
Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
September 13, 2023
Key Takeaways
- There are many sailboats that anyone can build from home depending on tastes
- Budget will be the biggest deciding factor on a majority of the process
- Consider kits that come with most of what you need or choose ones that are all-inclusive
- Design complexities and new materials may make the building time process longer
- Plan the best you can ahead of time to save money and your working hours
Buying a sailboat can be expensive, but building your own can save you money. So what are sailboats you can build from home?
Sailboats that you can build from home will likely be a small boat under 20 feet. These could be from many different boat suppliers such as B&B Yachts, Brooks Boat Designs, and Chase Small Craft. Boat plans will vary based on your budget and how much time you have on your hands.
Based on my previous experience, building your own boat will take much longer than if a professional were to do it. You also have to be able to study plans, consider various sailboat designs, and have tons of supplies such as fiberglass tape or fiberglass cloth. On top of that, you will also have to be good with your hands.
Table of contents

Top 10 Affordable Sailboats Anyone Can Build at Home
Building your own pocket cruiser or other styles from boat plans is an impressive feat, as this will need dedicated time and money to assure your boat sails safely. Boat building takes a lot of patience as well, especially since this will not be completed in a fast manner.
Finding boat plans and materials that fit your budget will be key to being able to complete the project. The time it takes to complete these projects will vary on your overall experience and needs. Below are 10 of the most affordable sailboats that you can build in the comfort of your home.
B&B Yachts

B&B Yachts have 14 different boat plans you can choose from to find the boat of your desires. Their shop is located along the Bay River in North Carolina where they construct all of the kits and have a 100 foot dock to show off your project once you complete it.
One popular model to check out is their Core Sound 15, as it is the perfect size for those wanting to build a modest size boat for a handful of people on board. Their website features some videos of completed projects and the plans or kits for purchase.
- 14 different models to choose from plus some dinghies
- Various monohull and multihull options
- Friendly customer service with attractive prices
- Might be too many options for some that are indecisive
- Not ideal for those wanting to have a motor sailer
Brooks Boat Designs

Brooks Boat Designs has a handful of options to consider for your next sailboat building project. They are located in Brookline, Maine and give the option to buy the kits or have them build one from scratch for you. They have plenty of knowledge, so do not be shy to ask about modifications or custom features you are looking for.
Depending on your specifics, they can attempt to accommodate some of their plans to help fit your desired outcome. By checking out their site, you can see many examples of their construction in progress and what the boats will look like when completed.
- Offers a variety of kits
- Plans vary around $50 and up, while materials will obviously add more costs
- Some plans can be rowing boats that can convert to sailboats
- Might take a while to hear back from them, as their contact section is a little outdated
- Their plans may not accommodate a ton of extras for your taste
Chase Small Craft

Chase Small Craft offers a simple process for building boats. Their kits are equipped with everything you need and will help save you time than just buying the materials outright and other parts you could need. This is arguably one of the best bang for buck instances if you want to save time and money searching for pieces to your boat.
They are located in Saco, Maine and will ship everything to your home from there. All the necessary materials are included and all you need are the proper tools and working space.
- All-inclusive kits with what you need
- Tons of knowledge on their site for boat building
- Easy process to order and customize
- Complete kits can range over $20,000 for larger boats
- Kits may take up to eight weeks to ship out
Chesapeake Light Craft

You can expect high-quality boat kits from Chesapeake Light Craft . They feature 18 different sailboat kits that vary from eight to 20 feet in length. This should be more than enough to find one for you if you are newer to boat building.
They also have a wide variety of other kits in addition to the sailboat, in the event that you wanted to order a small kayak or paddleboard in addition to your sailboat. The prices vary considerably when considering a small or larger boat, so check the complete list of options to in order to potentially fit your needs.
- Plenty of sailboat offerings to choose from
- Different beautiful hull form options to consider
- Easy to build and perfect for sailing
- Only has basic materials needed for kit, so you may need to purchase other items
- Has epoxy shipping fee no matter if you pick up item
Dudley Dix Yacht Design
Dudley Dix Yacht Design has an extensive list of plywood and single skin sailing boat options. They have plenty of sail plans and kits to consider depending on your goals. These follow a classic look for sailboats, which are aesthetically pleasing.
If you are wanting one to accommodate a small family, they have more than plenty to look through. The cost is not as bad compared to others, but keep in mind that you may need to throw in your own supplies or specific tools to get the job done.
- Plans start at $30 and range up to $7,500 or more for kits
- More than enough of options to consider
- Affordable variety of sailboat offerings
- Might be too many options for those new to sailing
- Most are wood without the use of aluminum or steel
Farrier Marine

If you are in search of a multihull to build, then Farrier Marine is what you need. They offer a unique folding catamaran that is trailerable and give you the option to build it yourself. This not only makes it an appealing option, but anyone can take this multihull boat wherever they want with ease.
It features a thorough construction guide once you receive all of the materials. These also come with stainless steel fasteners and an aluminum mast for high-quality materials. Pricing will vary since you must request which model type you are considering.
- Ability to build a unique catamaran
- In-depth construction guide to help
- Easily handled and trailerable
- Price may be too high
- Limited offerings since only a few multihull options
Glen-L Marine Designs

Building a boat from Glen-L Marine Designs can save you time and money. They feature an easy system to order and receive the kits, as well as an in-depth guide to building them. This is an appealing option compared to most boat kit sellers.
The beauty about Glen-L is that anyone can build these from scratch, so you do not have to be the best boat builder in the world to get it done. They offer guides and helpful insights from their team to point you in the right direction. Plans vary around $15, while kits can range well over $1,000 depending on boat size.
- Nearly 50 designs to choose from
- Complete guide to help anyone build it
- Plenty of price points depending on size
- Might be overwhelming with the amount of options
- Could take a while to get parts since they are popular
John Welsford Boat Designs

John Welsford Boat Designs invites new and veteran boat builders that want a taste of quality small wooden boats. The boat plans are designed to meet your specifications and are catered to your desires.
There are seven sailboat designs to choose from so you do not feel overwhelmed in the process. However, they do not sell kits all the time, so you would need to have the materials or be on the lookout for the best prices when they are available.
- Seven sailboat plans with different sizes
- Quality boat builder and supporting community
- In-depth knowledge provided to you when you order
- Might be too small of boat size
- Kits are not always available
Iain Oughtred
There are plenty of options on the wooden boat store, but you should narrow down your search for Iain Oughtred’s line of sailboat kits and plans. There are 25 different plans to choose from, which should accommodate most everyone looking to build their own boat.
While they do offer some kits, they do not routinely offer sailboat kits. You would need to purchase all of the materials if you are considering one of their sail plans. Keep this in mind if you are considering, as you would need to hunt down the parts yourself.
- 25 different sailboat plans to look through
- Various sizes to contemplate for you sailing needs
- Prices will vary but are not bad compared to market
- No sailboat kits, only plans
- Newer boat builders might find too many options unappealing
Paul Gartside Boat Builder and Designer
Gartside Boats is a boat builder company based in Long Island, New York that showcases a variety of boats from traditional and newer methods of boat building. Within that variety, they have boat plans meant for six to 50 feet in length.
With an abundance of options, you will need to contact them regarding prices and any customizable options. Kits may vary as well, as they typically design in-house and build for you.
- Experienced boat designer that can accommodate with custom plans
- Many options are trailerable
- Can have plans for up to a 50 foot boat
- You will need to contact them for prices
- Customized options may make process more complicated for new boat builders
How Much Does it Cost to Build a Sailboat at Home?
As you have likely already done so, the math between building your own boat and buying one may be a huge difference. Likewise, you may even enjoy the challenge of taking an older boat that is gutted and restoring with parts from a kit to build one new again.
But how much does it cost exactly to build a boat from the comfort of your own garage or workshop? The prices are going to vary dramatically depending on your situation and material needed to get the job done. In addition, the time that it takes to complete this will also vary.
Sail plans are rather inexpensive if you are aiming to build a small boat. These plans allow you to see the workings of the boat design and what you need to build the boat.
Without these plans, you will not know the exact details of the design and it can cause major issues with the boat’s hull or other areas of the boat. Think of these as the backbone or instructions of the boat’s infancy before being built.
Price Per Square Foot
You should assume to pay anywhere between $300 to $600 per square foot if you are interested in building a boat. Buying a kit outright can be a good way to save time, but oftentimes these do not come with everything you need.
Instead, you should try to source as much of the materials at the best price as possible. Thinking ahead is part of the process and you might be able to score a deal at a lumber yard or hardware store for parts.
Boat Designs Matter
The design of the boat will be much different from one boat to the next, regardless if they are the same size in length. If you are pondering boats that range anywhere between 16 and 20 feet, you should factor in the shape of the hull, any rigging, and various appendages.
Prices tend to increase when there are more complexities within the designs. If you are considering a kit with more details than others, you will also have to pay more for the designs on that as well.
Kits Can Differ
It is important to understand that all kits are not going to be the same. As you gander at sailboat kits online to stitch together, you need to thoroughly look over to see if you have everything you need before buying.
It would also be at your advantage to ask the seller if any additional parts or supplies are needed. This may change your dynamic on the kit buying process and you may pass up one for another if it has everything you need. An all-inclusive kit may cost several hundred, if not thousands, of dollars more to have the convenience of everything in the bundle.
Construction Approaches
Some boat plans may require you to have certain tools to get the job done. This means special saws or planers, which the average person simply does not have.
Purchasing specialty tools might be expensive upfront and hard to find depending on what it is. Your best bet would be to check locally for others trying to sell their tools or consider a boat plan that does not require extensive tools to finish the job.
How Long Does it Take to Build a Sailboat?
An easy to build sailboat could take a while to build from scratch. Many different variances come into play that are difficult to pinpoint for everyone. But how long is that exactly and how will your experience play into this?
A fun project to sail in the wind could take you several months to well over a year depending on the boat plan and how big your boat is going to be. In addition, the materials all need to be accounted for prior to starting in the event a hardware store does not have them in stock.
Time Varies
The time that passes for simple boat designs on small sailing vessels can be done in a few weeks. This is assuming you have everything you need and work non-stop around the clock.
Certain complex situations may make the process long, such as the difficulty of working with some materials. If you are a skilled laborer, it may take you half the time compared to a novice. The amount of time it can take will vary on your availability and skill level.
Planning ahead will undoubtedly offer the most time-saving features. It also helps if you can tackle parts of the project at your own pace.
Complexity of Design
The design of the boat may make the construction process longer. For example, it may take you longer to build a catamaran compared to a similar lengthed monohull.
More complex designs might require more materials, therefore making the process a bit longer to complete. Furthermore, you will also need more experience working with difficult designs and that will affect you more as a newbie.
Be sure to manage your expectations well and do not allow yourself to become too stressed over this fun project. If you can, seek expert boat building advice from a local builder or the company you purchased sail plans through.
Quality Materials
The quality of the materials will matter significantly when building a boat and will greatly affect the time it takes to construct it. Handling fiberglass or carbon fiber might require specialty tools, while wood also demands a certain level of craftsmanship.
If you are not skilled at working with the material at hand, it might affect the quality of the build and you may have to go back to fix mistakes. This will definitely add more time to your project, because mistakes are bound to happen with your first project.
To save time, consider adding the tools and materials throughout the year or as often as your budget allows. You may want to try testing your skills on fiberglass or other materials to get a feel for how to work with it.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Best Sailboats
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Best Small Sailboats With Standing Headroom
December 28, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023

Best Bluewater Sailboats Under $50K

Hunter Sailboats: Are They Built for Bluewater Cruising?
August 29, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

- About Modern Wooden Boats
- Tips & tricks
- What’s inside a boat plan ?

Idea 21 sportboat
The development of the family of small offshore capable sailboat plans : chined hull for the highest stability, vertical lifting keel, trailerable, suitable for club racing or cruising (two interior versions) , plywood and epoxy hull with the radius chine system, sparkling performances while sailing and reasonable interiors for coastal cruising.
First boat launched : read the first impressions here
Idea 21 small sailboat plan is the latest development of my family of small plywood & epoxy sailboats plans for homebuilders : it was quite a time since i was thinking of an evolution of her smaller 19 footer sister, so i finally take the decision to publish this new plan. the goals of this plan is simple: add interior volume, simplify the work for homebuilders switching to a complete plywood & epoxy radius chine hull, enhance slightly the sparkling performances of idea 19, keeping the sailboat very balanced and suited for sailors ranging from enthusiast beginners to experienced seamen., first boat launched and several other boats in building stage make idea21 the most sparkling project on our catalogue, hull: chined hull on a small light sailboat has a simple reason to exist: it gives more stability to the sailboat when heeled, much more than a round hull similar sailboat. i managed to keep a very low wetted area of the unheeled hull, in order to achieve a good pace in light air and avoid excessive drag. stern sections are quite flat to gain speed downwind (idea 19 has been clocked with speed steadily in excess of 15 knots)., bow sections: experiences on racers showed that “knife-blade” bows may give you less resistance, but the price to pay is high in terms of buried bow sailing downwind, so i decide to provide this plan a large u-shaped section on the bow ; sails provide the sailboat plenty of power to defeat the small amount of added drag., sailplan: i have a very good starting point with idea 19, so we’re doing small adjustments and no revolutions: square top mainsail, 7/8 fractional rig , very wide single swept spreaders, no backstay, deck stepped mast with sturdy section, 110 % j jib, code zero, jennaker hoisted on swinging retractable bowsprit, and a good amount of sail area., keel and ballast: idea21 have a solid hard wood cored & unidirectional glass epoxy laminated lifting keel, with a naca optimised profile and a low resistance hydrodynamical shaped 280 kg lead bulb bolted on the keel tip; it can be made by a homebuilder, no need for professional welder; the fin area is on the low side, speed will help generating the required lift without adding too much drag. keel case is in 20 mm thickness plywood and epoxy laminated glass reinforcements, and it’s perfectly waterproof while sailing., full lifting keel version : after a request from a builder, idea 21 cruise is available in a version featuring an integral watertight keel case running form hull bottom to cabin top panels, this feature called flk (full lifting keel) will allow the boat to sail with keel partially raised or to motor with keel totally up, a good option if you sail in shallow waters frequently., cockpit: was one of the strongest point in idea19, we simply keep the same arrangement and dimensions, so we have a really huge area for the crew and a simple and sturdy building in plywood panels epoxy glued on a structure of bulkheads and stringers., interiors: here i focussed on several upgrades; i decided to split the project in two versions (so two different sets of plans, you have to specify on order), “sport cruise” or “racing” ; both versions have 4 berths, a classic v berth on bow and two quarter berth after; in the cruising version cabin is 55 cm longer, giving wider interiors, enough room for a separate toilette and more comfortable after berths ; in the racing version we have a marine toilet (there’s room for a jabsco compact one) under the bow v-berth; cabin height is 1.65 m in both versions. interiors plywood panels are detailed on plans., taking advantage form the first season of sailing, i can now say that i strongly advice the cruise version as long as you are not going to run a sailing school, thus needing extra space in the cockpit., wooden rig: starting form summer 2019 we deliver two extra drawings with the plans, both for race and cruise version, describing how to build a wooden rig suited for this boat. keep your budget low at the price of a small extra weight , how to build the boat: we chose the plywood & epoxy resin “radius chine” system, as for petrel 28 and hirundo 750, so the hull planking is in okume marine grade plywood ; planking the hull is quite fast , and the internal structure of the boat is made by plywood bulkheads, floors and solid wood longitudinal stringers, all glued with epoxy and strengthened with epoxy laminated glass tape, assembled on a cheap wood scaffold, keeping the hull light, sturdy and quite easy to build for homebuilders ; the goal is to keep the total weight of the 19 footer, raising the ballast fraction of the sailboat at the same time. here are a couple of pictures of the first planked hull perfectly showing the radius chine planking system.
a HUGE Thanks to Nils Theurer ([email protected]) for the awesome pictures taken during the first sea trials

Plans availability: Plans are available in italian and english. Plans are available in imperial units upon request (send me a mail before purchase).

By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information Accept
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this.

- Basic Kayaking Knowledge , Learn
15 Free Boat Plans You Can Build This Week (with PDFs)
Boatbuilding is one of the most ancient forms of craftsmanship still alive today. As long as our ancestors have had a curiosity about exploring open waters, they have been practicing and honing their boatbuilding skills.
To be honest, however, building a boat is no small task. It will require a lot of work and patience to ultimately create a finished product that you are happy with and that is actually seaworthy.
Of course, we have also included a few free boat plans. You can keep in your back pocket for the next time you are asked to build a cardboard boat as part of a contest or lakefront teambuilding adventure.
We hope that these resources help you in your journey to build your own boat!
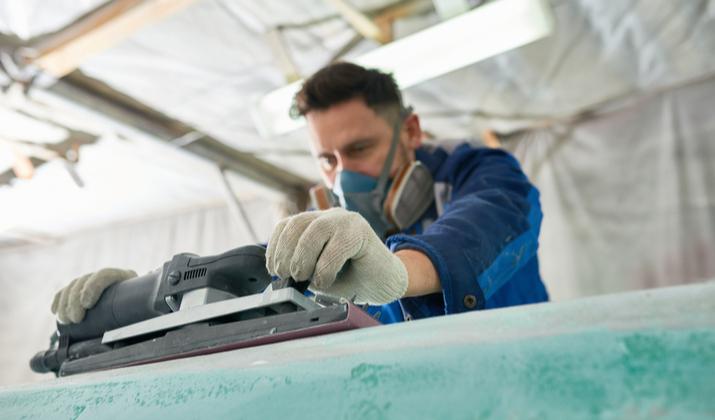

Photo by SeventyFour via Shutterstock
Free Boat Plans
Why build your own boat, 1. the wanigan, 2. the mouse, 3. the slipper, 4. the handy andy, 5. the junior, 6. the jolly roger, 7. the cork, 8. the hobby kat, 9. the tern, 10. the falcon, 11. the white duck, 12. the sea midge, 13. the zephyr, 14. the gypsy, 15. the crazy cardboard boat, 15 free boat plans you can build this week (with pdfs) – final thoughts, share on pinterest.
- The Wanigan
- The Slipper
The Handy Andy
- The Jolly Roger
- The Hobby Kat
The White Duck
- The Sea Midge
The Crazy Cardboard Boat
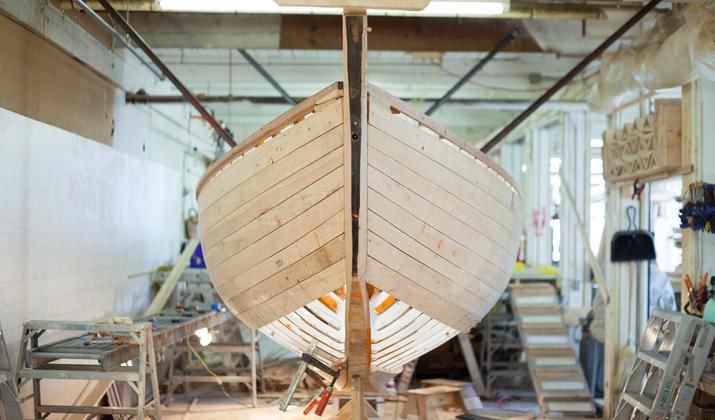

