26 feet (7.93 meters), and level flotation if swamped for boats 20 feet (6.1 meters) and under. ABYC has distributed American versions of ISO CE Standards and Recommendations…but, they are strictly voluntary. Most critically, there are no ABYC design categories to differentiate between boats of different capabilities suitable to differing sea and wind conditions.
NMMA certification in the U.S. requires only about 70% of the ABYC recommended standards. While most U.S. builders follow the ABYC standards, and indeed many exceed those required by the NMMA, they are not mandatory as is the case in Europe with ISO CE mark standards and don’t involve the cost and post-build survey inspection of ISO.
The MJM Category A Ocean certification ensures MJM owners are boating on a stronger, more stable yacht, designed and built to exceed the highest standards in the world. It means having the peace of mind that comes with knowing that should you find yourself in weather and sea conditions outside your prior boating experience, you will be in one of the safest powerboats in the world. At sea, that comfort is the most important form of comfort a yacht can have.
MJM Yachts – The Luxury of Effortless Driving

© 2024 mjm yachts, all rights reserved.
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Models * I'm Interested in* 3z 35z 43z 43zi 53z 53zi
- Home Port *
- Boat Model & Year Built
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Pamlico Yachtworks Department: Accounting Position: CFO
Pamlico Yachtworks seeks CFO well-versed in all aspects of financial management ranging from simple accounting to broad investment and banking operations.
Key attributes for candidates:
- High-plant-touch orientation
- High technical financial, accounting and tax expertise, along with
- Exceptional “affability/teaming” attributes, in
- Complex, mid-tier manufacturing environments
Employee Duties & Responsibilities
- monthly/periodic financial reports and analyses.
- projections and budgets
- reconciliation with requisite supporting information for accurate presentation of the financial reports.
- Oversees the accounting function (accounting, accounts payable and payroll) and billing and collections functions of the organization.
- forecasting cash flows and operating results
- presenting financial and other information to the leadership team and the Board of Directors.
Requirements and skills
- Proven experience as CFO, finance officer or relevant role
- In depth knowledge of corporate financial law and risk management practices
- Excellent knowledge of data analysis and forecasting methods
- Proficient in the use of MS Office, MS Excel, QuickBooks, ERP and financial management software
- CPA is a strong advantage
- BSc/BA in Accounting, Finance or relevant field; MSc/MBA is a plus
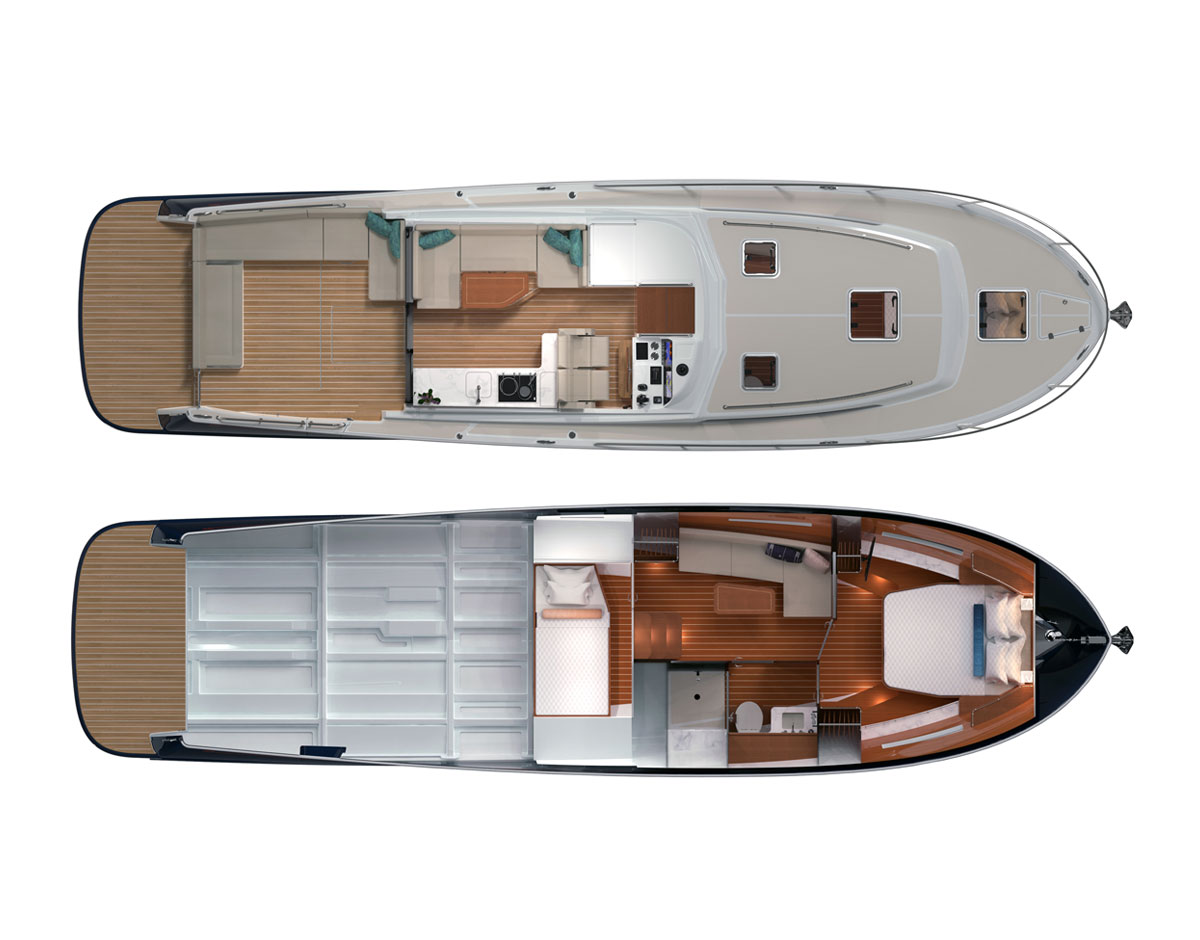

