Yachting World
- Digital Edition


Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 7: should the worst happen – with Nigel Irens
- Belinda Bird
- October 1, 2015
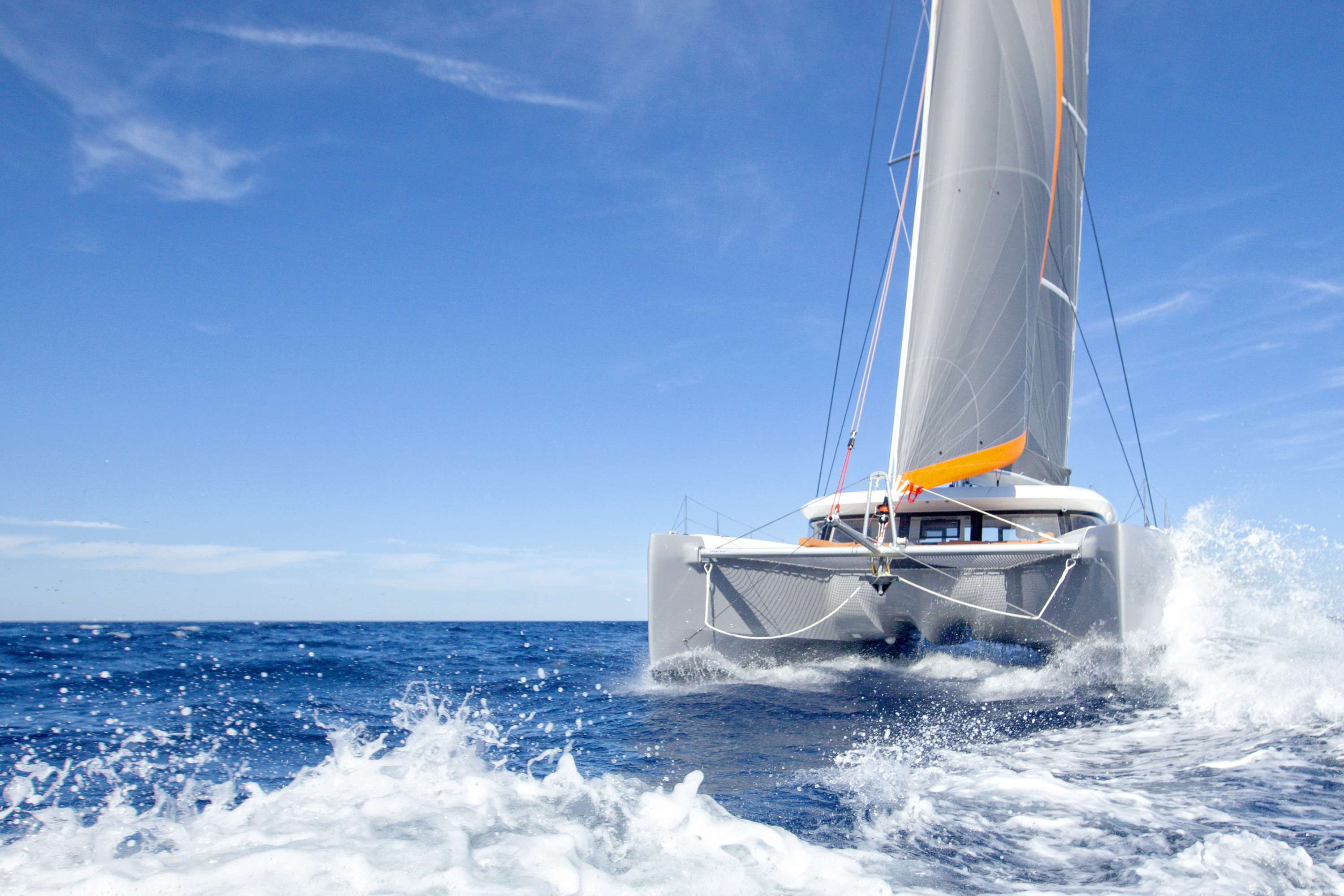
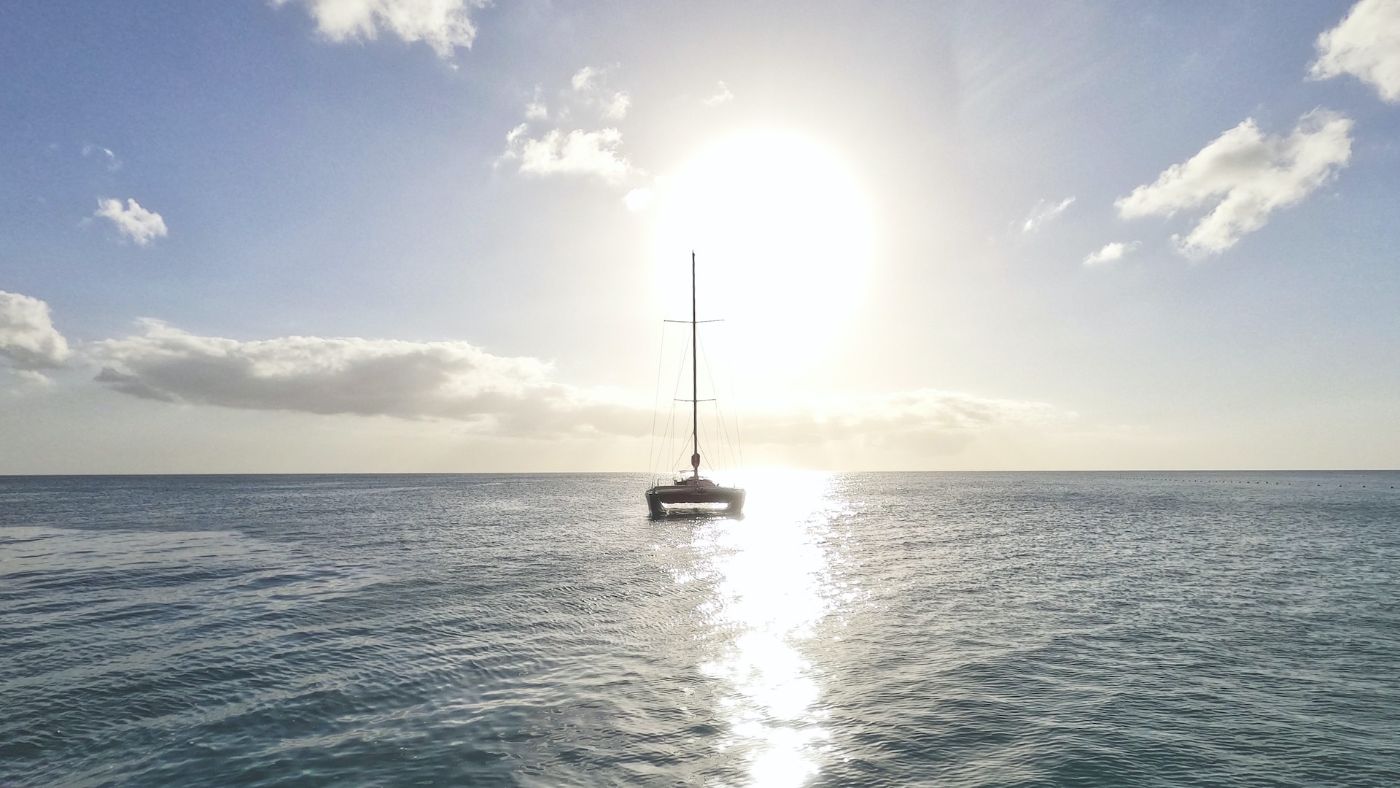
Capsize is very unlikely in most modern catamarans, but should the worst happen it is as well to be prepared, says Nigel Irens
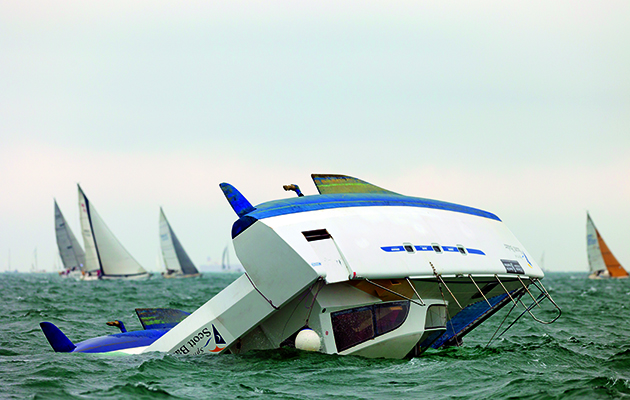