Photo by Halsey via Shutterstock
There are a lot of reasons why you should explore building your own boat versus buying a pre-made model. Here is a quick breakdown of the most obvious benefits:
- You will know the ins and outs of your finished boat better than anyone
- It can be a great project to work on with your teenage or even adult children
- You will gain valuable skills molding and shaping wood and other materials
- You can design your boat for your specific needs
- You don’t have to trust the sometimes-questionable manufacturing of mass-produced boats
- You can create a boat that functions as your second home on the water
- You can save money if you source materials mindfully
Of course, most first-time boatbuilders still experience some level of trial-and-error. With patience and perseverance, however, you can craft a one-of-a-kind vessel that has no equal anywhere in the world.
Free Boat Plans You Can Build This Week (with PDFs)
PC Duckworks Boat Builders Supply
The Wanigan boat began as a garvey design, which is one of the older boat plans known to the Americas. Traditionally, these boats were built as work scows and were very popular among American summer camps.
The design itself is very simple, but these boats can carry heavy loads. It can also handle a trolling motor being mounted to the stern so you can cover more ground if you want to use it as a fishing boat.
The creator of this boat plan became aware of some of the downsides of the garvey design, such as the heavier weight that made it less efficient than some other designs. So he combined elements of dory and wanigan designs to create a hybrid.
The main changes include an enlarged beam, tilted lathes to provide a stiffer hull, and knocking off the top strakes to reduce the boat’s overall weight.
The Wanigan text
These additional The Wanigan drawings  may also prove useful for your build process!
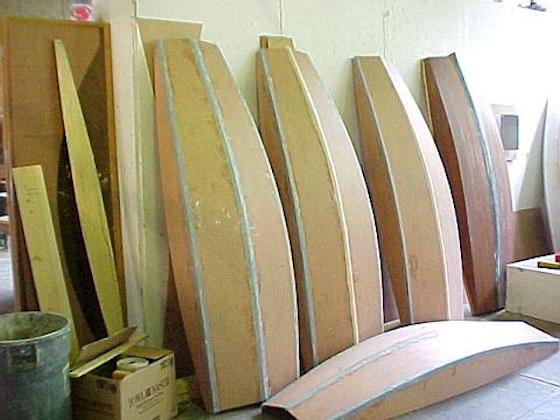

The Mouse is one of the most compact and nimble boat plans we have found for this list. It is an easy build and also a great boat for two kids or a single teenage paddler.
The original builder began with a one-sheet boat design in an effort to create the lightest and most affordable boat possible. This means it is only suited for calm waters and should not be used in high winds or wavy conditions.
That said, it was built in roughly 12 to 24 hours of work time and doesn’t require a full workshop to construct. The main material that is required for building this boat is quarter-inch plywood. But the builder recommends using one-inch by half-inch pine or something a little sturdier.
The plywood and pine components are held together using a method called ”˜stitch and glue’. This method requires choosing one of the best glues for kayak outfitting , which are typically made of epoxy and glass tape rather than something cheaper like polyurethane.
The Mouse Instructions
Also, here are a few extra useful The Mouse Notes for builders
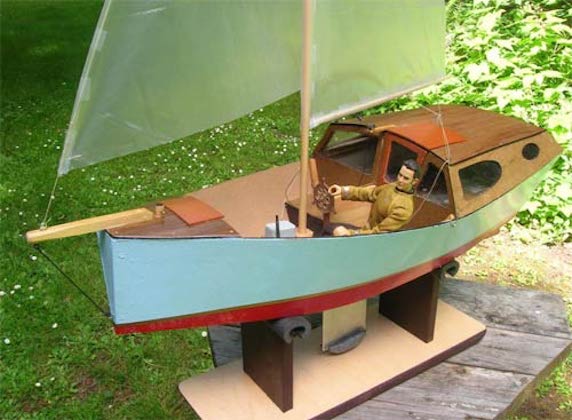

The Slipper is the first of many sailboat plans on our list and it is faster, easier, and cheaper to build than most. It also features a deeper cockpit than many other sailboat designs, which makes it safer for intermediate sailors.
This sailboat plan features dual steering stations so that you can sail from inside or outside of the helm. It also includes a centerboard trunk that hardly intrudes into the cabin at all. So that, it is easier to work around while you are in the cockpit.
The exterior hull and cabin of this sailboat feature a modified dory design using two sheets of plywood ripped to three feet wide before being joined together. The resulting hull is a modified V-shape that reduces drag.
The centerboard of this boat can also be winched up to the level of the top of the cabin or lowered down to alter the draft. This allows you to customize the boat design for a stiffer and more weather-worthy vessel if you need it.
The Slipper was also intentionally designed with an aft cabin that naturally helps to keep the bow pointed into the wind whether you are underway or the boat is anchored in the port.
The Building Slipper
PC DIY Wood Boat
The Handy Andy is a great little 10-foot portable rowboat for hunting, camping, fishing, and other recreational uses. It is actually the only folding boat design on our list, which makes it best for folks that need the most portable boat plan possible.
This boat features a 42-inch beam and a depth of about 15 inches at the mid-section. It also weighs roughly 80 pounds when assembled and can handle up to three average-sized human passengers.
The design boasts a flat bottom with canvas-bound edges and the primary material used for construction is ⅜-inch marine-grade plywood. Despite its lightweight nature, this rowboat can handle trolling motors or even outboard motors with a maximum of five horsepower.
Once finished, the hull can be folded or unfolded in less than a minute’s time.
This design makes it one of the only boats on this list that can be stored in a truck bed or easily carried by two people to be launched at more remote locations.
If you are looking for an all-purpose dinghy that can handle almost any use you might imagine, look no further than The Junior free boat plan. It can carry three or four average-sized adults and is much easier to row than a traditional dinghy.
It is also durable enough to be equipped with a small outboard motor. You could even set it up with sailing equipment if you want to use it as a sailing vessel. As we said, this is truly an all-around boat design!
This boat plan requires constructing three frames that will provide the majority of the load-bearing support. The builder recommends using ¾-inch framing with ⅜-inch plywood as the exterior material for this boat build.
Resin glue and flathead screws are also required to hold this boat together. But there is a full list of materials included in the plans we have linked to below. Sticking to that plan should also give you enough leftover materials to construct two six-foot oars for rowing this boat until you install a trolling motor or outboard motor down the line!
Channel your inner Captain Morgan when you are following these plans to build your very own Jolly Roger boat. This flat bottom boat design is designed for pond fishing . It can also be a useful yacht dinghy for getting from your dock to a larger vessel anchored offshore.
The plan follows conventional dinghy construction methods but also includes a few modifications that will save you time and energy. The wide design is super stable for boaters of all ages.
The keel, frame, chines, and risers are all cut from ¾-inch oak, ash, or any other trusted hardwood you can get your hands on. For the smaller components, the builder recommends using cedar, cypress, fir, or white or yellow pine.
Because this boat plan is also sturdy enough to handle a small motor, it includes important points for protecting the wooden hull from spark plug damage.
Be careful to follow these guidelines to build the safest boat possible if you imagine installing a motor down the line.
The Jollyroger

The Cork is another simple rowboat design. This one trends away from the flat bottom plans that we have included thus far. Instead, it features a deeper, V-shaped hull that makes it better suited to more efficient rowing and easier maneuverability.
It can be rowed easily from either seating position and is durable enough to handle up to three average-sized adult passengers. The ends of the boat are identical, which allows for multi-directional rowing.
The list of materials required for this boat plan should cost you between $30 and $50, depending on your location and hardware costs there. The resulting build is lightweight enough for two people to be carried and also to be transported on top of a vehicle .
Inside the boat, the builders use aluminum tubing to secure the struts that hold the seats. This material choice keeps the overall weight of the boat down while still adding the necessary rigidity across the beam of the boat.

The Hobie Cat is one of the most iconic and recognizable small sailing vessels ever made. This Hobby Kat plan is your answer to building your own iconic sailboat without spending thousands of dollars.
Your finished boat will be able to handle speeds of up to 20 miles per hour. It will be a super fun vessel for windy days on the lake or bay. The builder was able to construct the hulls, decking, and rudder for this boat while spending little more than $200.
From there, they purchased and installed the mast, boom, sail, and rigging, which brought the total amount spent to roughly $650 (still much less than a name-brand Hobie!). Without the mast and sail, this boat weighs roughly 165 pounds and is constructed using primarily 3/16-inch marine plywood.
You can also elect to build your own mast, boom, and sail if you have the time and skills to do so.
Those elements are not included in this boat plan, but they do offer some recommendations for where to buy these components!
The HobbyKat
Named after the common seabird found around the world, the Tern is a lightweight and nimble sailboat with a 72 square foot base design. She is made for inland sailing and planes very well in moderate breezes.
The hull design also provides minimal water resistance and the small floor plan makes this boat easier for intermediate sailors to handle. Even though it offers a small footprint, this boat is sturdy enough to handle up to four adult passengers.
One of the best things about this boat plan is that it can be built almost entirely by using only common hand tools.
Of course, you can speed things up if you have power tools and you are skilled enough to use them correctly.
The Tern boat plan includes a 20-foot mast, but you can shorten that length if you desire. The plan includes a complete list of materials and step-by-step instructions on how to plane and assemble each element.

As you might expect from its name alone, the Falcon is an incredibly speedy sailboat for its size. It boasts a 14-foot centerboard and can handle two to four passengers, depending on its size and weight.
In tests of the original build, the creators claim that this boat out-distanced many Snipe and Comet sailing vessels as well as pacing evenly alongside longer 18-foot sailboats. When finished, your boat will have a six-foot beam and a total weight of roughly 475 pounds.
For the main framing components, they recommend using white oak and plywood will be the main material used in the hull construction. The hull features a V-shaped that was inspired by larger schooners.
The Falcon is best suited to sailing on bays, lakes, and wide rivers. It is also a boat plan with just under 120 square feet of deck space and it is a great build for amateur craftsmen and sailors.

The White Duck is a flat-bottomed rowboat with a total length of 13’6” and a four-foot beam. The cockpit is approximately 15 inches deep all the way around and this boat can handle up to five passengers while maintaining buoyancy and stability.
When fully constructed, it will weigh roughly 200 pounds, but the final weight will depend on the type of lumber you choose for your build. This boat plan features plywood planking over solid wooden frames.
The White Duck is built with a pointed bow that cuts nicely through the water. The flat stern of this boat design will make it easy to attach a small outboard motor with a maximum of six horsepower.
As you might expect from its name, this rowboat is a great option for duck hunting trips. That being said, it is a highly versatile craft that can also be used for pond fishing or casual rowing on your nearby lake.

The Sea Midge is one of the smallest rowboats on our list and it is ideally suited for one average-sized rower or two small paddlers. It is only about 8 feet in length and offers a 52-inch beam at its widest point.
The Midge’s small dimensions make her ideal for navigating narrower creeks and streams. With an approximate weight of 62 pounds, she is easy to maneuver on the water and can also be much more easily transported than some of the larger boat plans on our list
The Seamidge
The Zephyr is a compact and speedy dinghy sailboat that measures roughly 14 feet long and approximately five feet across. This boat style was originally developed for safely crossing the English Channel. This means it can stand up well in rough waters.
When finished, it is also light enough to be transported on a small trailer or on top of a larger vehicle.
The boat plan calls for using hemlock or fir for the framing and oak or Douglas fir for the keel and chines.

The Gypsy is a small cruising sailboat that is meant to be equipped with an outboard motor for powered locomotion. The original design resulted in an incredibly seaworthy vessel that logged more than 6,000 nautical miles in her lifetime.
It includes a comfortable cabin that makes it well-suited for multi-day sailing adventures. This boat plan includes improvements on the original design that will help you build an extremely durable and long-lasting sailboat.
The Gypsy boat design will help you construct a vessel that can handle a motor up to 25 horsepower so that you can enjoy cruising speeds of up to nine miles per hour.
While it may require a bit more of an investment in time and money, it will also help you produce one of the best boats you can build with a free boat plan!
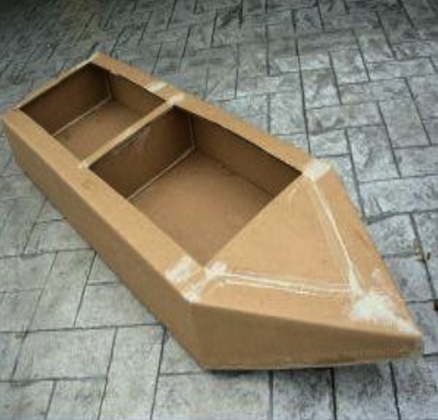

PC Saint Dominic Catholic School
Finally, let’s talk about a crazy cardboard boat plan that you can build in less than a day. This is a great boat plan to bookmark for your next teambuilding project so that you can earn bragging rights with your coworkers.
The plan calls for using 1.5 sheets of cardboard. But you can use the remaining half sheet to build your own boat paddle if you want to get creative.
Triple-thick cardboard is best for this boat plan. But you can always double up thinner sheets if that is all you can find.
These plans include an easy-to-follow diagram for marking, cutting, and folding the cardboard sheets to create the hull of your boat. From there, it calls for using contact cement and construction adhesive to seal the edges and corners.
If you are looking to save a little money on this build you could also use duct tape and then wrap the entire design in plastic sheeting to provide waterproof qualities.
Overall, this build is one of the cheapest and easiest on our list. It is also a great project for hot summer camp days on the lake or river!

Photo by Alexandra Soloviova via Shutterstock
We hope that you now have a couple of free boat plans to inspire you to begin your own construction project.
Don’t hesitate to check out YouTube for some useful boat-building videos when you are getting into the nitty-gritty of these build processes!
Enjoyed 15 Free Boat Plans You Can Build This Week (with PDFs)? Share it with your friends so they too can follow the Kayakhelp journey.

Peter Salisbury
Pete is the Owner of KayakHelp.com. Born and raised in Cleveland, Ohio, he grew up kayaking, fishing, sailing, and partaking in outdoor adventures around the Great Lakes. When he’s not out on the water, you can find him skiing in the mountains, reading his favorite books, and spending time with his family.

Great Projects
Build a small sailboat free plans.
These plans are for a small 15 foot knockabout sailboat.
I like these plans for their ease. Building a smaller boat is a lot more attainable than a cabin cruiser! And these plans get right to the specifics of building. From the plans:
ANY SAILBOAT fancier will like "Tramp," the trim, 15-ft. knockabout that's so easy to build in plywood. The first operation is to cut the stem, transom and side planks and assemble the forms.
Use casein or waterproof glue under the butt strap joining the side planks together. Forms can be made of almost any scrap material on hand. If you are a good enough mechanic, they can be dispensed with and correctly beveled frames made to their exact shape can be placed permanently in the boat. Screw-fasten the oak frame at sides and bottom on the inside of the transom. Then notch out the bottom of the frame to receive the keel batten...
The transom is placed last and must be beveled so that the side planks fit tightly against the cleats and the transom edge. Be sure to place white lead and a thin thread of cotton between planks and stem and transom prior to joining them together...
Related Plans

All Our Vintage Projects Categories
Vintage projects.
All rights reserved, 2020 [email protected] Copyright, Safety and Legal Information Terms of Use - Privacy Policy Site Map
Discussion Forum
Ask questions, get answers, share stories in our discussion forum!

Step-By-Step Guide: How to Build a Wooden Sailboat – Complete DIY Tutorial
Alex Morgan