Stay in the know. Get the latest information on MJM Yachts including new models, events, & more.
By submitting this form, you are consenting to receive marketing emails from: MJM Yachts. You can revoke your consent to receive emails at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.
A Zurn Design

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Demystifying yacht classification : Class A, B, C and D. Since 1998, CE certification is required for all recreational boats entering or being sold in Europe obliging boat manufacturers to respect certain building and security standards. Therefore, yachts ( boats ) are classified into four categories depending on their aptitude to confront ...
Category D - Inland or sheltered coastal waters. This rating is for boats in small lakes and rivers with winds to Force 4 and significant wave heights to 18 inches. The number of people onboard can alter the seaworthiness of a boat which can change the CE rated category. The more people there are aboard, the more weight on the boat and ...
Since 1998, Europe (EEC) classifies yachts according to 4 categories A or B or C or D and this is a law. In order to sell a boat in the large territory of the EEC, it must be classified with a plate that mentions its classification and it must be clearly visible inside the boat, usually near the helm. At first glance, it sounds very good when ...
29 March 2016. The CE Yacht Compliance Classification System is the European (CE stands for " Conformité Européenne " in French) dictating the standards for CE Certification for construction and sale of boats. Vessels in one of the categories of controlled products cannot be legally sold in the EU unless they have passed the tests to ...
Yacht classification definitions. The yachting industry is still adapting to regulations and conventions which apply to private and commercial vessels alike. The merchant shipping sector is ruled by safety regulations developed since the beginning of the 20th century, and is familiar with international conventions such as SOLAS, MARPOL and Load ...
As a result, all new and used boats being sold in Europe must be certified as conforming to one of four CE (Conformité Européenne, meaning European Conformity) categories: A, B, C and D. This obligation applies to newly built and imported boats and yachts. These categories have been put in place to determine the seaworthiness of any vessel ...
Have you ever wondered what the different Beaufort scales are and what CE categories A, B C and D boats actually mean? In this video, I walk you through what...
A classification certificate attests that the yacht complies with the standards developed and published by the issuing society. Periodic surveying of a yacht in service by the appropriate class surveyor, at intervals dictated by the appropriate classification society, is also required to ensure the vessel continues to meet the rules and thus ...