Photo: David Harding

The first thing to say is that as a general rule floating home-type catamarans are, in principle, less likely to be at risk than those designed with performance in mind.
That said, before making such a sweeping statement it’s important to mention that the level of risk involved is much more about the skill and experience of the skipper than about the qualities of the boat on which he or she goes to sea.
Over the years buyers of catamarans have tended to go more and more for the model with enhanced accommodation space (and de facto diminished performance). The bottom line is that in sailing on most ‘charter spec’ catamarans you’d have to be trying hard to win a bet to bring about a capsize.
Building catamarans down to a budget often seems to result in under-sizing of deck gear so that powering up the rig is not really possible. This really is not intended as a criticism – just a reflection on the real-life economics of this market.
If these factors combine make such a catamaran very hard to capsize then this could surely be perceived as a positive result.
Once the discussion turns from the prevention of capsize to the reality of it information and advice is not readily available. There are two different areas that need to be addressed.
The first is about actually surviving the incident in the short term. The second assumes you have managed to do that and is about surviving life on an upturned boat while summoning some help as soon as possible.
Rule one is that if you are on the inside of the boat you should immediately get away from the bridgedeck and head for one or other of the hulls as fast as possible. That’s easier said than done because you’ll be disorientated – especially if it’s dark outside and any lights inside won’t last long.
At the very least if sailing in challenging conditions (especially on a performance boat) it makes sense to bed down between watches in a hull rather than in the central saloon.