Building a wooden sailboat is a rewarding and fulfilling endeavor that allows you to create your own vessel for sailing adventures. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a woodworking enthusiast, constructing a wooden sailboat requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a love for craftsmanship. This comprehensive guide will take you through the step-by-step process of building a wooden sailboat, from choosing the right design and gathering the necessary materials to assembling the framework, building the deck and cabin, and installing the sails and rigging. We will also discuss the finishing touches and regular maintenance required to keep your wooden sailboat in optimal condition for years of enjoyment on the water. Let’s dive into the world of wooden sailboat construction and embark on this exciting journey together.
Key takeaways:
Key takeaway:
- Choosing the right design and plans is crucial: Research different sailboat designs and select suitable plans based on your skill level to ensure a successful project.
- Gather the necessary materials and tools: Pay attention to wood selection and preparation, as well as acquiring the tools and equipment needed for building your wooden sailboat.
- Attention to detail in the construction process is important: Prepare and assemble the framework carefully, focusing on lofting, laying out the keel, constructing the ribs, and the hull structure to ensure a sturdy and reliable sailboat.
Choosing the Right Design and Plans
When it comes to building a wooden sailboat, one of the crucial steps is choosing the right design and plans. In this section, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of sailboat designs and explore the vast array of options available. From researching different sailboat designs to selecting plans that match your skill level, we’ll guide you through the exciting process of bringing your wooden sailboat dream to life. So, hop aboard and let’s set sail on this exhilarating journey of craftsmanship and adventure.
Researching Different Sailboat Designs
When conducting research on sailboat designs, it is important to take into account a variety of factors in order to select the most suitable design. One of the primary considerations is whether you prefer a monohull or a multihull sailboat. Monohulls are more commonly found and offer superior performance when sailing upwind, whereas multihulls provide both stability and speed.
Another aspect to consider is your level of sailing experience. If you are a beginner, it is advisable to seek out designs that are easier to handle and forgiving. On the other hand, experienced sailors may gravitate towards performance-oriented designs that are ideal for racing or long-distance cruising.
It is crucial to think about how you intend to use the sailboat. Are you looking for a day sailer , a cruiser , or a racing boat ? Each design comes with its own set of distinctive features and characteristics.
Determining the appropriate size of the sailboat is another crucial step, which should be based on the number of people and activities you plan to have on board. You must also decide whether you prefer an open cockpit or an enclosed cabin .
To find the perfect sailboat design that aligns with your sailing goals and preferences, it is imperative to thoroughly research various options and take into consideration all of these factors. By doing so, you will be able to make an informed decision and select the ideal sailboat design.
Selecting Suitable Plans for Your Skill Level
When it comes to building a wooden sailboat, it is crucial to select suitable plans that match your skill level. This is important as it ensures that you have the necessary knowledge and expertise to effectively complete the construction. In order to help you with this, here is a table that outlines the different skill levels and the corresponding plans:
Choosing the right plans for your skill level is essential as it enables you to navigate the construction process smoothly, avoid any complications, and ultimately achieve the desired result. It is crucial to honestly evaluate your woodworking skills and then select plans that align with your abilities. Keep in mind that building a wooden sailboat demands patience , attention to detail , and a willingness to learn and improve your woodworking skills.
As a pro tip, if you are a beginner, it is advisable to start with simpler plans and gradually work your way up to more complex projects. This allows you to gain experience and confidence in your woodworking abilities over time. So always remember to select suitable plans for your skill level and enjoy the process of building your wooden sailboat.
Gathering the Necessary Materials and Tools
When it comes to building a wooden sailboat, gathering the necessary materials and tools is key . In this section, we’ll dive into the exciting world of selecting and preparing the right wood for your sailboat, as well as the essential tools and equipment you’ll need to bring your project to life. So, start sharpening your creativity and let’s sail away into the realm of wooden boat construction!
Wood Selection and Preparation
Incorporating the provided keywords naturally in the provided text:
1. Conduct research on the different types of wood used in boatbuilding, such as mahogany , teak , or oak . This will help you make an informed decision regarding the most suitable wood for your sailboat.
2. Determine the specific requirements of your sailboat design in order to guide your wood selection process. Each design may have different needs and preferences when it comes to the type of wood to be used.
3. Take into consideration the durability and resistance to rot of the wood options available. This is crucial to ensure the longevity and overall quality of your sailboat. Choosing a wood that can withstand exposure to water and other elements is essential.
4. Look for straight , dry , and defect-free wood. This will contribute to the structural integrity of your sailboat. Any defects or irregularities in the wood may compromise its strength and performance.
5. Calculate the amount of wood needed based on the specific design and measurements of your sailboat. This will help you estimate the quantity of wood required for the construction process.
6. Mill or cut the wood into the required dimensions and shapes as outlined in the sailboat design. This step is crucial for achieving the desired structure and appearance of your sailboat.
7. Prior to assembly, it is important to sand the wood surfaces thoroughly. This will remove any rough edges or splinters, ensuring a smooth and safe finish.
8. Apply a protective coating or sealant to the wood in order to prevent water damage. This will help preserve the wood and extend its lifespan .
By following these steps, you can ensure that the wood selected and prepared for your sailboat construction is suitable and of high quality.
Tools and Equipment Needed for the Project
When embarking on the construction of a wooden sailboat, it is crucial to have the appropriate tools and equipment to ensure successful completion.
To accurately measure and obtain precise alignment and dimensions, essential measuring tools such as a tape measure , combination square , and level are indispensable.
For shaping wooden components, cutting tools like a circular saw or table saw , jigsaw , and hand saw are necessary.
Joinery tools, including a chisel set , mallet or hammer , and drill with different-sized bits, are vital for smoothly joining parts together.
To achieve a polished finish, sanding and finishing tools such as sandpaper with varying grits, sanding blocks , and a random orbital sander are crucial.
Additionally, brushes and rollers are required for the application of finishes.
When it comes to safety, it is imperative to prioritize the use of safety goggles , ear protection , a dust mask , and work gloves to ensure personal protection during the construction process.
When selecting tools and equipment, it is essential to invest in high-quality items that are specifically designed for the tasks involved in wooden sailboat building.
By doing so, not only will efficiency be maximized, but the overall quality of the finished boat will also be greatly enhanced.
Preparing and Assembling the Framework
As we delve into the world of building a wooden sailboat, we now find ourselves in the exciting phase of preparing and assembling the framework. In this section, we’ll discover the essential steps that go into setting up the lofting and laying out the keel , as well as the intricacies of constructing the ribs and hull structure. Get ready to immerse yourself in the hands-on process of bringing this magnificent vessel to life!
Setting Up the Lofting and Laying Out the Keel
To properly set up the lofting and lay out the keel for a wooden sailboat, it is important to follow these steps in a systematic manner:
- Firstly, prepare the lofting area by clearing a large, flat space where the plans and measurements will be placed.
- Next, securely attach the keel stock to the lofting platform, making sure it is both level and aligned with the boat’s centerline.
- Using battens, rulers, and pencils, transfer the measurements and lines from the boat plans onto the lofting platform.
- Ensure the accuracy of the waterlines, buttock lines, and other reference lines on the lofting platform by drawing them according to the measurements provided in the boat plans.
- Utilizing the dimensions indicated in the plans, measure and mark the positions of the keel, stem, and transom on the lofting platform.
- Thoroughly examine and adjust all lines and measurements to guarantee their accuracy.
- Identify the locations where any additional frames, bulkheads, or structural elements will connect to the keel, by marking them accordingly.
- Prior to proceeding, double-check all marks and measurements to ensure their accuracy.
The process of setting up the lofting and laying out the keel is an integral step in the construction of a wooden sailboat. It serves as the foundation and reference points for the boat’s overall structure. It is crucial to pay close attention to detail and maintain accuracy throughout the build. By following these steps, you will be on your way to constructing your very own wooden sailboat.
Constructing the Ribs and Hull Structure
When constructing the ribs and hull structure of a wooden sailboat, follow these steps:
– Measure and cut the ribs: Use the plans as a guide to mark and cut the dimensions on the wood. Cut the ribs accurately.
– Attach the ribs to the keel: Position and attach the cut ribs evenly along the keel using marine epoxy and screws.
– Install chines and stringers: Attach the chines to the bottom edge of the boat and install the stringers along the sides for strength.
– Attach the planking: Cut and fit planks to cover the rib and stringer structure, securing them tightly.
– Reinforce the joints: Apply epoxy and fiberglass tape over the joints to strengthen the structure.
– Shape the hull: Use tools to shape and smooth the hull, paying attention to fairing for optimal hydrodynamics.
– Apply a protective finish: Coat the hull and ribs with marine-grade varnish or epoxy for durability.
– Perform a thorough inspection: Check for defects, cracks, or imperfections and make necessary repairs before moving forward.
The process of constructing wooden sailboats has evolved over time, combining traditional techniques with modern materials and tools. Craftsmanship, attention to detail, and an understanding of wood’s properties are still essential in constructing the ribs and hull structure. This blend of artistry and engineering ensures sailboats can withstand the demands of the sea while providing a smooth and enjoyable sailing experience.
Building the Deck and Cabin
Let’s dive into the exciting world of building a wooden sailboat! In this section, we’ll focus on the crucial element of constructing the deck and cabin. Get ready to explore the process of creating the deck framework and adding those essential interior features . From laying the foundation to crafting a cozy cabin space , we’ll uncover the key steps and considerations for bringing your wooden sailboat to life. So, grab your tools and let’s set sail on this exhilarating construction journey !
Creating the Deck Framework
When creating the deck framework for a wooden sailboat, follow these steps:
- Measure and mark the desired deck size and shape on the boat’s frame.
- Cut and shape the wooden planks or panels to match the marked measurements.
- Align the planks or panels horizontally across the frame, ensuring they are straight and evenly spaced.
- Secure the planks or panels to the frame using screws or nails, ensuring tight fastening.
- Add additional support beams or joists underneath the deck for added strength and stability.
- Sand the deck surface to create a smooth and even finish.
- Apply a weather-resistant sealant or paint to protect the deck from moisture and UV damage.
- Install necessary features or fixtures on the deck, such as hatches, cleats or railings.
Pro-tip: Enhance the deck’s strength and durability by adding epoxy or marine adhesive between the joints before securing the planks or panels.
Installing the Cabin and Interior Features
When building a wooden sailboat, it is important to pay attention to every step, including the installation of the cabin and interior features. To install these features, follow the following steps:
1. First, measure and cut the materials for the cabin walls, floor, and ceiling.
2. Next, securely fit the cabin walls in place.
3. Then, attach the floorboards to the cabin base using screws or nails.
4. Align and install the cabin ceiling.
5. If desired, add insulation for extra comfort.
6. Attach interior features such as cabinets, storage compartments, and seating areas.
7. Install windows and hatches to allow for natural light and ventilation.
8. Properly wire the cabin for electricity, ensuring that lights and outlets are installed and functioning.
9. Finish the interior by sanding and applying a protective coat of varnish or paint.
10. Ensure that all installations meet safety standards.
Precision and attention to detail are key when installing the cabin and interior features of a wooden sailboat. By carefully measuring, cutting, and fitting each component, you can ensure a secure fit. It is important to optimize the layout and functionality of the interior features to create a comfortable living space with ample storage. The addition of windows and hatches will enhance comfort and enjoyment by providing natural light and ventilation . If electricity is needed, proper wiring is essential to ensure necessary lighting and power outlets. Finishing the interior with a protective coat of varnish or paint will not only enhance aesthetics but also provide durability.
Remember, the goal is to create a cozy retreat for sailors, so it is important to put in the necessary effort to install the cabin and interior features correctly.
Installing the Sails and Rigging
Set sail with confidence as we dive into the exciting world of installing the sails and rigging for your wooden sailboat. Discover the key considerations in choosing the perfect sails and master the art of setting up and adjusting the rigging. With expert tips and tricks , this section will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the waters with ease and experience the thrill of sailing your wooden masterpiece .
Choosing the Right Sails
When choosing sails for your wooden sailboat, consider the following factors:
– Type of sailing: Determine if you plan to cruise , race , or do both. Different sails are designed for specific purposes.
– Boat size: The size of your sailboat determines the size and number of sails you need. Larger boats require bigger sails , while smaller boats may need fewer and smaller sails .
– Wind conditions: Consider the typical wind conditions in your sailing areas. Different sails perform better in light winds , heavy winds , or various wind conditions.
– Sail material: The material of the sails affects durability and performance. Material choices include Dacron , laminate , and nylon . Each material has different trade-offs between longevity, performance, and cost.
– Reefing options: If you sail in varied or unpredictable wind conditions, choose sails with reefing options. Reefing allows you to adjust the sail area for stronger winds, improving control and safety.
– Manufacturer reputation: Research sail manufacturers for their reputation and reliability. Read reviews, seek recommendations, and consider warranty and customer support.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing sails for your wooden sailboat. Remember, the right sails greatly impact your sailing experience, so take your time and choose wisely.
Setting Up and Adjusting the Rigging
When setting up and adjusting the rigging of a wooden sailboat, it is important to follow these steps to ensure proper and safe rigging.
To start, attach the mast to the deck using a mast step or mast partner for stability and support. This will provide the foundation for the rigging.
Next, secure the standing rigging , which includes the shrouds and stays , to the mast. This will help distribute the forces from the sails and ensure the stability of the mast.
Connect the forestay to the bow of the sailboat. This will keep the mast in line and control the position of the headsail.
To counteract forces from the headsail and maintain rigging tension, attach the backstay to the stern of the boat.
Use turnbuckles or rigging screws to adjust the tension in the standing rigging. This will ensure proper alignment and support of the mast.
Install the running rigging , including halyards and sheets , to control the position and tension of the sails.
Before and during sailing, it is important to regularly check the tension in the rigging to ensure performance and safety.
Make any necessary adjustments to the rigging during sailing in order to optimize the shape of the sails and enhance the performance of the boat.
By following these steps, you will be able to properly set up and adjust the rigging of your wooden sailboat, allowing for safe and enjoyable sailing experiences.
Finishing Touches and Maintenance
When it comes to completing your wooden sailboat and keeping it in top shape, this section has got you covered. We’ll dive into the art of applying exquisite finishes to the hull and deck, giving your sailboat a stunning appearance. And don’t worry, we won’t neglect the nitty-gritty details of regular maintenance and care, ensuring your wooden vessel remains seaworthy for years to come. So, let’s get ready to add those finishing touches and keep your sailboat sailing smoothly !
Applying Finishes to the Hull and Deck
When building a wooden sailboat, applying finishes to the hull and deck is crucial for durability and aesthetic appeal. Here are the steps to follow:
1. Prepare the surfaces: Sand down rough spots, fill in cracks and imperfections, and ensure a smooth and clean surface.
2. Choose the right finish: Consider the type of wood and desired look. Varnish provides a glossy and traditional appearance, while paint offers different colors and styles.
3. Apply the primer: Enhance adherence and create an even surface for the final coat by applying a primer.
4. Apply the finish: Use a brush or roller to apply the chosen finish coat to the hull and deck. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for drying times and application techniques.
5. Allow for drying and curing: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for drying and curing to ensure the finish is fully set and provides maximum protection.
6. Inspect and touch up: After drying, inspect the hull and deck for missed spots or imperfections. Touch up any areas that require additional finish for a seamless and polished look.
By following these steps and applying finishes properly, you can protect and enhance the hull and deck of your wooden sailboat, ensuring it looks beautiful and lasts for many years.
Regular Maintenance and Care for Your Wooden Sailboat
Regular maintenance and care for your wooden sailboat is crucial for its longevity and performance. Here are the steps to follow:
1. Inspect the hull and deck for damage like cracks or rot. Promptly repair any issues to prevent further damage.
2. Clean the boat regularly with mild detergent and freshwater to remove dirt, salt, and grime that can accumulate over time.
3. Apply a protective coating to the hull and deck using marine-grade varnish or paint to prevent water penetration and protect against UV damage.
4. Check the rigging and sails for wear or damage. Replace worn-out lines or rigging components for safe sailing.
5. Inspect wooden components such as the mast, boom, and rudder for rot or decay. Replace or repair as necessary to maintain structural integrity.
6. Keep the interior of the sailboat clean and dry to prevent mold and mildew growth. Use a dehumidifier if needed.
7. Regularly check and maintain the boat’s systems , including electrical, plumbing, and navigation equipment. Address any issues promptly.
8. Store the wooden sailboat in a suitable location, such as a covered boat dock or boatyard, when not in use. Protect it from extreme weather conditions.
Pro-tip: Establish a regular maintenance schedule and keep a detailed record of all maintenance and repairs. This will help you stay organized and ensure your wooden sailboat remains in optimal condition.
Some Facts About How To Build A Wooden Sailboat:
- ✅ Building a wooden sailboat can take approximately 100 hours over a span of 3 months. (Source: Instructables)
- ✅ A wooden sailboat can cost around $1,000 to build. (Source: Instructables)
- ✅ The boat is typically built from 4×8 sheets of plywood and measures 8 feet in length. (Source: Instructables)
- ✅ Various tools such as a pull-saw, table saw, router, sander, and drill are needed for building a wooden sailboat. (Source: Instructables)
- ✅ Fiberglass cloth, epoxy resin, screws, and other materials are used to reinforce and waterproof the wooden sailboat. (Source: Instructables)
Frequently Asked Questions
1. how long does it take to build a wooden sailboat.
Building a wooden sailboat typically takes about 100 hours spread over approximately 3 months.
2. What materials are needed to build a wooden sailboat?
To build a wooden sailboat, you will need 4×8 sheets of plywood, epoxy resin, oak plywood, various tools (such as a pull-saw, table saw, router, etc.), fiberglass cloth, screws, fasteners, and other supplies like glue, clamps, and mixing cups.
3. How much does it cost to build a wooden sailboat?
The estimated cost of building a wooden sailboat is around $1,000, including the materials and tools needed for the project.
4. Can I learn to build a wooden sailboat if I have no prior experience?
Yes, building skills can be learned gradually, and mistakes can be avoided along the way. With patience and guidance from boat building plans, even beginners can successfully build a wooden sailboat.
5. How long is the wooden sailboat described in the reference?
The wooden sailboat described in the reference is an 8-foot long pram, featuring classic lines and made from 4×8 sheets of plywood.
6. Can I launch the wooden sailboat in any body of water?
Yes, the wooden sailboat is designed to be light enough to fit in a small pickup truck or be rolled to a local lake on a dolly, making it suitable for various bodies of water.
About the author
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

The history of sailing – from ancient times to modern adventures
History of Sailing Sailing is a time-honored tradition that has evolved over millennia, from its humble beginnings as a means of transportation to a beloved modern-day recreational activity. The history of sailing is a fascinating journey that spans cultures and centuries, rich in innovation and adventure. In this article, we’ll explore the remarkable evolution of…

Sailing Solo: Adventures and Challenges of Single-Handed Sailing
Solo Sailing Sailing has always been a pursuit of freedom, adventure, and self-discovery. While sailing with a crew is a fantastic experience, there’s a unique allure to sailing solo – just you, the wind, and the open sea. Single-handed sailing, as it’s often called, is a journey of self-reliance, resilience, and the ultimate test of…


Sustainable Sailing: Eco-Friendly Practices on the boat
Eco Friendly Sailing Sailing is an exhilarating and timeless way to explore the beauty of the open water, but it’s important to remember that our oceans and environment need our protection. Sustainable sailing, which involves eco-friendly practices and mindful decision-making, allows sailors to enjoy their adventures while minimizing their impact on the environment. In this…
How to Build a Wood Sailboat

Introduction: How to Build a Wood Sailboat
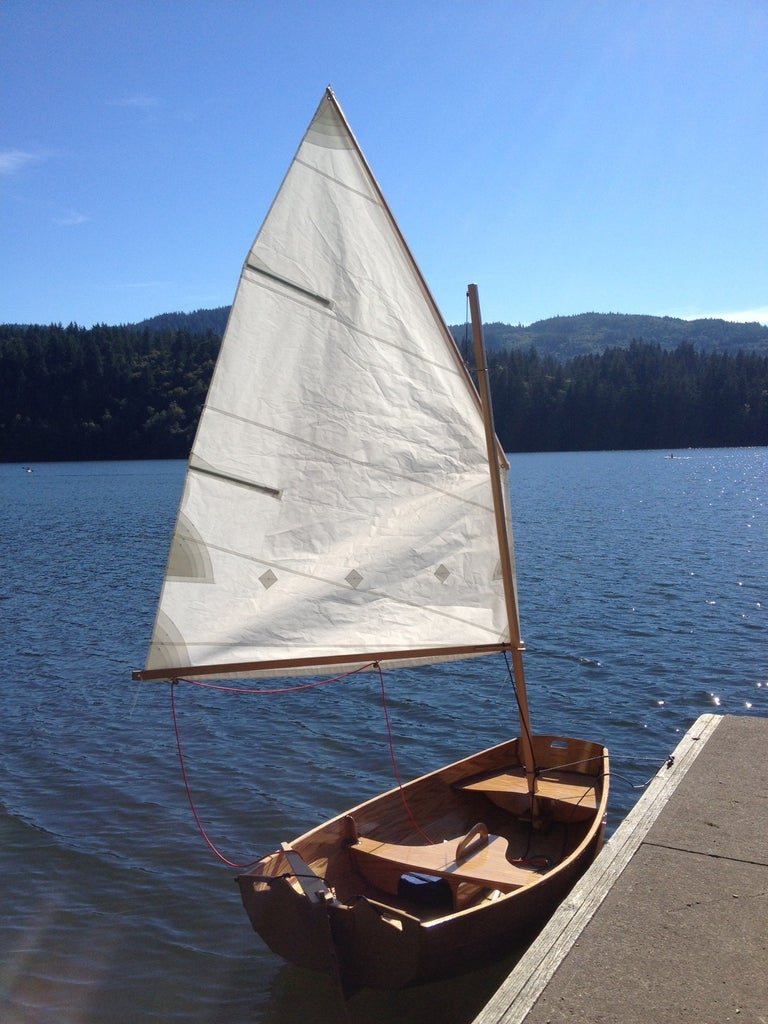

I've been wanting to combine my two favorite hobbies - woodworking and sailing for a long time, so I thought I'd build a boat. It's got classic lines and looks so dazzling in the sunshine that people constantly stop me at the boat ramp to ask me about it. There's something unbelievably rewarding about building something like this from scratch. This is definitely a boat that is much better built than bought . Here's how I did it.
The boat takes about 100 hours to build. I did it over 3 months, working a little bit just about every day and full days when my schedule permitted.
It will take about $1,000 in total to build if you buy everything at full retail cost (not including tools you might need to buy), but you can spread that across the length of the project. For example, you only need to buy one $30 sheet of plywood at a time, take it home, draw out the parts (loft) that fit on just that sheet and cut them out. That will take a couple of hours right there. Some boating supply stores (chandleries) might let you setup an account which might give you a discount if you tell them you're building a boat.
All of the skills needed to build a sailboat can be learned slowly, one step at a time. For example, if you've never fiber-glassed plywood before, just practice on a small piece first to get your confidence up. This was my first boat build, so I did a lot of learn as you go . Not only am I going to show you the right way to successfully build your own sailboat, but I'm going to share with you the mistakes I made along the way to hopefully save you from repeating them.
The end result will be a very attractive little 8 foot long pram, that is easily made out of 4x8 sheets of plywood that is light enough to put in the back of a small pickup truck or roll down to the local lake on the optional dolly. Anything longer would require you to either make a scarf joint (which is a bit tricky) or buy longer sheets of plywood (which is considerably more expensive).
What you will need:
Boat building plans
8 panels of 1/4" oak plywood 4'x8'
Pencil, Sharpie, ruler, tape measure, yard stick, etc.
Long flexible straight edge
Box of 1" brad nails
2 gallons of epoxy resin
1 gallon of epoxy hardener - SLOW
1 quart silica thickener
5 quarts wood flour thickener
1" masking tape
Japanese pull-saw
Table saw (helps, but optional)
Round-over router bit
Flush trim router bit
Palm/random orbital sander
220 sanding discs
Combination square
Drill bit set
Drill bit extension
Basic hand tools
Small diameter wire or zip ties
Wire cutter
12 C-clamps - 3"
Mixing cups, mixing sticks, rubber/nitrile gloves
16' x 60" of 6oz fiberglass cloth
2" plastic spreader
Gallon of waterproof glue
Glue roller
Silicone bronze screws
Stainless steel fasteners
Small blocks
Gudgeon & pintle - dinghy size
Patience - large
Elbow grease - large
For more detailed explanations on each step and more specific info/reviews on the materials and parts used, check out my boat build blog: www.Midnight-Maker.com
Step 1: Cutting Out the Parts...
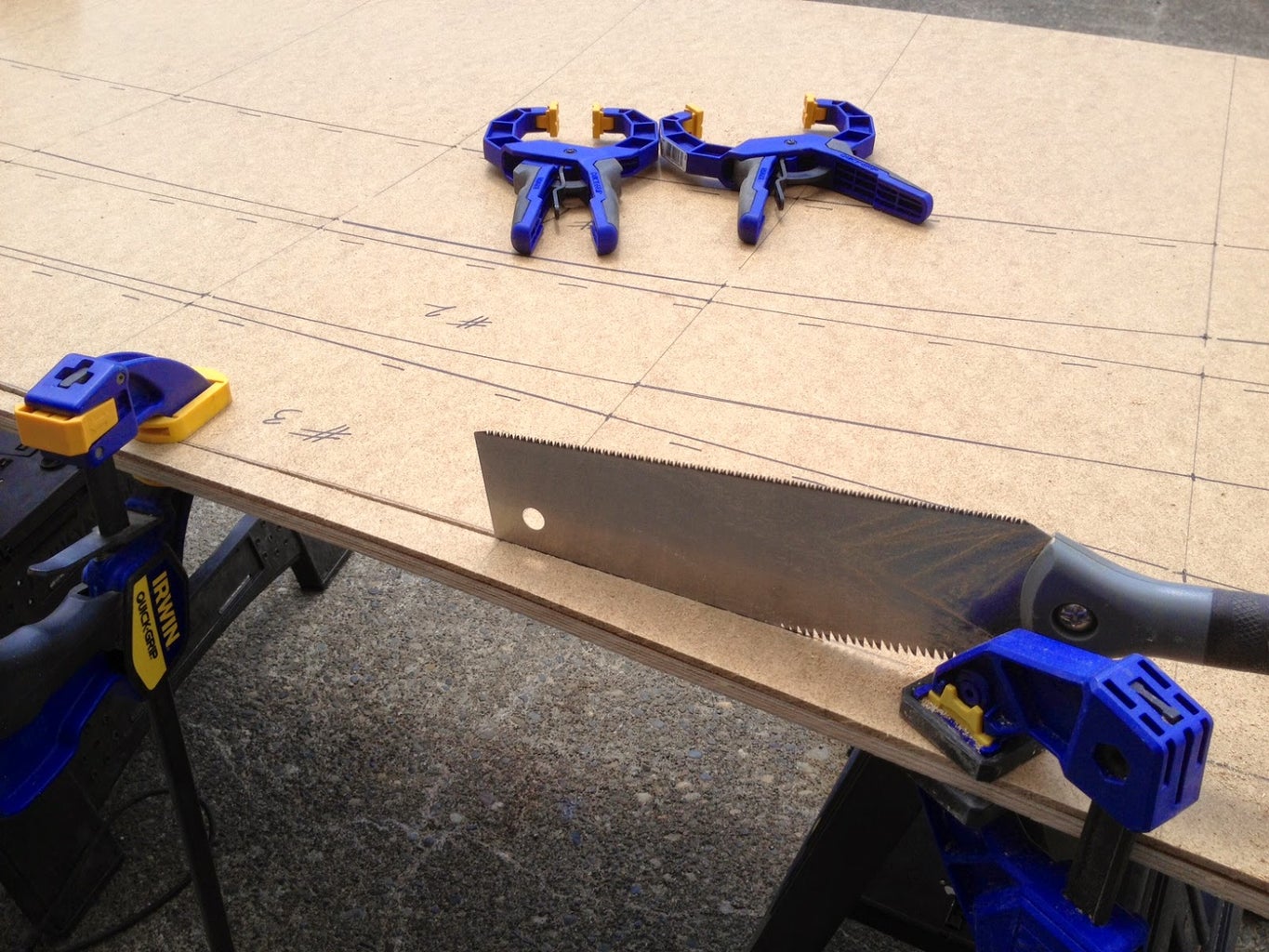