Design category D : recreational boats designed for conditions up to and including wind force 4, and up to and including significant wave height of 0.3 meters, and occasional waves of a maximum height of 0.50 meters. The recreational boats in each design category must be designed and built to withstand the design specifications of each of these ...
The following four design categories help quantify a boat's degree of seaworthiness, based on the wave height and wind speed the boat is designed to encounter and handle. ... Category C - Inshore: is for boats operating in coastal waters and large bays and lakes with winds to Force 6, up to 27 knots, and significant seas 7 feet high.
Category C -- Inshore - These boats may venture away from the protected harbors, but within striking distance of home… operating in coastal waters or large bays and lakes with winds up to 27 knots with and significant seas 8' (2.44m) high. Category D -- Inland or sheltered coastal waters - These are your typical day boats,
Owners moving from smaller yachts into those over roughly 80 feet will quickly learn a new alphabet: ABS, DNV, BV, LR, RINA, and more. These are organizations that set rules governing the construction, maintenance, and operation of yachts. Called "classification societies," there are 13 members of the International Association of ...
The CE Mark is issued on the basis of construction and fitting out criteria laid down by the Directive, and related to fundamental aspects, such as: protection of the consumer. The CE Marking process for recreational craft ensures both owners and manufacturers that their yachts meet the highest safety standards, enhancing their market and ...
Yacht classification is a system used to categorize yachts based on various factors such as size, construction, and intended use. The specific classification categories and requirements can vary between different yacht classification societies, but some common classifications include: Pleasure Yacht: A yacht intended for leisure use, typically not engaged in commerce. Charter Yacht: A yacht […]
EFP-M: for yachts having Enhanced Fire Safety Protection in machinery spaces, EFP-C: for yachts having Enhanced Fire Safety Protection in cargo areas, EFP-AMC: for yachts complying with all the requirements of this Section. For more information on Class Notations on Yachts - Classification of Yachts, please feel free to contact Allied Yachting.
Category A boat limits are a minimum mass of 3.0 tonnes and an AVS greater than [130 - (2 x mass)]º but always equal to or greater than 100º. Category B boat limits are a minimum mass of 1.5 tonnes and an AVS greater than [130 - (5 x mass)]º but always equal to or greater than 95º.. A Category A boat needs to be to the right of and above the blue line and a Category B boat to the right and ...
Category C: Designed for voyages in coastal waters, large bays, estuaries, lakes and rivers where conditions up to, ... Under the new 2013 revision, any boat falling within its scope, whether new or second-hand, that is placed on the EU market for the first time, must comply with the essential requirements and will have to individually undergo ...
Category "C" Yachts. A category C yacht is rated to be used inshore. This means that it can head away from the protected harbors, but it shouldn't go very far. Large bays and lakes can be navigated, and the boat can take on waves up to 8 feet high. Category "B" Yachts.
BoatUS Magazine associate editor Lenny Rudow steps aboard the Jeanneau Leader 10.5 and talks to Nick Harvey from Jeanneau America about CE certification and ...
Large commercial yachts classification and certification. Large commercial yachts are defined as those vessels which are: in commercial use for sport or pleasure. 24 metres load line length or ...
Classes of boats and types of boats are two different things. Every type of boat fits into one of four classes of boats. While a type of boat can vary significantly in appearance and function, class is easy to understand. Boat classes are all determined by the overall length of the vessel. The class of a boat is significant for you as a boat owner.
Let's take a look at the four categories. Computer design rendering of the MJM Yachts 50z. Category A — Ocean - This is the category with the toughest standards and covers vessels 40' and over designed to be self-sufficient for extended voyages. It is defined as the "category of boats considered suitable for seas of up to 23 feet (7 ...
Physical and mental fitness Regulation 17. No person may operate a vessel or vessel's equipment whilst under the influence of alcohol or drugs. (Maximum of 0, 05 gram/100 ml alcohol in blood or 0, 24 mg/1000 ml alcohol in breath). No person may refuse that a specimen of blood or breath be taken.