Not likely in a cruising cat!
The reasoning is that the boat is unlikely to be supported by the roof for very long when inverted and as she settles down in the water the bridgedeck will soon be close to the water, making an exit attempt risky – especially if there are warps washing around the cockpit.
Stay below if possible
As the hulls themselves are by definition watertight the boat will be buoyant enough to float with (at worst) the threshold of the companionways into the hulls at the surface.
It’s important not to rush for the escape hatch (fitted to the inboard side of each hull) because, although it provides a useful source of light, opening it will let some of the air that’s supporting the boat out of the hull, causing it to float lower in the water.
It is probably best to wait and take stock of the situation – together with anyone else who is in the same hull – and maybe wait for daylight if the capsize has happened at night. Try to find out if others are outside – or perhaps in the other hull.
If, on balance, the decision is taken to leave the hull then it is important to make a plan that results in the hatch being open for as short a time as possible.

Catamaran escape hatch
Clearly if the level of seawater inside the hull is high it is not going to provide a suitable environment for survival while waiting for assistance, so exit is the only option. If on the other hand it is only knee deep then the hull may be the place to stay.
Once again good planning for the worst before going to sea is the way to go and there is plenty of information available about that.
Discussion and planning
As part of the preparation for these dire circumstances it is important to have had a frank discussion about this whole scenario with the supplier of the boat. Has anyone ever capsized this particular design before, and what was learned from that?
Comparing the relative dangers of being at sea in a catamaran that could capsize with those of being in a monohull that could sink has always been a source of lively debate.
The truth is that there are now (and there have always been) risks in going to sea in any vessel. Our best hope in minimising that risk is to face the subject full-on and become as well informed as possible.
Man overboard
While discussing safety issues in the context of catamaran sailing we should take a brief look at that other seafarer’s nightmare – losing a man overboard.
All the normal recovery procedures apply to a catamaran with regard to the all-important location of the casualty, but there are some important differences in the way the approach is made for the recovery.
Because of the high windage of a catamaran and relatively small amount of lateral resistance under the water you can assume that, as you slow the boat down to attempt the pick-up, you’ll make a huge amount of leeway. As a result if you approach to windward of the casualty there is a real danger that the casualty’s legs will be carried under the leeward hull – with a real risk of serious injury from the propeller.

Because of high windage it can be a problem approaching a casualty in the water
To be absolutely safe from this peril just keep to leeward of the casualty. Of course this means that, despite you best efforts, you could pass too far to leeward and won’t be able to get a line to them.
A good way to avoid this problem is to motor at maybe two to three knots across the wind trailing a long line behind the boat (from the leeward stern). You should aim to pass at least 10m to windward of the casualty – which should be easy to judge because you have enough speed to have good steerage way.
Because the casualty will need to hang onto this line it should be easy in the hands – a 14-16mm 8 plait nylon mooring line or similar would be ideal.
When the casualty is directly to leeward of you turn sharply downwind, making a 180° turn that leaves you passing safely to leeward. Slow down at this point, being careful not actually to go astern and risk getting the line around the leeward propeller.
If all goes well the bight of the rope will now be encircling the casualty and at some point he or she will be able to grab hold of it.
From now on you shouldn’t need to engage the drive to either propeller. Keep the helm to leeward and the boat should lie with the wind somewhere on the quarter. If you’re moving too fast – making things difficult for the casualty – you could transfer the line to the bow so that the drag of towing will tend to make the boat round up somewhat – you should be able to control the angle at which the boat lies to the wind by moving the attachment point of the rescue line to different points along the sheer.
If all goes according to plan you should be able to haul the casualty in to the windward quarter of the boat, where they can use the emergency boarding ladder.
If they are not up to that then it should be possible to pass them another rope with a bight in the end of it big enough for them to pass it over their shoulders and under their arms so that they can be hauled aboard.
Do’s and don’ts
- DO take positive action to wise up on the risk of capsize on the catamaran you sail. Asking difficult questions of boat suppliers and collecting opinions from other owners are all valid.
- DO develop some kind of basic plan for the worst case – such as impressing on crew that if below in high-risk conditions then being in the hulls is much safer than being on the bridgedeck. In the case of a man overboard do always make the pick-up from a position downwind of the casualty.
- DON’T take the word of some designer who’s never capsized as gospel – ferret around online and find out what conclusions people who have actually been there have drawn from their experience.
- DON’T risk sailing in bad weather until you have plenty of experience with the boat in more moderate conditions.
- DON’T even think of steering by autopilot when in potentially dangerous conditions. Many accounts of capsize reveal that there was no one on the helm at the critical moment.
- DON’T make a meal of all this. Capsize is very unlikely in most cruising catamarans, but it does happen occasionally so, as with most seamanship issues, the smart move is to be on top of the subject and prepared for the worst.
Our eight-part Catamaran Sailing Skills series by Nigel Irens, in association with Pantaenius , is essential reading for anyone considering a catamaran after being more familiar with handling a monohull.
Part 8: the future of catamaran cruising
Series author: Nigel Irens
One name stands out when you think of multihull design: the British designer Nigel Irens.
His career began when he studied Boatyard Management at what is now Solent University before opening a sailing school in Bristol and later moving to a multihull yard. He and a friend, Mark Pridie, won their class in the 1978 Round Britain race in a salvaged Dick Newick-designed 31-footer. Later, in 1985, he won the Round Britain Race with Tony Bullimore with whom he was jointly awarded Yachtsman of the Year.
His first major design success came in 1984 when his 80ft LOA catamaran Formule Tag set a new 24-hour run, clocking 518 miles. During the 1990s it was his designs that were dominant on the racecourse: Mike Birch’s Fujicolour , Philippe Poupon’s Fleury Michon VIII , Tony Bullimore’s Apricot . Most famous of all was Ellen MacArthur’s 75ft trimaran B&Q, which beat the solo round the world record in 2005.
His designs have included cruising and racing boats, powerboats and monohulls, but it is multis he is best known for.
See the full series here
A special thanks to The Moorings, which supplied a 4800 cat out of their base in Tortola, BVI. www.moorings.com
If you enjoyed this….
Yachting World is the foremost international magazine for bluewater cruisers and offshore sailors. Every month we have practical features to help you plan and prepare to realise your sailing dreams. Build your knowledge month by month with a subscription delivered to your door – and at a discount to the cover price. S ee our latest offers now.
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter

What You Can Learn on a Quick Test Sail

Cabo Rico’s Classic Cutter

Bob Perrys Salty Tayana 37-Footer Boat Review

Tartan 30: An Affordable Classic

Preparing Yourself for Solo Sailing

Your New Feature-Packed VHF Radio

Preparing A Boat to Sail Solo

Solar Panels: Go Rigid If You have the Space…

Shoe Goo II Excels for Quick Sail Repairs

When Should We Retire Dyneema Stays and Running Rigging?

Rethinking MOB Prevention

Top-notch Wind Indicators

Worship Your Universal M-Series Diesel With the Marinized Kubota Block

Taking Care of Your 12-Volt Lead-Acid Battery Bank

Hassle-free Pumpouts

What Your Boat and the Baltimore Super Container Ship May Have…

Battle of the Teak Cleaners — Snappy Teak-Nu vs. Star Brite

New Seacocks for the Offshore Sailor

Bottom Paint Care

Quick and Safe Sail Cleaning

Are E-bikes Worth the Extra Weight and Cost?

How to Handle the Head

The Day Sailor’s First-Aid Kit

How to Select Crew for a Passage or Delivery

Re-sealing the Seams on Waterproof Fabrics

Waxing and Polishing Your Boat

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits
- Sailboat Reviews
Gemini 105Mc
This is the third version of an already thoughtful design that tony smith has been tweaking for years. it's a spacious, stable platform for a fast-cruising couple..

Tony Smith’s most recent design is the third iteration of a 34-foot catamaran that his company, Performance Cruising, Inc., of Annapolis, first introduced to the American market in the 1990s. The result of Smith’s continued tinkering, the 105Mc, is, he says faster than the original. Since this is our first review of the Gemini cat in any version, we can’t compare. But we can report that this boat is fast for a cruising catamaran. It’s also evidence that when a builder is willing to incorporate new and sometimes expensive ideas in design development, the results can be worth the investment.
Company History Tony Smith is a British expatriate who, with wife Susan, formed Performance Cruising in 1980. Following graduation from the University of East Anglia with a degree in engineering, he studied the mechanics of boat performance while participating in singlehanded races, including the first 2,100-mile Round Britain race, in which he finished fourth.
He began his boatbuilding career by constructing a 24-foot Piver trimaran in a shed in England. Then, in 1969, he developed a method of integrating foam coring with fiberglass, and produced the Telstar, a 26-foot, folding trimaran. During a 10-year run, 300 of the boats were sold worldwide. Along the way, he also was involved in the construction of 30- to 70-foot custom yachts.
Eventually emigrating to the US, he introduced the Telstar to the US market. Following the loss of the molds in a fire in 1981, he re-emerged on the scene with the design for a new catamaran, appropriately called the Phoenix, the first Gemini.