First, you'll need boat building plans. I purchased some very nice ones from a popular boat building website because I had a specific style in mind to build, a "pram". It's a Norwegian design with lots of buoyancy in the bow and building a pointy boat is a little more difficult. There are a bunch of free boat building plans (search "dinghy") online. Also, I wanted my boat parts to fit in a standard (read cheap) 4'x8' sheet of plywood. It also had to be light enough for me to load/unload/move myself. This boat weighs in at about 70 pounds. When on the custom dolly I built, it's very easy to move from the parking lot to the lake.
Next, you'll need to draw out the parts of the boat full-sized onto the plywood (lofting). I actually did this step on hardboard/masonite because I wanted to make templates of all the parts in case I ever wanted to build another one.
This step requires you to be very meticulous. Carefully transfer the measurements (offsets). They may or may not look correct because it's very non-intuitive to look at curved boat parts that are laying flat. Some parts actually bend the opposite way you think they should. To make the curves, I nailed a bunch of 1" brads into the panel and used a long, flexible straight edge (yard stick, etc.) bent to follow the curve, then I traced the curve with pencil/Sharpie. Once I removed the brads, I had perfectly smooth curves. Keep in mind that with the side panels that are symmetrical to both sides of the boat, only draw out one version and cut two stacked sheets at a time. This ensures the boat will not be lop-sided. Make sure to immobilize the two sheets together with screws outside of the boat parts or use double-sided tape/clamps, etc. to keep the parts registered properly.
Using a Japanese pull-saw allows you to control the cuts very carefully and it can follow the graceful curves. They cut on the pull stroke which means they're very easy to control. Make sure you leave a bit of your cut line, meaning cut just outside the line. This allows you a bit of a safety margin and you can always sand to the line to sweeten it up. This is where the elbow grease really kicks in. It takes hours to cut out the hull panels by hand, but it's worth it. I tried cutting the first part out with the jigsaw and it wandered all over the place and quickly cut inside the line before I knew it. Also, a jig saw blade can lean to one side which could mean two panels might not be the exact same shape. Using hand tools is a classic way to do woodworking and is a very gratifying process. With hand tools, things happen slow enough for you to be in total control, whereas power tools can quickly do unexpected damage. With the understanding that you're building a classic boat, using hand tools wherever possible is part of the philosophy.
The plans I bought were in metric and called for 6mm (1/4") and 9mm (3/8") plywood, but I wanted to make everything out of 1/4" plywood so the thicker parts in the plans were glued together with two layers of 1/4" (so at 1/2" they were a bit thicker than designed). I actually liked this because it made the boat feel sturdier and of course it was cheaper that way. The trade-off was that the boat would be a bit heavier.
For any of the parts that need to be doubled-up/laminated (e.g. the transoms), now is a good time to do that. Make sure you use "waterproof" glue instead of "weatherproof" glue like I did...
Spread a thin layer of glue over one of the "bad" sides (plywood usually has a good side and a bad side, glue bad sides together so good sides show on both outside faces), making sure it's completely covered (I used a special glue roller), then carefully place the other half on top. Align all of the edges together, then clamp them in place. Now put heavy things carefully on top to press the parts together. The glue should be dry in about 6 hours.
NOTE: It's considerably easier and safer to do any woodworking processes to the parts before you assemble the boat. This way, you can safely clamp pieces to the work bench and cut out handle holes, etc. Since my boat is a "lapstrake" design, I had to route a rabbet (groove located on the edge) carefully on the bottom edge of each side panel. This creates a shoulder for the parts to sit on, positively locating them while you're stitching the panels together. Likewise, the grab handles in the transoms are much easier to cut out before putting the boat together.
Also keep in mind that any mistake will be considerably more painful the further you are along in the build. For example, if I biff cutting out the grab handle holes while they're just loose pieces rather than when they're a permanent part of the boat, it's much easier to recover - just make another transom. If you had to patch a hole in the boat, it would be difficult and possibly never look perfect. No pressure...
Step 2: Assembling the Hull...

Once you have the bottom and sides cut out, you can start to "stitch and glue" the hull together. This is a technique used usually for smaller boats to be able to pull the hull form together without the need to build a frame or mold (which can take almost as long and as much wood as the boat itself).
I built a gauge stick to make sure my holes were perfectly spaced at 4" at 1/2" in from the plywood edge. It was 1" wide so either edge was the required 1/2" from the centerline. I worked my way down one side of each of each mated seam and drilled all those holes at once while the panels could lay flat on the bench. Make sure to use a backer block to prevent tear out on the back side, even with such a small drill bit.
With one mating panel drilled with a 1/16" drill bit, hold the mating panel in it's relative position. I used some spare twine to wrangle my panels into the proper orientation as I was marking them. Make a pencil mark where the mating hole should be, remove the pre-drilled panel and drill the second set of holes 1/2" in from the edge. This makes sure there's enough strength to hold the boat together.
The first pass on the stitches is just to get the hull together structurally. You can always go back and make the stitches fancier/tighter and tweak the position of the panels.
The stitches go from the inside out. Cut 6" lengths of wire and bend them into long, narrow U's that are the width of the distance between the holes. Stick the ends through the holes and carefully twist the tails together on the outside of the hull, making sure not to damage the plywood. If you're using zip ties, then the holes you drill will need to be bigger and you'll have to start on the outside, go in, turn around, then back out, then "zip".
Make sure your panels' rabbet shoulders are resting securely on the mating panel and carefully tighten all the stitches. For my boat, once I had two panels stitched to the bottom panel on each side, it was time to attach the transoms (ends). Once all of the exterior parts are stitched together, you should have something that looks like a boat. It will be a little rickety at this stage, but that's okay.
NOTE: In the photos I took of my build, you'll notice that the transom doublers (reinforcers) aren't in place. That was because I was following the instruction manual, but I think that was a mistake, so I highly recommend laminating (gluing) the doublers to the transoms before you stitch the boat together.
Step 3: Reinforcing the Hull Joints...

Now that the hull is stitched together, flip it over upside down. You'll be surprised at how stiff it is, considering how difficult it was to wrangle all those panels into position. Be careful, there's lots of poky wire ends sticking out all over the place.
I used a technique called "tabbing", meaning I made small, structural tabs from thickened epoxy that fit between the stitches, then I removed the stitches and made one long, larger fillet to connect the hull panels together.
Make sure your panels are perfectly aligned and tightened. I used a nipper to lop off most of the tails so they wouldn't get in the way, but that left very sharp spikes.
Make sure your boat is square. Take diagonal measurements from corner to corner, make sure the boat parts are parallel to each other, etc. because if there's a twist in your boat, the next step will make it permanent, which will affect the boat's performance.
Now mix up a batch of epoxy and silica thickener according to the manufacturer's directions (meaning each type of epoxy has a different resin to hardener ratio) until it's between the consistency of thick ketchup, but runnier than peanut butter (make sure to mix the 2 parts of epoxy together first very well before adding a thickener). Too thick and it won't fill the void, too thin and it'll run down inside the boat. Both are bad. I used a small syringe to inject the mix into the V intersection between the panels and checked underneath/inside to see if there were any runs.
Once the epoxy has partially set, use a glove wet with denatured alcohol to smooth out the "tabs" so they fit inside the V groove and don't extend above the intersection between the panels. This will give you good practice for the seams that will show on the finished boat. Be careful of the wire spikes.
Repeat this process for every seam on the hull. Let it cure overnight.
Once the tabs have cured, carefully remove the stitches. If the wire seems to be epoxied permanently to the hull, heat the wire with a lighter. That will soften the epoxy enough to pull the wire out. Be careful not to scorch the boat (you don't want a Viking funeral). Now repeat the thickened epoxy process for each overlap, except this time each seam will need to be one long, smooth joint. Let it cure overnight. This goes a long way in making the boat hull structural.
Step 4: Fiberglassing the Hull...
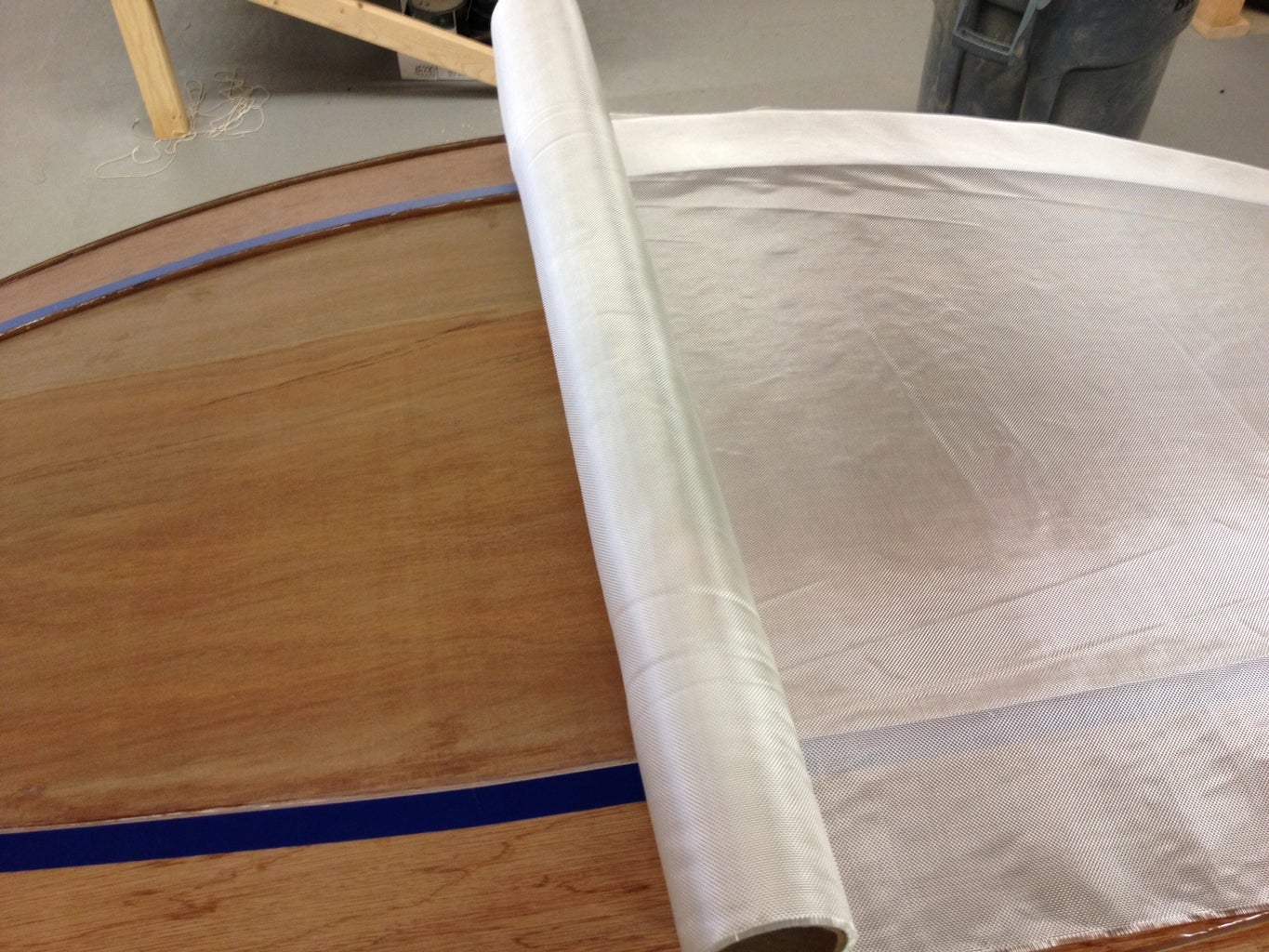

Now that you've got a permanent hull shape, it's time to make it waterproof and rugged. Fiberglass and resin over plywood is a tried and true Do It Yourself boat building technique which makes it strong and light.
Mask off the bottom panel and roll out your fiberglass cloth. Smooth the cloth out very carefully so as not to snag or tweak the fibers' orientation. Mix up an unthickened batch of epoxy (it will be the consistency of syrup). Starting at the stern, pour a small puddle of epoxy and spread it out nice and thin. You should be able to squeeze most of the epoxy out of the cloth, leaving only saturated cloth with no dry spots (which will appear white) but the weave should still be showing (meaning no extra epoxy is pooling). You should easily be able to see the wood grain through the cloth now.
Let the epoxy partially cure and using a razor, slice the dry fiberglass cloth away on the taped seam. Then remove the masking tape. Let the epoxy cure overnight.
Flip the hull over and mix up a batch of epoxy that is the consistency of peanut butter. I masked off the joint, but this step is optional, but keep in mind that it will be visible if you plan on finishing the interior bright (varnished wood). It's not as critical if you're painting the interior. With a plastic spreader, carefully make a large radius transition (fillet) between the bottom panel and the first side panel (garboard). Remove the masking tape when the epoxy mixture is partially cured and carefully scrape/wipe any unwanted mixture. It's much easier to remove now than having to sand it all off later. At this point, it's also a good time to fillet the transoms to the sides using 3/4" radius tabs between stitches and 1" finished fillets after you've removed the stitches. Let the fillets cure overnight.
Now, repeat the entire fiberglassing process on the inside. Except instead of just doing the bottom panel, make sure both the bottom and the garboard are fiberglassed. This is basically the waterline of the boat. The fillet should allow the fiberglass cloth to smoothly make the bend between boards. Remove the excess cloth when partially cured and let sit overnight. Some people fiberglass up onto the transom at this stage which will make the boat stronger, but that means you have to have already filleted the transoms to the bottom.
Step 5: Installing Interior Parts...
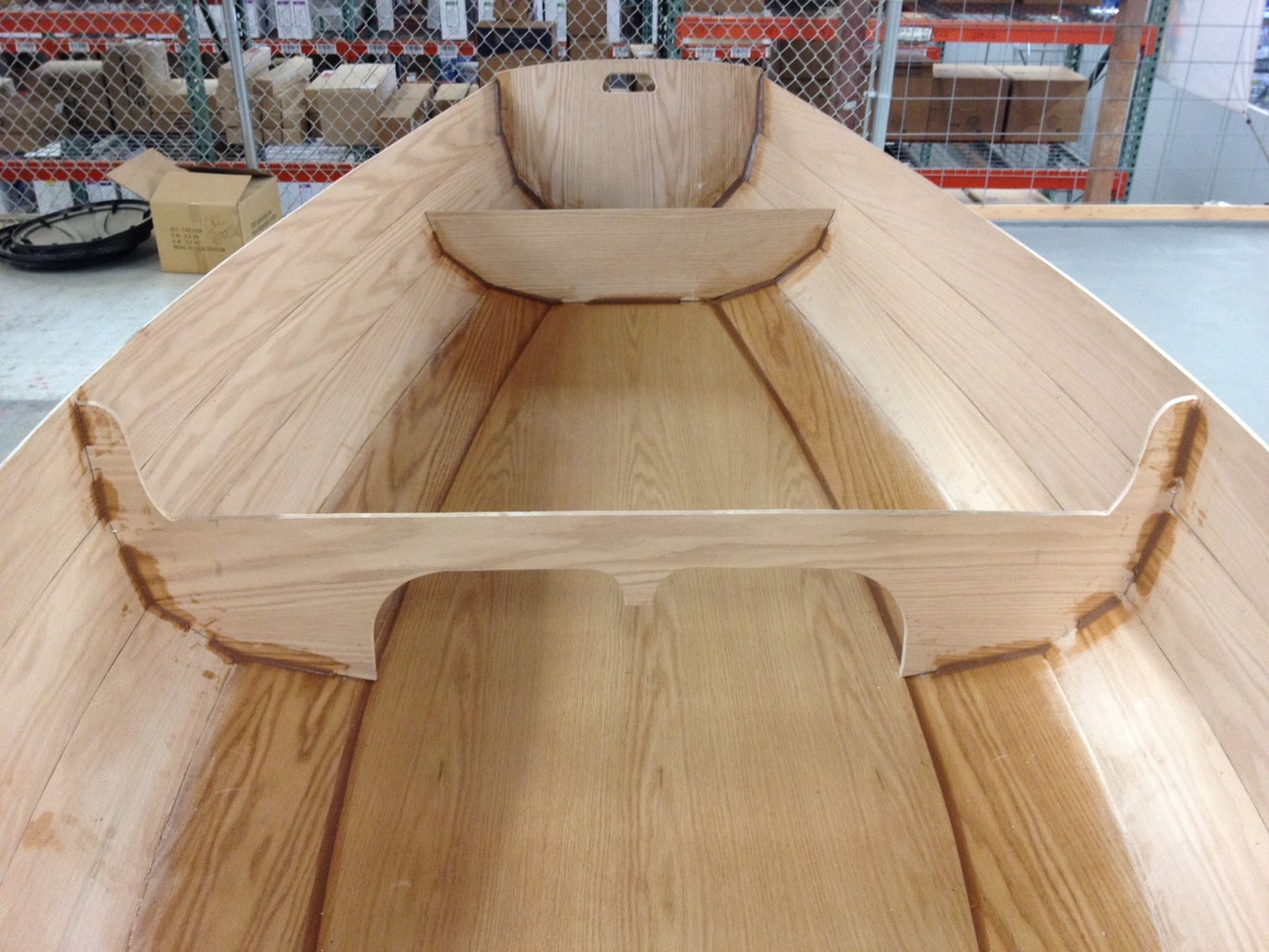