In 1993, the company launched the Gemini 3400, the first catamaran with a lifting underhung rudder system. It was eventually modified and reintroduced as the 105M, and the 105Mc is the most recent upgrade.
With 800 boats on the water, the company claims to be the best-selling catamaran manufacturer in the US. In 2002 the company’s 20 employees built and sold 54 boats, valued at $8 million, in a 16,000-square-foot factory. An additional 25,000 square feet of production space are currently under construction.
Six dealers are located in Florida, Maryland, California and Washington. Though the company also sells directly to customers, there’s no price advantage, and a connection to a local dealer would be an advantage if warranty issues arise.
A prototype for a new Telstar trimaran is undergoing sea trials, and can be seen on the Performance Cruising website.
Appearance/Design Smith’s perspective on sailing and yacht design fits the definition of a multihull advocate. From his standpoint, sailing is about speed, comfort, and stability.
From an aesthetic standpoint, comparisons of a 35-foot catamaran to a cruising monohull are usually akin to comparing a coupe to a delivery van. Though both may be designed to accomplish the same purposes, the execution varies greatly. Many cruising multihulls present a slab-sided appearance, and boxlike profiles with cabins extending high above deck level.
The 105Mc does not. When viewed from the quarter, the Mc has a relatively sporty appearance, even with the addition of a cockpit canopy that raises the boat’s profile. Viewed on the centerline, there’s no question she’s a cat, though the unsightly strakes of the 3400 version have been eliminated.
Smith says Gemini catamarans are designed for “serious ocean cruising,” adding that “a 23-day passage with son Neil across the North Atlantic opened my eyes to her capabilities.”
During the passage, he says, the pair encountered 45-knot winds and 35-foot waves, but never felt they were in harm’s way, and were comfortably ensconced in the cockpit wearing layers of fleece.
As most readers know, voyaging in multihulls offshore demands some different sailing techniques and priorities than sailing ballasted monohulls. The high initial stability of a multihull works both ways: the boat will mightily resist capsizing, but if it does go over and invert, it will be virtually impossible to right again without the assistance of a large ship with a cargo crane. Assuming the essential integrity of the hulls, the platform will be stable, and the crew will live in an inverted world pending rescue. However, very few owners of cruising multihulls have the occasion to take their boats into conditions that seriously challenge their initial stability, and (North Atlantic deliveries by designers notwithstanding) this Mc will usually be sailed in coastal or near-coastal waters.
The Mc has the same basic dimensions as the 3400. Note that the weights published in the company’s sales literature and on its website are at odds with each other. Dimensions in this article are accurate, Smith says: “The 105M and the Mc are the same weight—9,600 pounds. We realized after our trans-Atlantic trip that the weights we had given for the 105M were too low. We finally bought a pair of scales!
“The mast on the Mc is a foot taller than the 105M, and has a 1′ crane.” The mainsail now carries a large roach and full battens, increasing mainsail area from 260 to 340 square feet, a hefty jump. The 150% genoa carries 350 square feet.
A new option is a flat-cut overlapping genoa known in the multihull world as a “screecher.” This 490-square-foot sail produces spinnaker performance without adding a pole and guys.
The furling drum for the screecher tack can move athwartships on a curved track that is mounted at the prows of both hulls and across the bowsprit/anchor platform, forward of where the anchor is dropped through. This movable tack allows more flexibility with sheeting angles, especially when attempting to work to weather.
The cut of the sail allows it to be sailed to within 50 degrees of the apparent wind, and the tack arrangement doesn’t get in the way of the ground tackle.
Smith describes the hull shapes, introduced in 1995 on the 105M model, as “revolutionary in the multihull industry.” They have a 9:1 length to width ratio.
“They closely resemble a racing monohull,” Smith says. “They are shallow and fat, with a teardrop shape to produce more speed and increase load-carrying capacity. Compared to the 3400, narrower shapes allow hulls to be moved outward to produce stability without increasing beam.”
The foredeck has 39″ of clearance at the bow. (Note that the builders refer to the deck area forward of the cabin as the “bridge deck,” but we’ll use “foredeck” as we don’t want to confuse it with the bit of decking often found between the cockpit and the companionway.)
Asymmetric centerboards were designed to reduce turbulent drag and increase lift. Constructed of a combination of fiberglass mat and Kevlar surrounding closed cell foam, they pivot upward to allow shallow-water anchoring. Located in cavities on the hulls, they are raised from inside the main saloon, a convenient arrangement that does not interfere with galley or navigational chores. Smith says the combination of hull and centerboard redesigns produced a boat requiring “25% less energy to push it the same speed.”
The cockpit sole has been lowered slightly to increase headroom to 6′ 7″. However, the modification does not impair the helmsman’s view forward through a large Lexan window that spans the deck. The wheel was moved outboard, allowing the helmsman to steer from the rail. Mainsail controls are now located on a thicker transom that provides more comfortable seating for crew, and the stern has been modified to allow access from swim ladders.
Smith’s personality is that of a consummate tinkerer. However, unlike industry giants, he enjoys the luxury of being able to continually focus his attention on one product with an eye toward evolutionary improvements.
Deck One early impression while sailing this boat is that the cockpit doesn’t resemble a spaghetti factory, though the boat is as well-equipped with name-brand equipment as a similar-sized monohull.
Halyards are led to winches on the mast rather than sheetstoppers on the cabintop because, Smith says, “you’re operating on a stable platform, even in a blow,” so moving forward is not as treacherous.
The mast carries straight double spreaders and is stepped on deck atop the main bulkhead. The headstay is opposed by a split backstay with tensioner. Halyards are internal. Shrouds are dead-ended on chainplates at the main bulkhead. The chainplates are bolted through steel strapping bonded into the foredeck area.
The mast is rigged with permanent checkstays angled 20 degrees aft. These are supported through the deck by a stainless steel rod married to a steel plate mounted horizontally in the hull. The powerful sailplan is well supported.
As is true on most catamarans, movement forward is relatively effortless. The combination of 14″ wide steps, a handhold on the canopy, a stainless steel handrail recessed in the cabintop, and 10″ wide decks, allowed us to move forward safely in blustery conditions we encountered on a test sail.
The large sundeck and plastic seats attached to the forward rail provide passengers comfortable lounging spaces forward of the mast when underway. Unlike a lightweight monohull, the cat’s performance is relatively unaffected by weight on the foredeck. Storage compartments are located in each hull.
The helmsman steers seated on a 27″ wide x 16″ deep seat that affords unrestricted views forward. We sailed with three passengers under the canopy without interfering with the skipper. Though the saloon may be enclosed in stinky weather, clear windows on the top half of the cockpit bulkhead slide open to allow the driver to commiserate with passengers.
The mainsheet is attached to the end of the boom and a section of track mounted on the stern rail that affords excellent sail control. However, the task becomes difficult when the cockpit is enclosed by a clear vinyl cover.
Lockers for storage of propane tanks and an optional generator are also located in the cockpit.
Belowdecks Step over an 11″ doorframe into the saloon and there’s no comparing the open spaces of the Mc’s 14-foot beam to the view along the saloon of a typical 34-foot monohull. That impression is augmented by a portlight array that provides 360-degree visibility, and four Bowmar hatches that allow light and air to flow in from overhead.
Fiberglass surfaces are light and shiny, and veneers nicely finished. The fit of most cabinetry is above average.
The centerpiece of the saloon is a C -shaped dining area surrounded by cushions that, with the table removed, serves as a conversation pit. When lowered, the table converts to a double berth.
The space to port, amidships along the hull, is dedicated to the navigator. The master stateroom is forward amidships and to starboard, with the bunk set at a slight angle. The head is forward to port. There’s an elongated galley on the starboard side, matched by a navigator’s station along the port side, and twin staterooms aft.
The boat has enough bunks for 6-8 adults, but Smith rightly calls it “a couple’s boat.” This is a refreshing contrast to builders who overstate the livability of their products.
In addition to its spaciousness, the minimum headroom, even in the head, is more than 6′, so most passengers will be able to stand upright.
Though the interior is not dramatically different than typical production boats, several touches contribute to a favorable impression. The dining table is solid teak. Leaves increase the surface of the table to feed 6-8 adults, and it rotates 90 degrees to fit the crowd.
Part of the navigator’s 89″ long work surface is elevated and shaped so a chart kit fits securely.
Aft staterooms have a 28″ x 28″ area in which to change clothes without banging the hull. Both have double berths and opening ports. Propane sensors and fume detectors are standard equipment in the staterooms, as are audible alarms.
The size of the galley on the Mc was increased by locating countertops on the inboard and outboard sides of the passageway, and the addition of drawers and cabinets. Similarly, room for a built-in microwave was added. The space is filled with a Voyager 2000 two-burner stove with oven and broiler, and two-section stainless steel sink. A solar vent is located overhead. The four-cubic-foot refrigerator is a Dometic American.
Skipper’s quarters are filled with light by a port spanning the hulls that presents views through black Lexan. The queen-sized berth sits on an island with nothing below it but water. Storage is forward in the hull, and in bins to starboard. The aft bulkhead of the compartment is enclosed by smoked glass that slides out of the way to provide a view corridor for the helmsman.
The head compartment on the Mc is big, bright, and well-ventilated. A good touch is a siphon arrangement that allows fresh water to be pumped through the toilet after every use, helping to eliminate odors.
Throughout the catamaran, spaces are well-organized and proportioned, so crews will rest, eat, and sleep in comfort. The skipper’s quarters are large enough to help compensate for the monthly mortgage payment and slip fees.
Construction The Gemini plant is a model of efficiency, with no wasted space, as we learned during an afternoon tour. Boats typically require 5-7 days to proceed past six stations to a forklift waiting to launch them into a creek behind the facility.
Hulls, decks, and interior liners that provide reinforcement of the structure and a base for furniture are solid fiberglass. Liners are glassed and tabbed into the hull prior to installation of the deck.
The lamination schedule calls for vinylester resins bonding a barrier coat of 1.5-oz mat followed by two layers of 18 x 15 Cofab mat. The only coring is 1/2″ end-grain balsa across the foredeck and cabintop, and in cockpit areas in which there are no deck fittings.
The hull-deck joint is a shoebox design bonded with something Smith calls “black poly putty,” produced by Cook’s. Most builders prefer 3M5200 but Smith has used the putty for 20 years because “it has an 8- hour setup time that allows workers to be more precise in the placement of the two sections. It makes a phenomenal bond that is not brittle because it is chemically cured, a better alternative than air-cured products.”
Once installed, the deck is secured with stainless steel fasteners on 5″ centers and the joint is covered by a gunwale guard.
Following his trans-Atlantic trip, Smith decided that the boat needed to undergo a weight loss program. When constructed, most boats are heavier than designed, and the Mc was no exception. Smith estimates the boat was 1,000 pounds too heavy.
“It was not a matter of speed, but of comfort,” he said. “I felt that by reducing the boat’s weight I could increase its buoyancy and produce a more comfortable ride.”
To that end, he replaced drawers in the forward stateroom with bins, substituted 1/2″ plywood for 3/4″ in some areas, and lightened the lamination in some nonload-bearing areas.
The boat’s Achilles heel could be the solving of wiring or plumbing problems, should they occur. Wiring looms are attached to the liner prior to the installation of the liner to the hull, and are virtually inaccessible. Of the arrangement, Smith says “our looms are foolproof. Remember, we’ve been doing this for 20 years and the process is evolutionary, not revolutionary.” Spare hoses are installed during construction to ease retrofitting appliances, and 12-volt wires are run through PVC to avoid heat and chafe. Wires exit the mast into the forward stateroom, and can be accessed in a panel between the deck and liner. Still, we wouldn’t want to perform subcutaneous surgery on this boat.
Performance We sailed the 105Mc on the day after the Annapolis Boat Show ended, when multihull manufacturers congregate to offer rides to interested sailors. A northeaster arrived that morning, bringing winds that built to 25-35 knots and produced a 3-4 foot chop. We were the only multi hull on the water.