The bulkheads get stitched in place just like the panels. They will make the already stiff (and much heavier boat) completely structurally sound and push/pull the sides into their final shape. Then make 3/4" "tab" fillets between the stitches to lock them in place, remove the stitches and make long, smooth 1" fillets. The smaller fillets will get covered by the larger fillets. I used two different modified plastic spreaders to do this step. Each spreader was cut with a box knife and filed/sanded into its final shape.
While you're doing the previous steps, if you're in a time crunch, go ahead and build the daggerboard trunk. It's made of numerous parts that are pre-coated with a couple layers of unthickened epoxy, then glued together with silica-thickened epoxy. This makes it strong and waterproof as it will be below the waterline so must be completely waterproof.
The daggerboard trunk is the most important part of the boat, especially if you're making a sailboat version (this boat can easily just be used as a rowboat). Not only does it support the center seat (thwart), but it has to transfer all of the force from the sail to the water and if you run the boat aground, it takes all the shock loading from the daggerboard.
The daggerboard gets filleted into place like everything else. Make sure it's perfectly on the centerline of the boat as that will affect its sailing characteristics.
Next, let's make the daggerboard slot in the center thwart. I set up a straight edge with a spiral upcutting router bit. Make sure to enlarge the slots at the end of the center thwart so that it can fit around the fillets of the center bulkhead. Now is the time to ease the edges of the center thwart because you'll be sitting on it a lot, so it needs to be comfortable. Because it's so thin, I only routed the top edge of the center thwart that shows and just hand sanded the edge underneath (it's very problematic to use a round-over bit on the second side of a thin board). Paint all of the thwarts with three coats of unthickened epoxy, especially the undersides. Once the woodworking is done, the thwart can be epoxied into place with peanut butter (or you can jump to cutting the daggerboard slot in the bottom of the hull). Make sure the thwart fits snugly in place. Drop dollops of peanut butter on the top edges of the center bulkhead and daggerboard case and spread it out evenly (make sure none gets inside the slot to interfere with the daggerboard). Firmly seat the thwart (pun intended) into the goop and weight it down. Let it cure overnight.
While you've making sawdust, cut out the mast hole (partner) in the forward thwart by drilling holes in the four corners (for the square mast we're going to make), then cut out the sides, file it smooth, then round over the top edge with the router.
Any time after the bulkhead thwart fillets have cured, you can seal the airtank chambers. Paint the bottom, sides, inside of the bulkhead and transom up to the level where the thwart will be.
Step 6: Rail & Sailboat Parts...
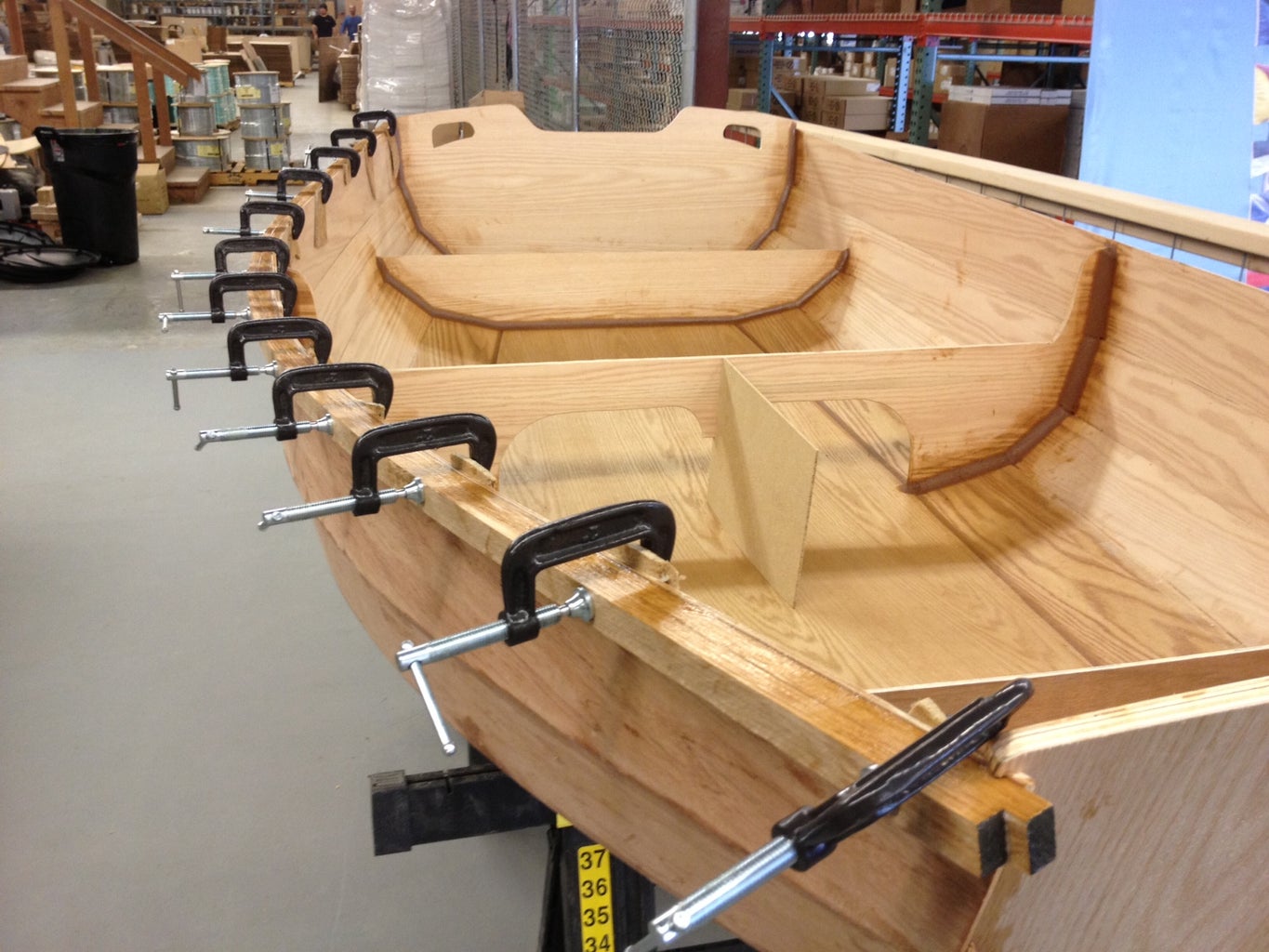

There are several processes in this boat building instructable that can be done concurrently. While you're waiting for the epoxy on one part to cure, you can be doing woodworking or epoxying another part. This step illustrates that point. While you're waiting for the epoxy on the rub rail (outwale) to cure, you can be fabricating the sailboat accessories (e.g. daggerboard, rudder, tiller, spars, etc.).
In order for the outwale to be thick/strong enough to be effective, you'll need to laminate it in two strips on each side. You can't bend a single piece that thick around the curvature of the hull without either breaking the wood or softening it by steaming it which is a complicated process.
Take a strip that's half the final thickness and a little longer than the boat edge (I made mine a bit beefier), mix up some peanut butter with the colloidal silica and carefully spread it on the inside of the strip. Starting at the stern, clamp it in place, perfectly align it with the top edge of the plywood. Now you have a long, springy lever to bend the wood strip along the compound curve. It dips both vertically (shear), and bows out at the widest part of the boat (beam), then back in toward the bow. At least every foot, clamp it as you go, moving forward. More is better. Toward the bow, the strip will get stiffer as it gets shorter. Once clamped in place, scrape/wipe off all the squeeze-out. It's much easier to remove now than after it hardens. Let it sit overnight. You'll have to repeat this three more times, meaning this step takes four days (if you're using "slow" epoxy hardener).
During those four days that you're dealing with the outwale, you can make major progress on the sailboat parts. They're completely separate from the hull. If you're just making a rowboat, then you can skip making these parts.
The daggerboard and rudder are cut out and laminated. Then a bevel is ground onto the leading and trailing edges to make it slice through the water more efficiently. Then they're covered in layers of epoxy. The mast step is assembled. This has to be very strong because all of the force of the sail is transmitted to the boat through the mast step and the mast is a very long lever arm. The rudder cheek plates and tiller also have to be assembled similarly to the daggerboard case.
NOTE: Whenever there's a hole to be drilled into any part of the boat, you must take additional steps to make sure the water doesn't penetrate and damage the wood. The correct procedure is to drill an over-sized hole, completely fill that hole with epoxy (I usually put a piece of masking tape on the back side to act as a dam), then once the epoxy cures, re-drill in the center of the epoxy plug the correct hole size. That makes each hole in the boat possibly a 2 day process, so plan accordingly. You can also use 5 minute epoxy to knock out a bunch of holes quickly, but be careful, they're not kidding. This stuff gets rock hard very quickly and will permanently glue anything touching. This is exactly how you drill the hole for the pivot point for the rudder/cheek plate assembly. If the pin is 1/4", then drill 1/2" hole and fill that with epoxy. Now the 1/4" hole will fit nicely in the center and be completely waterproof.
Since all the parts need several coats of unthickened epoxy and they just about all have holes in them, I hung them up with some twine and painted them on all sides, one layer at a time, for several days. Make sure the rudder doesn't get too thick to fit inside the cheek plates.
Step 7: Making the Spars...

More sailboat parts you can make while waiting for other parts to cure are the spars, the structural parts that support the sail. The mast is another glue up. I used 3 - 1x3's of hemlock. A relatively soft wood, but with a nice tight grain with no knots. A mast would break at a knot, regardless of how strong the wood is. Using the waterproof glue, align the pieces as perfectly as you can then clamp up the assembly and let dry overnight. Then run it through a table saw to get the final dimensions. Use a router and a round-over bit to ease the edges. Cut to length and sand the sharp corners. It should fit easily, but snugly into the forward thwart.
The boom (bottom of sail) is a little more complicated. Cut out the gooseneck (boom pivot point) by using a hole saw first, making sure to clamp it securely to the workbench, then cut out the profile. This gets attached to another piece of 1x3 hemlock, after it's been cut to length and the edges have been rounded over.
The yard (top of sail) is easy. Just cut to length and round over the edges. Drill and fill any holes in the spars at this time. You'll need at least one hole on each end to lash the sail grommets to.
This time, everything gets covered with several coats of varnish, epoxy is not necessary. The varnish protects the wood from water and UV damage.
The reason we had to make at least the mast at this point is because we'll need it in the next step to establish the location of the mast step.
Step 8: Finishing Up the Interior & Exterior...
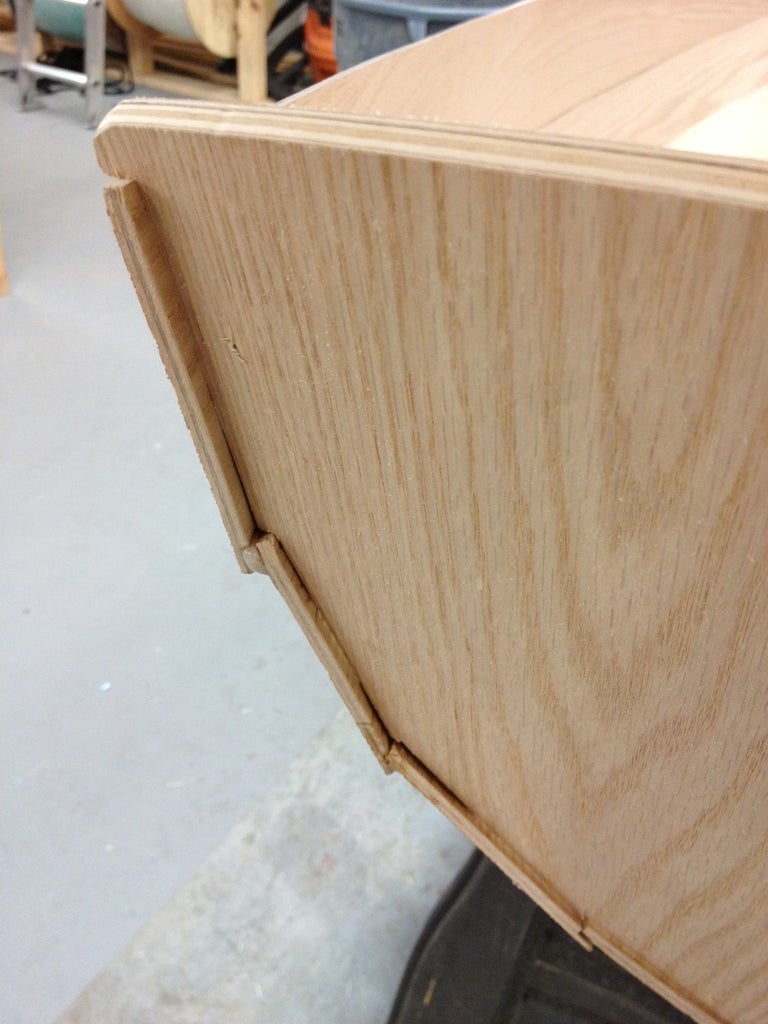

Once the outwales are successfully attached, trim them flush with the face of the transom(s). While you're at it, use a flush cut saw (with no sawtooth offset to mar the wood) to trim the sides flush with the transom. This will show you how well your injected silica mix worked earlier. Now you're ready to install the mast step.
The mast step must be precisely located on the floor (sole) of the boat to give the mast the proper angle (rake). This is very important because it directly affects the boat's ability to sail upwind. Using your mast, insert it into the forward thwart (partner) and into the mast step. With the mast at a 3° angle (mostly vertical but with a small, yet noticeable and graceful tilt toward the stern of the boat), trace the location of the mast step. Use a combination square to make sure it's perfectly aligned side to side (athwartship). You can now set the mast aside. Drill and fill holes in the bottom of the boat so that you can securely screw the mast step from the outside of the hull. The mast base must also be epoxied to the sole with peanut butter. After it's screwed into place but before the epoxy cures, make sure to test fit the mast again and verify the rake angle is correct. It would be a little messy at this point if you had to tweak it, but at least you wouldn't have to cut it off.
Now comes the most unpleasant part of the whole build. On your hands and knees, make a 1" radius fillet on the underside of every part in the boat. I didn't worry about making these pretty, just structural and water tight (these create the flotation tanks that keep the boat from sinking if you capsize). Let that cure overnight.
Next is the scariest part of the build, making the slot in the hull for the daggerboard. Using a drill bit extension, from the inside of the boat, reach down through the daggerboard case and drill a hole at each end of the slot through the bottom of the boat (make sure to use a backer board). Drill a couple holes in between, then take a jigsaw and connect the dots. This weakens the hull enough so that the router won't tear out any extra wood. Note, this step can easily be done prior to affixing the center thwart. Using a flush trim/laminate router bit, let the bearing run around the inside of the daggerboard case. This will make the hole in the hull perfectly match the slot. This is important because you don't want a shoulder on the inside for the daggerboard to hit and you don't want to damage the waterproof lining of the case. Last, ease the sharp edge of the daggerboard slot with the router and a small radius round-over bit.
The skeg must be cut to fit the curve of the hull (rocker), then using silicone bronze screws, attach it to the hull using the same drill and fill/peanut butter techniques. Make sure to snap a chalk line on the centerline of the boat for reference. Then make a 1" fillet where it meets the hull which will support the skeg and make it strong. The skeg keeps the boat tracking straight in the water. I optionally used some fiberglass cloth to cover the skeg and overlap onto the bottom to make the entire assembly stronger and more waterproof. The skeg will take the brunt of the abuse when launching, beaching, loading and unloading, etc. I also installed a stainless steel rubstrake on the aft end of the skeg with this in mind. In wooden boat building, silicone bronze screws are often used because they won't corrode when encapsulated like stainless steel screws can.
Install the skids parallel to the skeg. These are solid pieces of hardwood because they will also take a lot of abuse when the boat is sitting on shore, protecting the thin hull from rocks, etc. They get installed the same way as the skeg, although it's a little tough to bend the wood along the rocker. Scrape off the excess peanut butter once they're screwed in place.
I also installed the optional outboard motor pad at this point because I plan to use an electric trolling motor on the back to quietly putter around the lake in the evenings to relax with the family after work.
That should be the last parts that go into making the boat!
Step 9: Finishing the Hull...
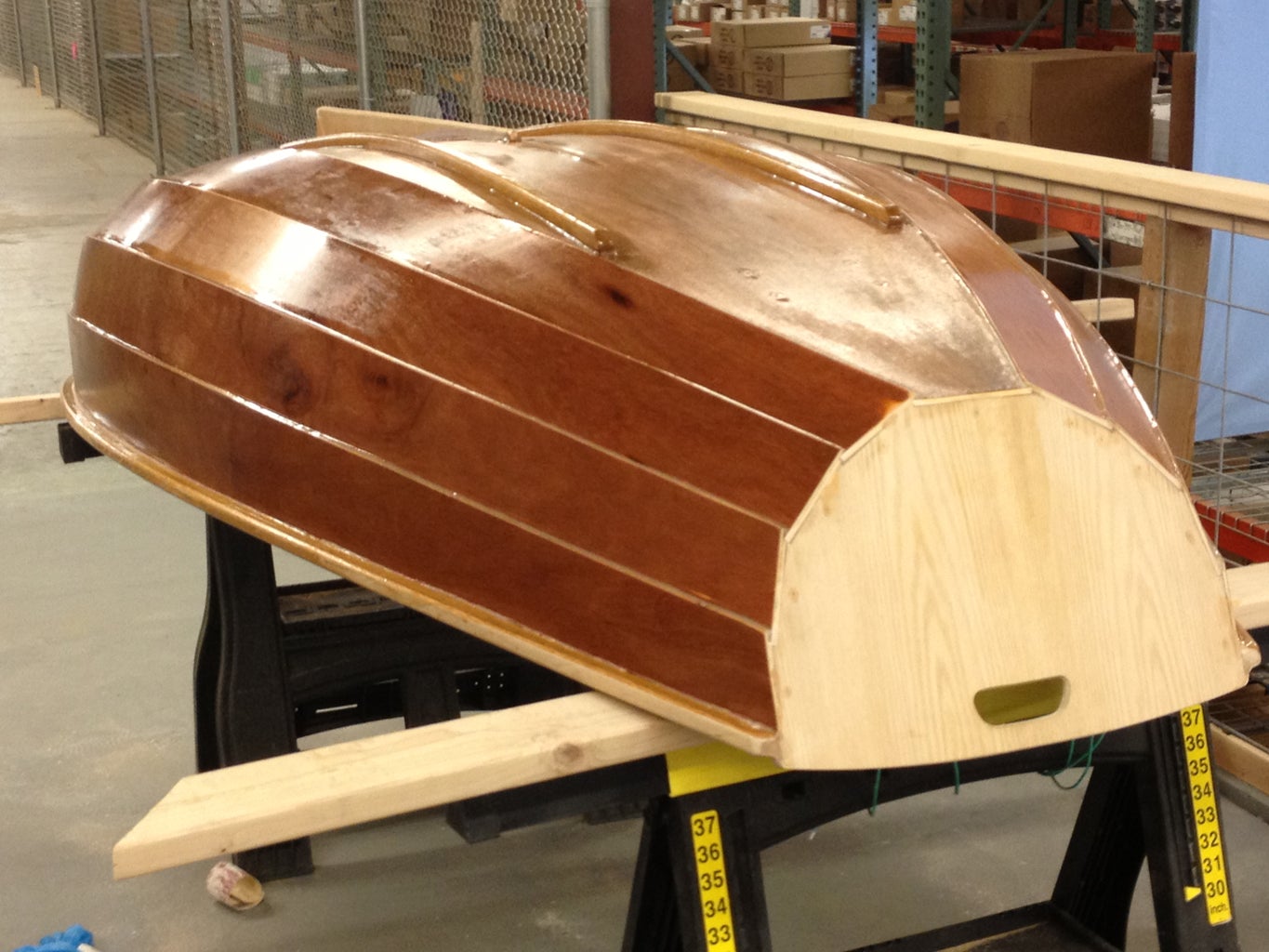

Now comes the last dash to the finish line. One of the more tedious steps is that you now have to sand the entire boat. I actually built the entire boat inside, but for the sanding stage, I took her outside. Several hours of sanding all of the fillets nice and smooth. Everything will show in the finished product whether you paint the boat or leave it "bright" (unpainted). If you've been careful about cleaning up the peanut butter as you go, you should be able to sand the boat with mostly 220 grit. Be careful not to sand through the thin veneer of the plywood. After the sanding is done (make sure to use a dust mask), vacuum the entire boat and then wipe it down with a tack cloth to remove any dust. I also reversed the hose on the shop vac and used it to blow the sawdust off since I was outside.
Next, you must coat the entire interior and exterior with 3-4 coats of unthickened epoxy. This makes the entire boat waterproof. It will also give you an idea of how beautiful the wood will look when varnished. This is why a lot of boat builders decide to leave their boats bright so the beauty of the wood shows through.
Mix up 1 cup batches of unthickened epoxy and pour out large puddles onto the surface. Taking a foam roller, distribute the epoxy in a smooth coat. Now take a wide foam brush and gently smooth (tip) the rolled out surface. This should remove any lap marks or bubbles. Move along to the next area, making sure to not touch the wet parts. Also, make sure no dust or bugs get on your finish or it'll mean even more sanding later.
Start with the exterior first. It'll be much easier to get good by practicing on the convex surfaces. The interior is more tricky because you want to prevent sags and pooling by only applying very thin coats.
Make sure to check with the manufacturer's directions during this step in case you have to deal with "blushing", a thin layer that can sometimes form on the surface of epoxy when it cures. This could cause your layers to not stick to each other. If your epoxy does blush, it's easy to just wipe the entire boat down with a rag soaked in acetone after each coat has cured. Some people sand between coats of epoxy. This is how you would make an extremely smooth/shiny finish, so if you want your boat to be museum quality, invest the effort. I'm planning on banging my boat around so opted out of an extreme, fancy, mirror finish.
I was originally going to paint the exterior of the hull, which would require priming and painting, but I'm leaving it bright for the time being. The good news is that you can always paint later if you change your mind, but if you paint it and change your mind, it's tough to go back. There aren't a lot of pics of this step, which took a couple of days because there wasn't much visible progress after that first coat went on. At this point, any surface that's not painted should be varnished using the same "roll and tip" method as the epoxy, with the optional sanding between coats. Note that epoxy has no UV resistance, so to keep your boat from getting sunburned, you must either paint or varnish every surface. Giving a boat a "museum quality" paint and/or varnish finish can literally take as long as building the boat.
Step 10: Making the Sail...
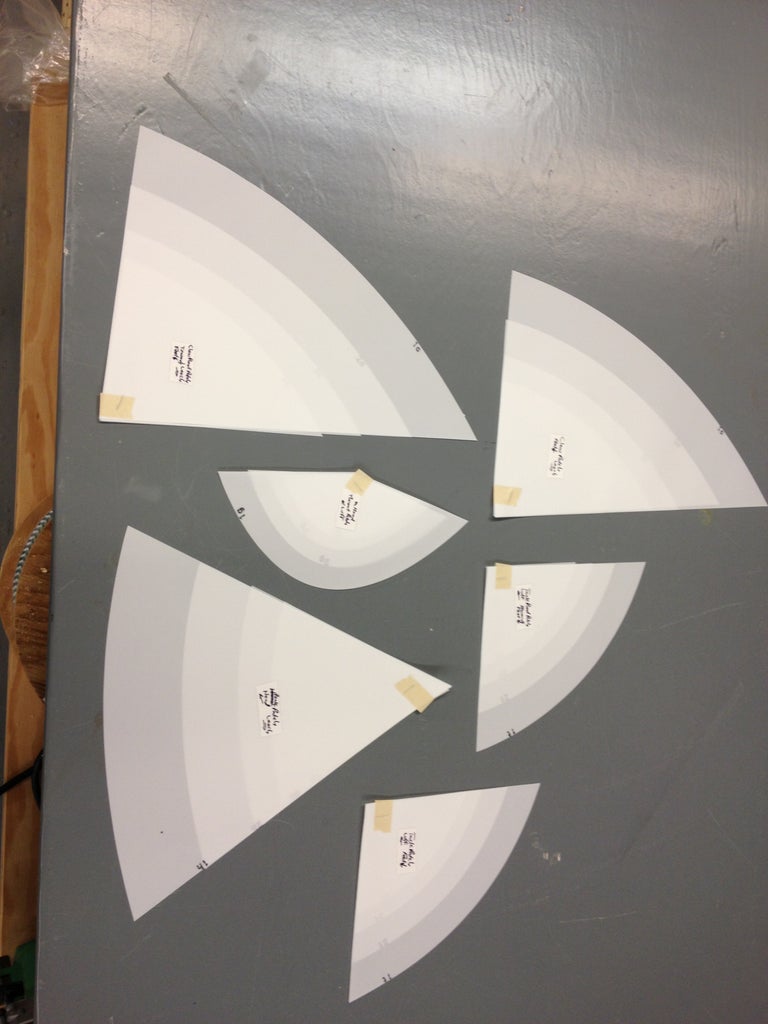

Another step you can do while other parts are curing is make the sail. This particular design uses a "lug" sail, a classic looking sail for small boats with wood masts. It increases the sail area (therefore the force generated by the wind) without it having to be as tall as a modern sailboat mast made of aluminum. There is a kit from an online sailmaking company that you can get for a reasonable price. The Dacron cloth panels are all cut out by a CNC machine, so they fit perfectly together. I used a regular, domestic sewing machine, not an industrial one. The only time I had trouble was when sewing through all 7 layers at the reinforcement patches. When I got to those parts, I had to manually push down on the foot of the sewing machine with a flat-bladed screwdriver (minus) to help push the needle through the Dacron. We jokingly call Philips head screwdrivers "plus".
The panels/parts all come labeled. The directions were a bit confusing because they suggest you make sub-assemblies after the fact to make wrangling the large sail easier but they mention it after you've already sewn the large panels together. It's important to understand what parts go together while the panels are still small and more manageable. For example, the batten pockets are tricky enough to build on a single panel, much less the finished sail. Building the sail was about as difficult for me as building the boat, but it was worth it.
The lug sail gets reinforcement patches on all four corners where you attach it to the spars (bend), and there's also a reefing point for when the wind starts to pick up (freshen). Modern sails have three corners (Marconi rig).
I opted for the less expensive white Dacron sail kit, but there's also a classic red (tanbark) colored kit that's $100 more expensive. Before I sewed a single stitch, I carefully traced every part of the sail kit onto painter's tarp poly film so I can always use the templates to build another sail, all I need to do is buy the tanbark cloth.
Step 11: Rigging Your Sailboat...

This seems to be the trickiest part for most people, probably because there are numerous ways it can be successfully rigged, depending on your experience, preferences or criteria. It's confusing because you have to know what the finished setup will look like in your mind while you're staring at a pile of ropes. I chose a setup that allows the most room in the cockpit for a full-sized adult, so the mainsheet is led forward of the skipper's position. This keeps the skipper's attention forward so they're looking where they're going. I have another boat where the mainsheet is behind the skipper and it takes some practice getting used to.
The lines I made up (rope becomes a line when you give it a job description) were the halyard (hauls the sail up), the mainsheet (adjusts the angle of the sail to the wind = trim) and a traveler bridle (where the mainsheet attaches to the boat). I got fancy and spliced all my ends, but you can just as well use a bowline knot.
I installed a cheek block at the top of the mast instead of the large diameter hole in the directions. I wanted the halyard to run as smoothly as possible when setting the sail. Then I installed a pair of cleats at the base of the mast, one for the halyard and one for the downhaul (cunningham). With both of these lines pulling in opposite directions, it locks the sail in place, flat, so it effectivley acts like a wing. The main halyard attaches to the gaff with a snap onto a padeye. This allows easy on/easy off when rigging at the boat ramp. I also used a small loop (parrel) around the mast and through the eye to keep the gaff located close to the mast. I looped the downhaul over the boom and down to the cleat to try to keep the gooseneck from twisting. Note, except for the blocks, just about all of the hardware used on rigging a boat this size can come in stainless steel or brass/bronze, depending on the look you're going for. If you plan on installing oarlocks to row the boat, this decision becomes even more important to the final look of the boat.
For the mainsheet, I made a short bridle between the handles on the transom with a small eye tied in the center. This allows a place for the snap on the end of the mainsheet to attach to. I could've just as easily allowed the snap to slide, which would give the bridle the function of a traveler, but would affect its pointing ability (sail upwind). The mainsheet is then run to a block on the end of the boom, then to another block in the middle of the boom. This leaves the main cockpit area unobstructed with running rigging. Make sure your mainsheet is long enough for your boom to swing forward of 90° to the boat, with enough to still come back to the cockpit for the skipper to control. A stop knot at the end of the mainsheet will keep the mainsheet from getting away from you and give you something to grip.
The rudder pivot hardware (gudgeons and pintles) must be installed perfectly vertical and on the exact centerline of the boat so that she will sail well. Drill and fill the necessary holes for this hardware. Be careful with the spacing. It's designed to be easily installed and uninstalled while underway.
With this particular rigging layout, when under sail, the skipper must constantly keep the mainsheet in hand, which is a good idea anyway for safety reasons (if you get hit by a gust of wind = puff, you won't get blown over = capsize). The tension on the mainsheet is easily manageable for any size skipper. On larger boats, the mainsheet is held by a fiddle block with a cam cleat, which is not necessary for a boat this size. With that being said, a possible future upgrade would be to install a block and a camcleat somewhere on the centerline of the boat so that more advanced sailors wouldn't need to constantly have to oppose the tension on the mainsheet. Of course the trade-off would be the hardware would probably be somewhere you might want to sit.
Another upgrade I figured out after actually taking her sailing would be to rig up a bungee/shock cord system that will hold the daggerboard both in an up and down position. With the current setup, the centerboard is held down by gravity and must be pulled out of the slot when beaching.
Step 12: Go SAILING!
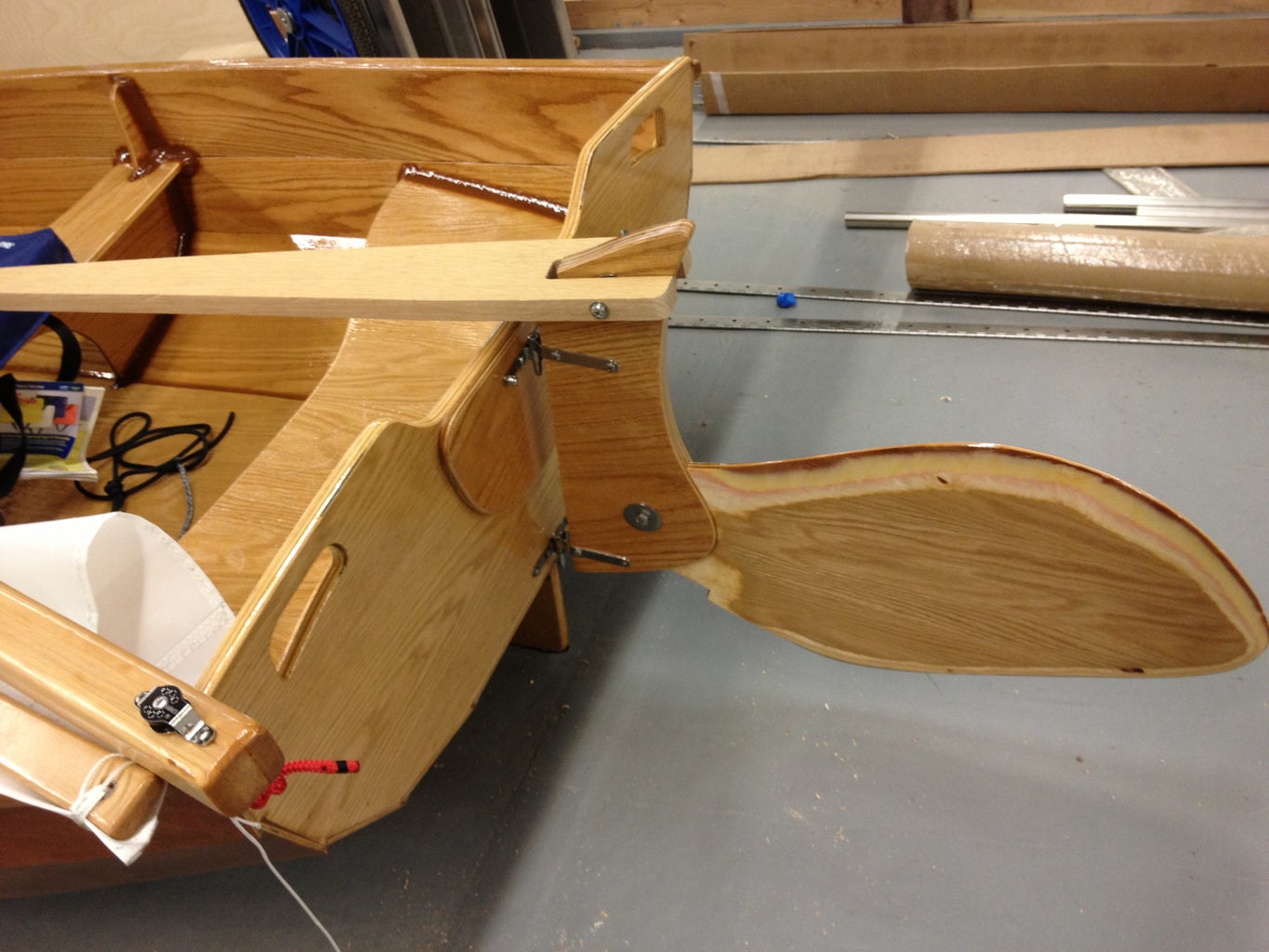

Because I wanted to be able to go sailing by myself if needed, I made a dolly out of 2x4's and large pneumatic tires (which makes the dolly float). The dolly fits securely between the center and aft thwarts when driving out to the lake. The sides on the dolly lock against the skids on the bottom of the boat so it can't twist. Roll the sail up with the spars and wrap it with the main halyard. At the designed length, the mast doesn't fit inside the boat, but it seems a bit long, so some people have cut the mast down enough so that it fits inside the boat.
Out at the lake, unload the boat, slide the dolly underneath and you're ready to roll down to the ramp. At the launch, roll the boat out into the water until it floats off the dolly, toss the dolly off to the side out of everybody else's way. Drop the daggerboard into the slot and install the rudder assembly. Facing into the wind (important), stick the mast into the receiver hole (partner), tie off the downhaul (cunningham) and hoist the sail until the downhaul is tight, then cleat off the main halyard. Reave the mainsheet (run the line through the blocks) and you're ready to go sailing.
I've found that this boat sails very well. The lug sail makes it very easy to sail upwind (weather helm), it's a little more tender for a large adult, more so than a boat with a hard chine, like an El Toro/Optimist but it's a lot more graceful looking. The payload is very reasonable for a boat this size. My wife and son can easily (and safely) go sailing with me and I don't even need anyone's help to get it rigged and launched. All in all, this is one of the best projects I've every built. I hope you too can discover the joy of building your own boat and then take her sailing. Remember, in sailing, the wind is free, but nothing else is...
This is my very first Instructable after many years of referencing this excellent site to build numerous cool projects (you should see my next post). Anyway, I hope you enjoy it and please feel free to ask any questions you may have and I'll do my best to answer them. I'm planning on building a larger boat in the near future so stay tuned...

Participated in the On a Budget Contest

Participated in the Wood Contest
Recommendations

Green Future Student Design Challenge

Made with AI - Autodesk Design & Make - Student Contest

Books and Bookshelves Contest

I’m Arch Davis – I learned boatbuilding and design in New Zealand in the 1970s. I have been helping people to build beautiful wooden boats since 1988. You can see a few of them by clicking on Picture Gallery . My approach to design is to put into your hands the means to use modern materials – marine plywood and epoxy resin – to build a truly lovely boat with classic lines.
I believe that a boat should be beautiful, not just by virtue of her lines, but also in her construction. No material makes this possible like wood. My aim is to take advantage of wood’s unique strengths, in a structure that captivates the eye. I want you to feel that you are always doing good work in building one of these boats.

You’ll see that I have a small collection of designs. That is because I understand your need for clear, comprehensible, detailed plans and instructions. I put a lot of time into my drawings, building manuals and DVDs. I also spend a lot of time helping people through their projects, on the phone or by e-mail. I really am here to help!

If you see something that you like in my collection, please feel free to contact me with any questions. I am available on the phone at 207-930-9873, or email me at [email protected] .
Wooden Boat Plans and Boat Kits by Arch Davis

Grace's Tender - More than just a tender, this little dinghy is a fine vessel in her own right. She is a pleasure to row, and sprightly under her simple sailing rig - a great boat for youngsters to mess about in. Bay Pilot 18 - an 18 ft pilothouse cruiser for outboard power. Laughing Gull - 16 ft self-bailing sailing/rowing skiff. Ace 14 - 14 ft performance daysailer Penobscot 13 - 13 ft little sister to Penobscot 14. Penobscot 14 - 14 ft glued lapstrake sailing/rowing skiff. Penobscot 17 - big sister to the Penobscot 14 Sand Dollar - 11 ft sailing/rowing skiff. Jack Tar - 26 ft plywood lobster boat design Jiffy 9-7 - suitable for rowing or a small outboard motor Jiffy 22 - outboard powered cabin skiff Jiffv V-22 - vee-bottom sister of the Jiffy 22
About My Boat Kits
I also have epoxy kits and plywood packages for all my designs, plus sails, rigging, and numerous other items. Here's my daughter, Grace, setting up the frames for a Grace's Tender kit.

Please call or write to me at: Arch Davis Design 37 Doak Road Belfast, Maine 04915 Tel:207-930-9873
If you would like to receive a newsletter from Arch Davis Design, send me an e-mail at [email protected]
RETURN TO HOME PAGE

- No products in the cart.
Build your own sail boat with Hartley Boat Plans. Hartley sail boats are the benchmark in reliable and sea worthy trailer sailers, in fact the name trailer sailer was coined by these amazing craft. Many of these build plans also have a printed study pack available to help you through your project.

Cape Bay 45

Cape Otway 37
Chuckles 18

Dateline 51
Eastcoaster 16

Easthaven 34

Hartley 16ft (5m) Trailer Sailer

Hartley 30 (Plywood Version)

Hartley 30 (Steel Version)

Royal Suva 52

Samson ‘C-Baron’ 55

Samson ‘C-Breeze’ 45

Samson ‘C-Deuce’ 45

Samson ‘C-Fever’ 62

Samson ‘C-Lord’ 53

Samson ‘C-Quence’ 36

Samson ‘C-Witch’ 63

Tahitian 27

Tahitian 33

Tahitian 38

Tahitian 45-50

Westhaven 32
- Tenten 10-305
- Tenten 14-425
- Carabela 650
- Prao Vaka 600
- Prao Vaka 990
- Projects 2022
- Projects 2021
- Press review
Boats plans for self builder - in metric
Imperial plans on duckworks.
Jérôme Delaunay Naval Architect - Nautline design office in naval architecture: I design and draw custom boat and sailboat plans, in plywood epoxy and other materials. Sailboat plans for shipowner construction and professional construction. Plans of multihulls, plans of catamarans, praos and trimarans. CFD hull study, digital hull basin, engine optimization. I offer scantling calculations, keel calculations, mast and rig calculations. Composite sampling calculations. DXF digital plans for CNC digital cutting.