With the wind abeam when we slipped dock lines, once we were underway she motored well despite her windage. On the bay, the boat sailed with little heel, and fast, under a reefed mainsail and a flat, 90% jib. Nearby, the three-person crew aboard a 30-foot monohull struggled to keep their boat on her feet.
Sailing closed-hauled, speed fluctuated between 6.5 and 7 knots. The short chop produced a bumpy ride and water over the bow, but we stayed on course with very little leeway. When we cracked off, speed fluctuated between 7 and 12 knots in wind speeds ranging from 17 to 25 knots. She was easy to steer, and responsive when we made sudden maneuvers to avoid crab pots.
The canopy protects crew from the elements, but may provide a false sense of security, as we learned when we moved forward from its protection and stepped into a chilly breeze and seaspray. Handrails are well located, and the nonskid was effective on the wet deck.
The boat is propelled under power by a single Westerbeke diesel, using an outdrive leg than can be lifted clear of the water. The current standard engine is 27-hp, up from the 20-hp engine previously installed.
Conclusions This third generation of Gemini cat is an improvement over her predecessors. She sails as well to windward as can be expected of a cruising catamaran (better than many) and shows good speed and stability off the wind. She’s easy to operate, and well-built. Spaces belowdecks are comfortable and larger than those on similar-sized monohulls, though the lack of a second head will be an inconvenience for skippers overnighting with large crews. With the 27-hp engine, a 150% genoa and furler, and electronics, the tab for the 105Mc is $129,500. Add a screecher for another $5,400.
Contact – Performance Cruising, Inc., 410/626-2720, www.geminicatamarans.com
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Where is the production site, and can a tour of the facility be arranged?
The boat is no longer in production. Tony retired and sold the company. I think during the 2005 market crash everything fell apart. The outdrive and engine aren’t made anymore. The new owners redesigned the boat and ruined the original idea. They tried to design a boat for the single handed rental market in the Caribbean with a deeper draft and fixed keels. It didn’t sell well.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