How to Build a Boat
Classic boat plans from a 1937 issue of Popular Mechanics , updated for the 21st century.
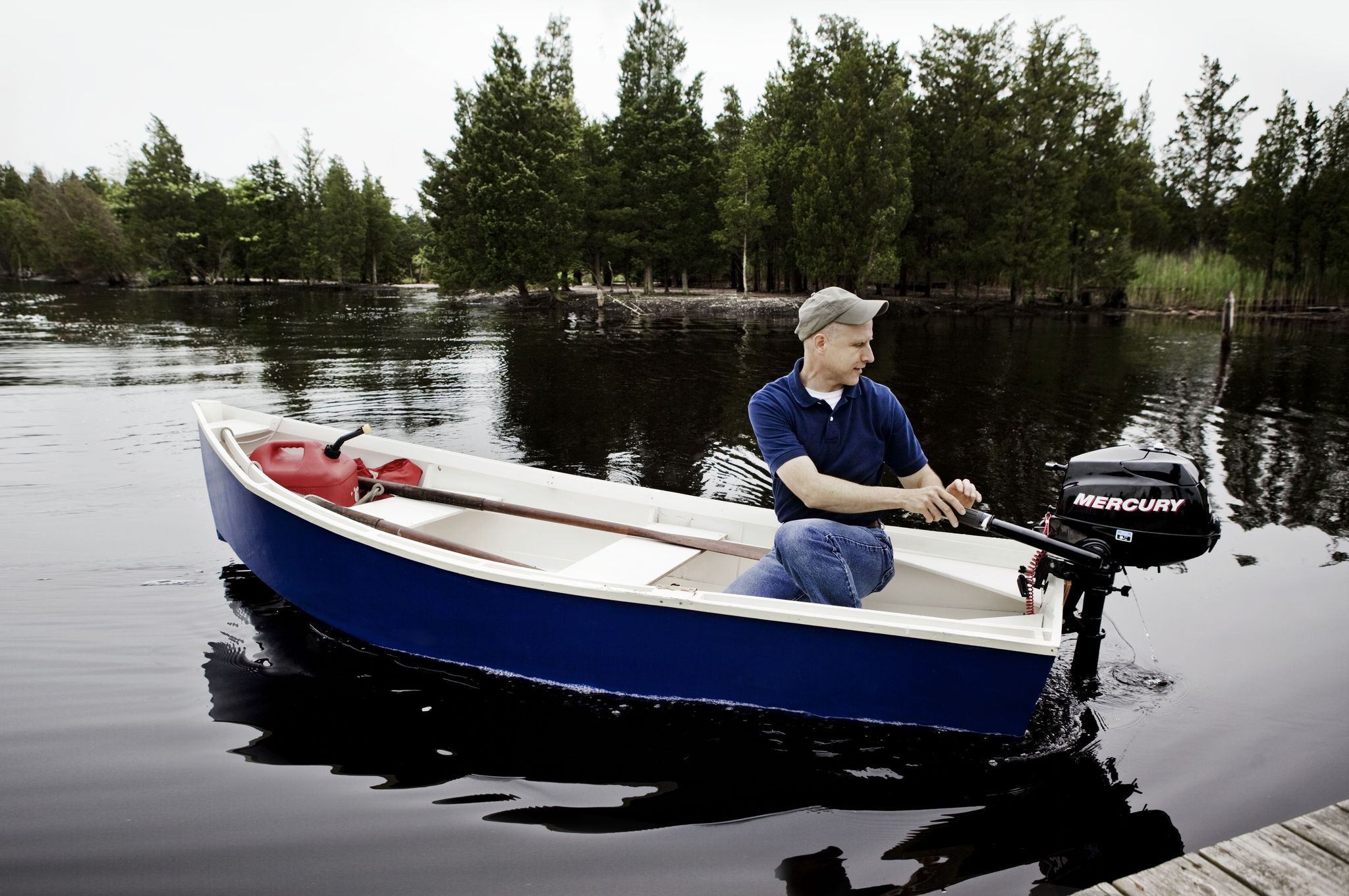

It was a long time since anyone in my family had built a boat. The last was my Uncle Paul. He was a shipbuilder who learned his trade beginning at age 14 in Hamburg, Germany. Every morning, the boy rowed from the family's dock out across the shipping lanes of the Elbe River, which flows into the North Sea.
The trip to the shipyard where he was apprenticed took an hour and a half, longer in winter, when there was fog and floating ice on the water. After three years, Paul received a journeyman's certificate and a berth aboard a gigantic four-masted windjammer named Passat—"trade wind" in English. That was in the 1920s, before the fascists confiscated his family's own small shipyard and the Berendsohns left for America.
A few months ago, I decided to try my hand at the ancestral trade. I've built everything from houses to a blacksmith's forge , but there's no more evocative project than a boat, at least to me. Since before Austronesians first gazed across the Pacific, wooden vessels have stood for craftsmanship and the drive to explore. I sifted through PM's archives looking for a classic design and eventually settled on a 10-foot dinghy from our May 1937 issue . It looked elegant, yet simple enough to build on a pair of sawhorses.
It's been many years since my Uncle Paul was around to lend advice, so I ran the drawings past Timo White, a boatbuilder at Tuckerton Seaport, a small maritime museum on the New Jersey coast. It turned out that Timo was in the midst of restoring a surfboard built from plans in the July 1937 issue of PM. (It was a big year for seafaring projects, I guess.)
He confirmed that the dinghy was a good candidate for a first-time builder and agreed to lend a hand if needed.
Shipyard in the Driveway
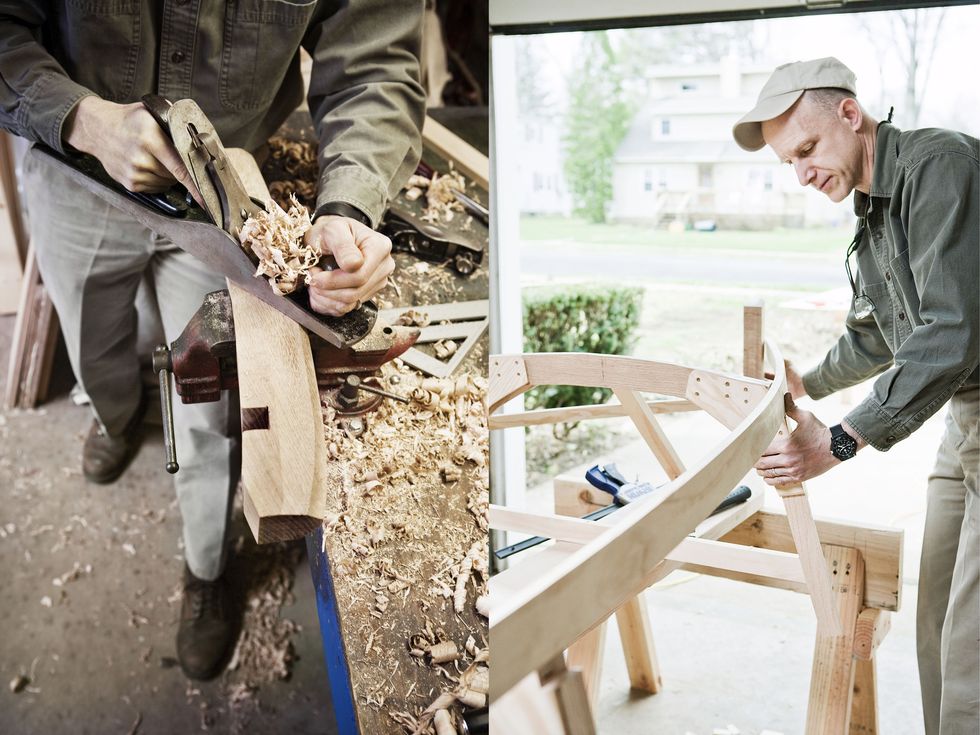

On a wintry early spring morning I set out for Willard Brothers Woodcutters, a sawmill and lumber dealer in Trenton, N.J. You can spend hours there, roaming stacks of delicious-looking walnut, cherry and oak, some of the boards as wide as your arm is long. I bought red oak for the Sea Scout's frames (that was the name of the craft in the plans, and I chose to keep it) and a 2-inch-thick slab of white oak for the wedge-shaped stem at the bow.
Back home, I started making a racket feeding planks through a table saw. My skills were creaky--I've spent too much time in recent years fixing stuff and not enough building--but over a few days my old confidence returned. The Sea Scout began to take form.
Most boats begin with the frames, the ribs that provide structure to the hull. I roughed them into shape, along with the stem and the gracefully shaped stern wall, or transom, which I cut from ¾-inch plywood. Then I braced it all to a building board--which is nothing more than a 2 x 10 with a chalk line marked down the center.

⚠️ To simplify the project, I omitted the mast and centerboard. Instead, I built the Sea Scout, named after the craft in the original article, to be rowed or powered by an outboard motor. She works well in either configuration. You can find the original plans and materials list here.
The boat's skeleton was in place, but each member still needed to be precisely beveled before I could secure the curved planks of the hull. The next step was to clamp thin strips of wood, called battens, to the frame to stand in for the planks, so I could measure and mark all those angles. Then, I took the parts off the board and finished shaping them.
Often, the weather confined me to the garage, but when the sun emerged I worked in the driveway. If you want to get to know the neighbors, start building a boat. Linda from next door asked whether the craft would be sailed, rowed or powered by an outboard motor. Others wondered where I would go with it, how I'd get it there and what I would name it. A truck driver from Tulnoy Lumber, dropping off some marine plywood, approached respectfully. "This is beautiful," he said, with an old-fashioned New York accent as broad as the hand he ran over the frames.
Anatomy of a Boat

Working the Plank
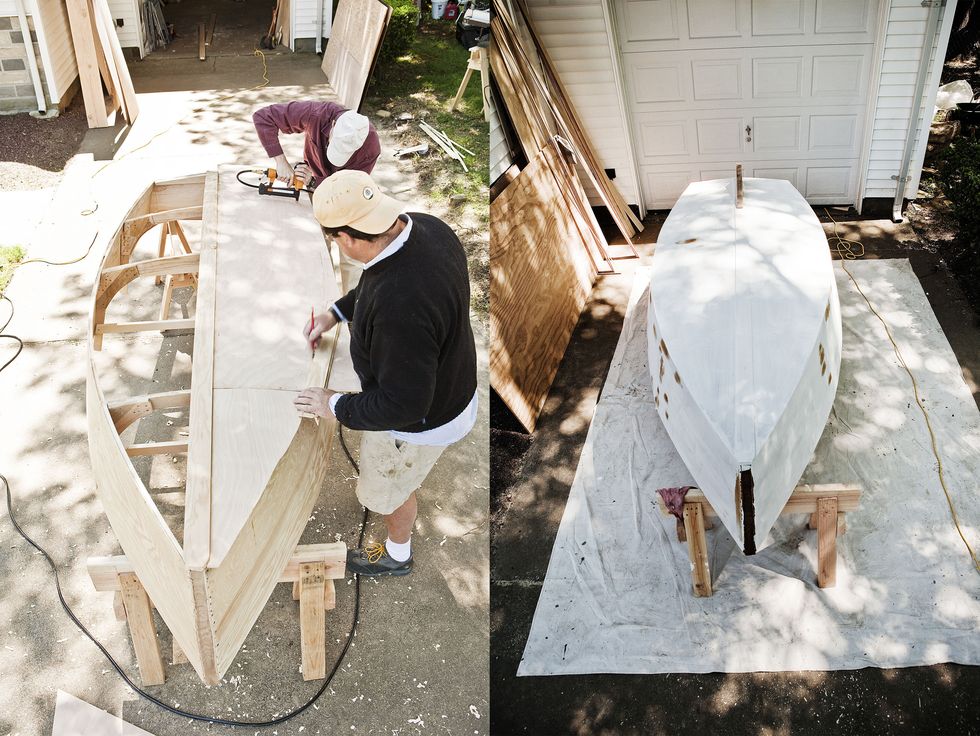

I don't know how Uncle Paul felt about it, but boatbuilding can be acutely frustrating. The bane of my weekends proved to be a small bronze screw. A No. 6 Frearson flat-head, to be exact. Like most modern DIYers, I'd been spoiled by drywall screws and other aggressive fasteners that practically plow into the lumber. Even using a specialized, tapered drill bit and a waxlike lubricant with the unlikely name of Akempucky, I managed to wreck screws by the dozen. The head on one would strip a moment before the screw was fully seated, while another would shear off on the last eighth of a turn, leaving me with a shiny Frearson-head penny.
Timo had tried to downplay the arcana I'd face--"It's more like house carpentry than fine-furniture building," he had said--but I still found myself floundering on occasion. One challenge was that the 1937 article was more an overview than a detailed set of plans. And, though it pains me to find fault with my forebears at Popular Mechanics, the sketch contained suspicious discrepancies. Timo helped me recalibrate some of the dimensions midway through the project—and I had to trim several pieces after they were assembled.
The biggest hurdle came when it was time to plank the hull. The classic way is to bend strips of solid wood to the frames. I'd chosen marine-grade fir plywood instead to save time, but now I was barely able to force the hull's 14-inch sheets into place. There was no way the half-inch plywood I'd planned for the bottom was going to work.
Timo advised me to switch to a special, wafer-thin marine-grade plywood and plank the bottom in two layers. He came swooping in one Thursday morning to show me the technique. He stepped out of his truck with a broad smile, and a block plane in each hand, and my mood lifted. He politely took a sighting down the chine logs where we'd attach the bottom, and spent a few minutes planing them to the last measure of precision. Then we got to work with staples, glue and screws--and in a couple of hours the project went from a plywood flower bed to a small craft with sensuous compound curves.
It was satisfying, but my mistakes still showed in details like the placement of screws and the shape of the stem. "You know what they say," Timo told me. "Putty and paint makes a boat what it ain't." I got out my paintbrushes.
Maiden Voyage
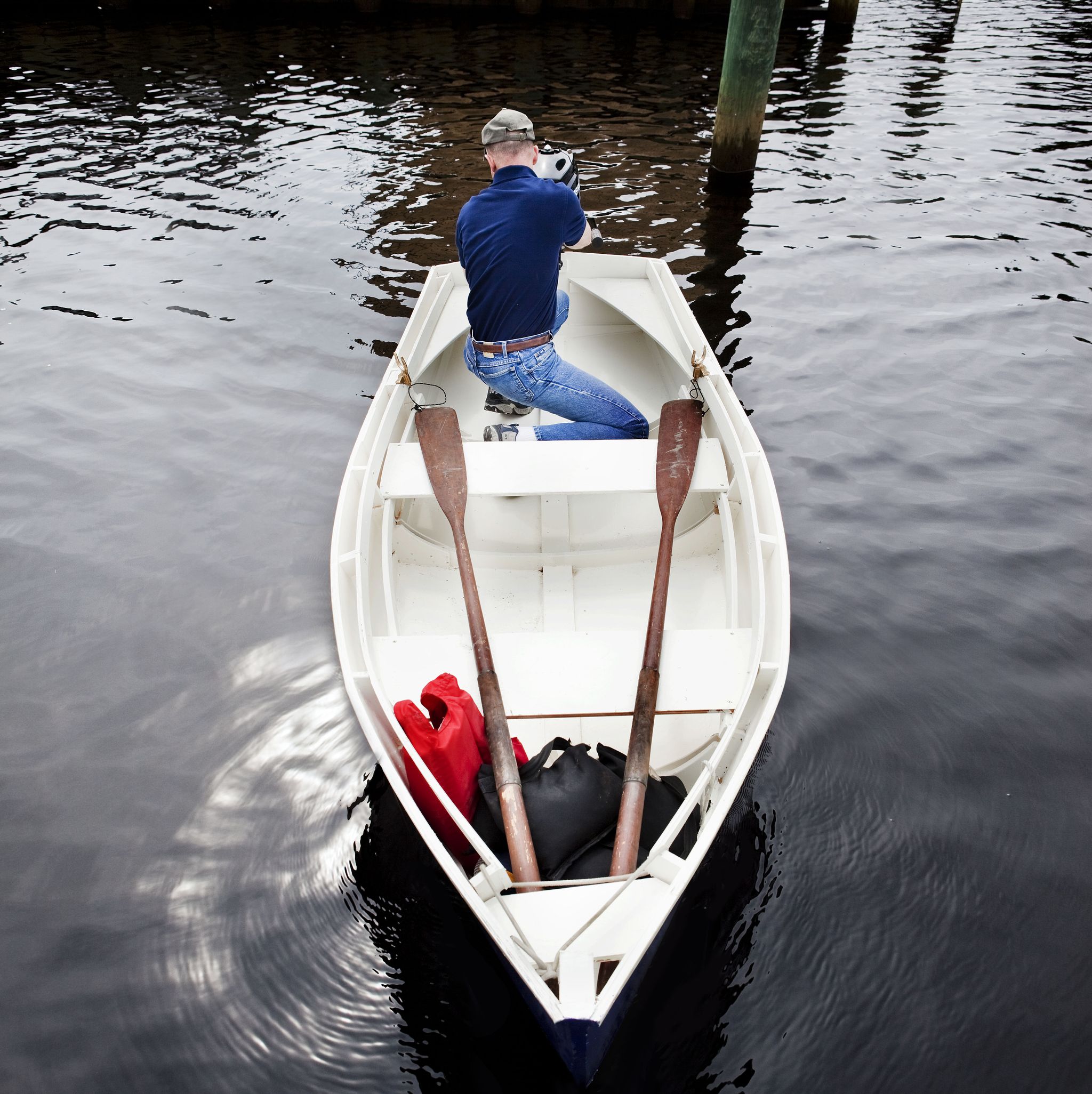

We launched the boat at Tuckerton Seaport on a cool, overcast day that felt more like September than June. Down at the dock, Timo produced a can of Amstel Light in lieu of champagne. "Go ahead," he said, "pour it over the bow." I popped it open and emptied the beer over the paint. "I christen thee Sea Scout," I said. Then we slid the little craft off the dock and into the water.
You might think a feeling of triumph came over me. Not so. The Sea Scout looked very small, almost helpless, as she sat bobbing at the end of the painter, the little rope that Timo had threaded across the bow. I felt humbled. A phrase from the Book of Psalms flashed in my mind: "They that go down to the sea in ships, that do business on great waters."
I wasn't aiming for any great waters myself. I eased off the dock and into the boat. Timo handed me the oars. Awkwardly, I drew the handles back, just above my hips. The craft slid forward gracefully, almost like she was on ice. As Timo watched, I braced the left oar down in the water and swept the surface with the right. The Sea Scout pivoted neatly, unexpectedly elegant and spry.
If the oars were a kick, you can imagine the thrill I felt when I mounted the 2.5-hp Mercury Marine outboard on the transom. It's a clean-running four-stroke engine, compact yet almost zippy on a boat this small. I gave the engine full throttle and cut some nice straight lines and a pleasingly tight curve complete with a crisp little wake.
With the afternoon gone, my first voyage was complete. In the end, I decided to donate the boat and engine to Tuckerton Seaport. Frankly, I needed the space in my garage and driveway: The Sea Scout was a good first foray into wooden boatbuilding, but I knew I could do better—and I'm already sifting through plans.
The Sea Scout, a Decade Later
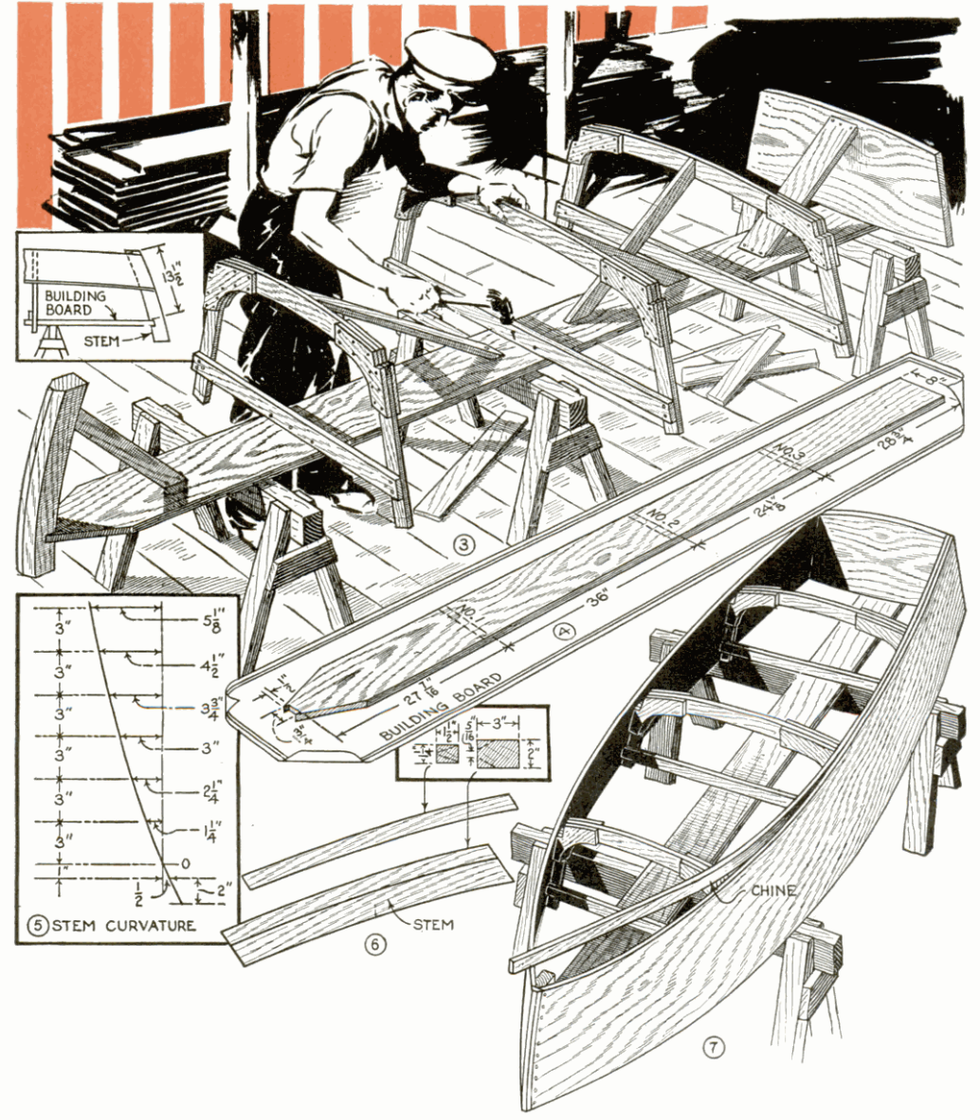
Ask anybody who’s ever built a boat, and they’ll tell you one thing about it: you’re not the same after you’ve built one. And that goes for me, too. The little boat, which I built back in 2009, shaped me as much—or perhaps more—than I shaped it.
The Sea Scout project brought a flood of mail from our readers, some of whom had built the boat or knew someone who did. One woman still had the boat that her father built. She sent a picture of it and recalled the many pleasant hours she spent with her dad as her father taught her how to sail in it. She kindly offered to donate the boat to us, thinking that perhaps we could put it in our lobby. I wish I could have taken her up on the offer.
When you build a boat, you take your place in the long line of craftspeople—professional and amateurs alike—who have plied that trade and learned about the unique burden of building a craft upon whom someone’s safety and enjoyment will depend. Building a boat is humbling, you remember every mistake you made building the thing as it bobs up and down, and waves wash over its bow or crash into it from the side.
You feel it shudder, but it doesn’t give way as you look over the side at the murky depths. And afterward, you look at every boat with a more knowing eye, a greater respect...and you wonder if you could build it.

Roy Berendsohn has worked for more than 25 years at Popular Mechanics, where he has written on carpentry, masonry, painting, plumbing, electrical, woodworking, blacksmithing, welding, lawn care, chainsaw use, and outdoor power equipment. When he’s not working on his own house, he volunteers with Sovereign Grace Church doing home repair for families in rural, suburban and urban locations throughout central and southern New Jersey.
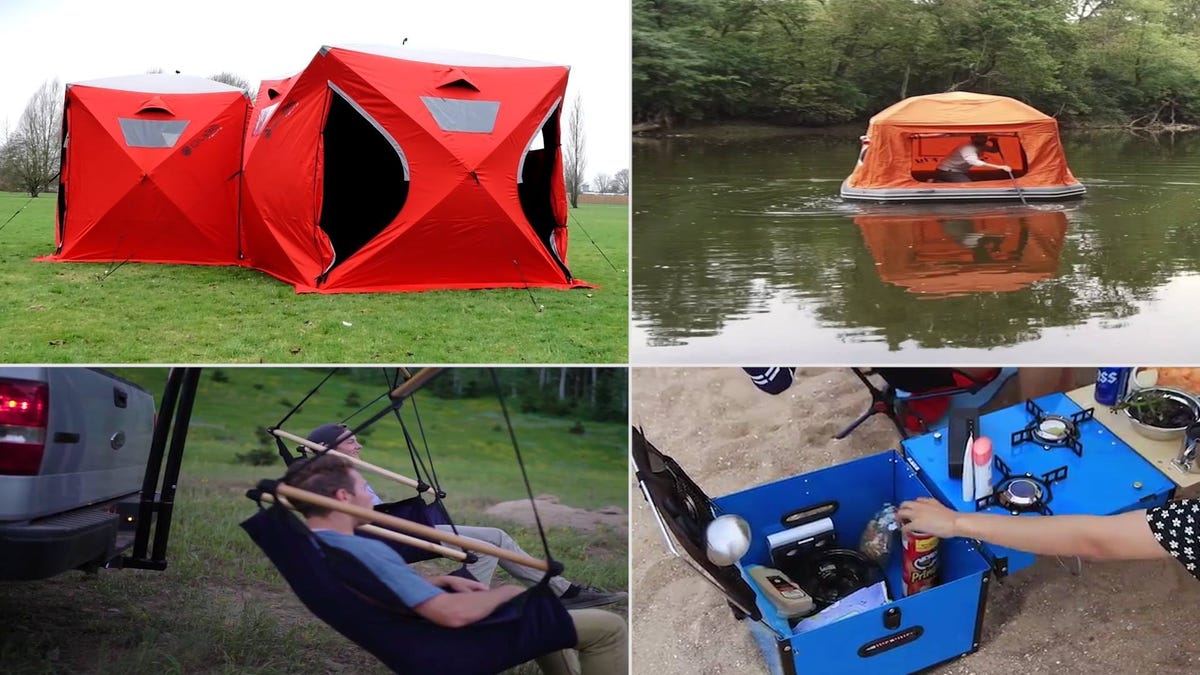

.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Pop Mech Pro .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

The Incredible Case of NASA’S Missing Moondust

Could New Evidence Revive the Black Dahlia Case?

America's Next Stealth Bomber Will Rule the Skies

Can AI Help Solve Math’s Thorniest Mysteries?

You Can Give Your Body Back to Nature When You Die

The History of Pi

Why the Bobcat Is Such a Badass Job-Site Machine

Can Smokejumpers Still Protect a World on Fire?

Stand-by Power: Eco Flow’s Smart Home Panel 2

Stop Wasting Lubricant

How Does UFO Footage Play Tricks on Your Mind?
March / April Issue No. 297 Preview Now
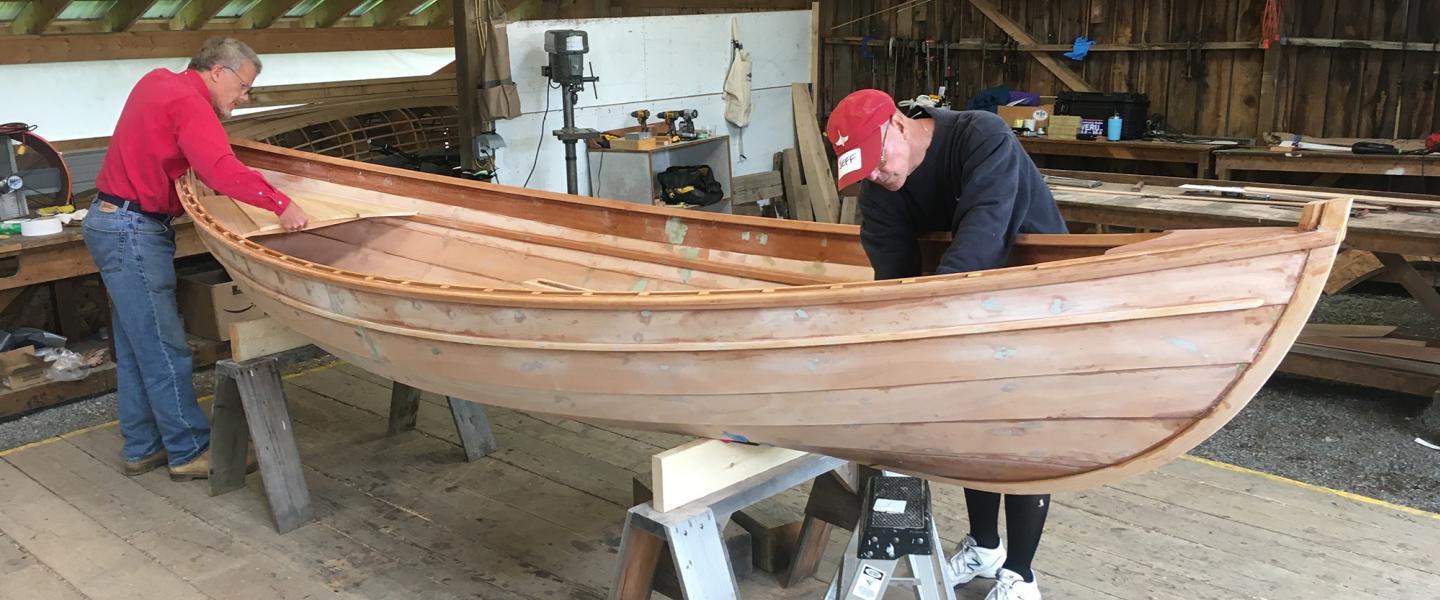

Plans & Kits
If you’re in the market for a boat to build, this directory of Boat Plans & Kits is a fine place to start. And if your company sells plans or kits, we invite you to list your offerings here. There is no charge for listing, but the featured boats must be built of wood. To refine your search of this directory, use quotation marks. If you search Nutshell Pram Kit, you’ll receive all the listings that include the words Nutshell, Pram, and Kit. To refine your search, enter “Nutshell Pram Kit”; you’ll then see only the results for Nutshell Pram kits.
Post Your Boat Plans & Kits
Post Your Plans/Kits login or register
Search plans & kits.
To refine your search, add quote marks. If you search Nutshell Pram Kit, you will get all the listings which include Nutshell, Pram, and Kit. To refine, search “Nutshell Pram Kit” and you’ll see just Nutshell Pram Kit results.
715 Results

Sailboats - Cruising
Presto footy.
Flavio Faloci’s Presto Footy is a gaff-sloop with solid wood hull made of balsa for easy carving/shaping and light weight.
My client wanted to circumnavigate, Cape Horn and all! He wished to build the boat himself and had limited skills in boatbuilding, limits on his budget, and a space about the size of a double garage.

Sailboats - Daysailers
Our Skerry™ is that rare boat combining excellent rowing and sailing qualities into one attractive craft. Sail when there's wind, row when there's not. You'll cover the miles either way.

Oar / Paddle
Here is a small dinghy which can be used for fishing, pleasure rowing or as a tender of a bigger boat. TWEAK was born by tweaking the popular D4/D5 dinghy.
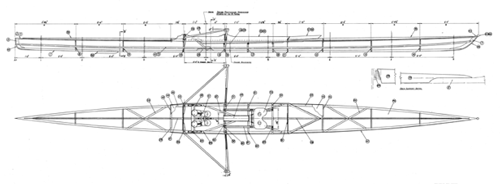
22'6 Kingfisher Shell
V-bottomed single shell with sliding seat, outriggers and light plywood construction.
Construction: Plywood planking over bulkhead-type frames.
No lofting is required.
Plans include 4 sheets.

Mill Creek 13
The Mill Creek 13 looks good, they're easy to build, and even though they are more stable than most kayaks, the Mill Creek 13 offer good speed and handling that you'll never get tired of.
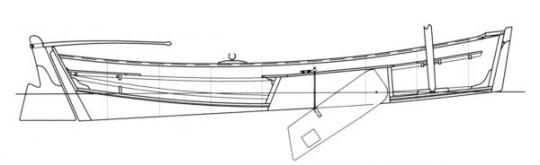
Chesapeake Crab Skiff
Based on traditional crabbing skiff documentation by Howard Chapelle, this has proven to be a fast and stable boat that can carry a real load.

The i550 is a fast modern sharpie type hull shape owing its roots to the historic sharpies of Long Island Sound. The sharpies were known for their speed and seaworthiness, the i550 picks up where they left off.

Wood strip/epoxy plans and kits

Sailboats - Racing
Didi 38 radius chine plywood cruiser/racer
Share your boatbuilding plans or kits today.
Login Sign up
From the Community

AURA III, 1986 custom built Covey Island yawl
Custom built cruising sailboat constructed with a 1 1/8″ thick spruce, edge nailed, strip-planked

1901 Lozier 26' Launch. $27,500
1901 26′ Lozier launch. Restored by Cutts & Case 2006. Universal diesel LT 100 hours.

Faering - Norwegian Faerings or similar wanted
Please contact if you have or know of any Faerings for sale or in need of new home.

Beautiful 15' Crab Skiff Sailboat. Built at the St. Augustine Lighthouse. $5,000.
From Online Exclusives
Extended content.

Tools and Materials Required to Build a Kaholo Standup Paddleboard

Choosing Proper Length Oars

WoodenBoat Live with Sean Koomen

Free Boat Plans
The plans offered here are free public domain boat plans.
Cabin Cruisers

Canoes and Kayaks
Fishing and Utility

Speed Boats

Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sailboats that you can build from home will likely be a small boat under 20 feet. These could be from many different boat suppliers such as B&B Yachts, Brooks Boat Designs, and Chase Small Craft. Boat plans will vary based on your budget and how much time you have on your hands. Based on my previous experience, building your own boat will take ...
The most beautiful small boats may be lapstrake: the parallel flow of sweeping lines creates a visual rhythm that makes the boat seem like an organic creation. Although some designers bitch and moan about amateurs' irrepressible urges to tweak their plans, building your own allows personalization that would be impossible in a production boat.
Idea 21 small sailboat plan is the latest development of my family of small plywood & epoxy sailboats plans for homebuilders: it was quite a time since I was thinking of an evolution of her smaller 19 footer sister, so I finally take the decision to publish this new plan. The goals of this plan is simple: add interior volume, simplify the work for homebuilders switching to a complete plywood ...
Boat plans to help you build your dream. Since our first plans were sold for home construction in 1938, over 100,000 boats have been built from our plans. ... Hartley Boats has the widest range of boat plans for sail boats, power boats, catamarans and trimarans, dinghys and small craft, canoes and kayaks, surfboards and surf skis, vintage power ...
Because this boat plan is also sturdy enough to handle a small motor, it includes important points for protecting the wooden hull from spark plug damage. Be careful to follow these guidelines to build the safest boat possible if you imagine installing a motor down the line. The Jollyroger. 7. The Cork.
These plans are for a small 15 foot knockabout sailboat. I like these plans for their ease. Building a smaller boat is a lot more attainable than a cabin cruiser! And these plans get right to the specifics of building. From the plans: ANY SAILBOAT fancier will like "Tramp," the trim, 15-ft. knockabout that's so easy to build in plywood.
Human Powered Boats; Plans by Building Method; Boat Trailer Plans; RV Plans; Electrical Circuit Plans ... This enables you to focus on building your boat, not searching around for all the bits and pieces needed to complete the project. Free online book: Rigging Small Sailboats; Sailboat Hardware Notes; Sort By: Topper $96.00 - $387.00. Tango ...
To guarantee a smooth sailing experience, follow these steps: 1. Carefully inspect the hull of the sailboat for any damage or cracks. Be sure to check the seams and joints thoroughly. 2. Take the time to check the rigging, including the mast, shrouds, stays, and halyards, for signs of wear, fraying, or corrosion. 3.
With patience and guidance from boat building plans, even beginners can successfully build a wooden sailboat. 5. How long is the wooden sailboat described in the reference? ... Yes, the wooden sailboat is designed to be light enough to fit in a small pickup truck or be rolled to a local lake on a dolly, making it suitable for various bodies of ...
Boat building plans. 8 panels of 1/4" oak plywood 4'x8' Pencil, Sharpie, ruler, tape measure, yard stick, etc. Long flexible straight edge. Box of 1" brad nails. 2 gallons of epoxy resin. ... This allows easy on/easy off when rigging at the boat ramp. I also used a small loop (parrel) around the mast and through the eye to keep the gaff located ...
Please call or write to me at:Arch Davis Design37 Doak RoadBelfast, Maine 04915Tel:207-930-9873. If you would like to receive a newsletter from Arch Davis Design, send me an e-mail at [email protected]. Arch Davis Design - Offering Boat Plans, Kits, Videos and DVDs For The Amateur Boat Builder including sail boats, row boats and power boats.
A short overview of the building of Southern Cross, a Matt Layden influenced shoal draft coastal cruising sailboat. I built this boat in my house over the c...
BOAT PLANS & FULL SIZE PATTERNS - Package Includes latest sail boat plans, SAILBOAT building plan updates & revisions, PLUS direct contact with the designer. This design is for those that want a fast cruising sailboat and one that can accommodate the family or a racing crew and is a joy to sail as well as being easy to build in a variety of ...
An oldie but goodie. Chase Small Craft produces precut, DIY wooden boat kits for people worldwide who want to build their own sailboat kit, rowboat or motorboat We provide a manual and plans, precut, CNC plywood boat kits and all the precut timber parts selected for boat kit. We include all the hardware and epoxy to make truly complete boat ...
To download these plans, click HERE The Drifter 12 is a small trimaran that can be paddled or sailed, and is perfect for exploring rivers, bays, and lakes. The rig is simple, using a windsurfing mast.
Westhaven 32. $ 285.00 - $ 300.00 (USD) Build your own sail boat yatch from 9 feet to 63 feet in length. Fully featured wooden boat plans for home construction in Plywood, Steel and Fibre Glass.
Small Rowboats; Tenders; Sailboats . All Sailboats; Cabin Sailboats to 15' Cabin Sailboats 16' to 19' Cabin Sailboats 20' - 25' Cabin Sailboats 26' up; Open Sailboats to 14' ... Note: you will also need the plans in order to build this boat. Thanks to our friend Joel Bergen, we are now able to offer full size patterns for bulkheads, stems and ...
Two sailboats plans in one ! A pocket cruiser with a double chines hull. - LOA 4.50 m x beam 1.80 m - SA 12 m² - Weight 295 kg - Weight full load 580 kg - Cruiser for three ( CE D/3 protected waters ) One double berth, a single bunk, galley and toilet locker. Full plans in PDF with 3D building guide and photos.
Sailboat plans for our earlier designs are on 24" x 36" paper; parts that fit within those dimensions are shown full size. ... "PocketShip" is a small cruising sailboat of refined model, meant to sail well on all points, provide dry camping accommodations for two adults, and tow behind a four-cylinder car. More than 60 are sailing or under ...
I roughed them into shape, along with the stem and the gracefully shaped stern wall, or transom, which I cut from ¾-inch plywood. Then I braced it all to a building board--which is nothing more ...
A small, simple, seaworthy microcruiser For Souriceau Study Plans, click HERE There are 3 versions of this boat: -1- Standard rig / Retractable vertical keel -2- Furling rig / Retractable vertical keel -3- Furling rig / Bilge keel Comments about...
Plans & Kits. If you're in the market for a boat to build, this directory of Boat Plans & Kits is a fine place to start. And if your company sells plans or kits, we invite you to list your offerings here. There is no charge for listing, but the featured boats must be built of wood. To refine your search of this directory, use quotation marks.
Free Boat Plans The plans offered here are free public domain boat plans. Cabin Cruisers Caballero Flight Dolphin Eager Eve Ha'Penny Ranger Sea Angler Sea Babe SeaHawk Whizz Sportsman Canoes and Kayaks Blue Bill 13 Canvas Back Canvas Kayak for Junior Glide Easy Hunting Kayak King Canvasback Pintail Little Chief Plyak Fishing and Utility Buddy […]