Beneteau 423: What You Should Know | Boat Review

Buying A Sailboat Is Scary! Yacht Broker Interview

The Great Loop – The Basics

Bottom Paint Showdown – Six Paints, One Winner!
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager

Why Catamarans Capsize, A Scientific Explanation (For Beginners)
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions if you purchase products from other retailers after clicking on a link from our site.
When people see a catamaran, many think of capsizing, which has proven to be a way less common event than your average forum thread would lead you to believe. This article will use a scientific approach to look at the data available for stability incidents with catamarans.
This article is based on a study made by the UK government concerning recommendations for regulating catamarans. I have used that knowledge to discuss some of the common misunderstandings considering catamaran stability. Let’s get to the short answer!
A Catamaran will capsize when rotational forces overcome the stability of the boat. Capsizing can happen in two ways, either the ship overtakes a wave and sinks it bows into the next one, inducing something called pitch-poling. Or a breaking wave, with the same height as the boat’s length, hits the vessel’s side, making it roll over to its side(a.ka. flipping).
Are you like me and need to understand why? Read on!
What Does It Mean to Capsize?
In the context of boats, to capsize means to flip the boat upside down unintentionally.
On a small dingy, it is part of the sailing experience, and the boat can quickly be righted, but on a cruising cat, it can be the difference between life and death.
This can happen in numerous ways that will be discussed in great detail below. The most common is a combination of high seas, strong winds, and sailor error.
Not only is it dangerous to be in the middle of the sea stuck on what has now become a very expensive chunk of plastic, but the act of capsizing is also hazardous. Depending on where you are, inside, outside, or in one of the hulls, you may face the risk of getting thrown overboard, stuck in a hull upside down in the dark, or getting hurt by flying objects.
Much of the discussion around capsizing and what to do after it has happened is theoretical. In this article, I will show you the science behind catamaran stability and how that interacts with the power of the sea.
Why Does a Catamaran Capsize?
Catamaran stability can sometimes be a little tricky to understand. To get us off to a good start, here is some terminology that will be useful;
- Wind heeling moment is the effect wind has on the rotational(heeling) movement of the boat.
- Apparent wind angle is the angle of the wind when the boat is moving; this can differ from true wind, which is measured in a fixed position.
The study reaches a couple of conclusions, some of which are of interest to this discussion.

Heeling Is Greatly Dependent on Apparent Wind Angle and Sheeting of the Sails
This means that a catamaran (or any other sailboat, for that matter) will have a greater rotational force if the sails are sheeted in hard. This is because the wind gets “caught” in the sails, and the forces act directly on the sails, mast, standing rigging, and onto the hulls.
If, instead, the sails were loosened or “sloppy,” the amount of wind “caught” would be less, and therefore, more wind would be able to pass around the sails, thus decreasing the heel.
When it comes to apparent wind angle, the study shows that the forces are most significant when the wind is forward of the beam. This is primarily due to the aerodynamic effectiveness decreases aft of the beam.
Large Waves From the Side or Aft
Large waves are always a factor con safety at sea; they can be divided into breaking waves, waves whose amplitude (basically when waves get so big that they start coming apart(breaking) reach a threshold where the shape of the waves suddenly changes.
The other category is non-breaking waves or rolly waves. These are more gentle and cannot change shape in a violent and uncontrolled manner.
The study concludes that (1)catamarans have less roll response than monohulls during non-breaking waves, which means a catamaran will generally follow the motion and wave shape as it goes up and down it in a predictable manner, and that (2) this behavior shows no indications of being dangerous.
A monohull will instead rock from side to side and show a pendulum-like behavior.
On the other hand, breaking waves pose a real threat and are something to be aware of if traveling on a smaller catamaran. The test showed that a sufficient beam-to-wave ratio is needed to avoid capsizing.
A common beam-to-length ratio is 50%; that is, the length of the boat is at least double the size of its width.
Together with wind forces, breaking waves seem to be the most significant factor affecting the risk of capsizing.
Breaking waves with a height equivalent to the beam of a catamaran, half the beam of a trimaran may be sufficient to cause a capsize. Smaller or narrower yachts are, therefore, more vulnerable.
What makes breaking waves dangerous is their ability to bring the boat past its tipping point (or range of stability); much of this is due to the steepness of the wave. A 30ft non-breaking wave will act as a rolling hill in the English countryside, while a 15ft breaking wave is more of a black slope in a French ski resort.
The closer a boat comes to its tipping point, the less energy is needed to move past it. This is why the combination of factors is essential, large breaking waves, high apparent wind forward of the beam, and a minor error from the cockpit, and disaster is around the corner.
Effect of Keels (Daggerboards, Centerboards)
When a catamaran is hit with a breaking wave from its side, one factor that reduces rotational forces is the ability to move sideways with the wave, in other words, to slide sideways.
Usually, this is not wanted since it reduces the cat’s ability to go windward; this issue is sometimes addressed by adding mini keels, dagger, or centerboards.
The issue with keels is that the crew cannot withdraw them into the hull to reduce drag; this means that they can become a security issue when hit by large breaking waves to the side. It will hinder the sideways sliding actions and increase the risk of capsizing, as the study indicates.
Here’s an article I wrote comparing daggerboards to centerboards .
Placement of Weight (Vertical Center of Gravity, Vcg)
We have already discussed the importance of having a big enough beam to create sufficient stability. Moving the hulls wider apart will lower the center of gravity (or center of weight) and increase stability; this is true if all other factors are the same.
I f we move the hulls closer to each other, the catamaran becomes narrower, and the center of gravity will move upwards. What happens then? You guessed it, removing the wide base makes it less stable and more prone to heeling.
The same effect can be had by moving weight on the ship vertically (VGC); lower = more stable, and vice versa (a monohull moves it below the surface using a heavy keel).
Pitchpoling (Frontflip)
Pitchpoling is when a catamaran sails with the winds and waves, and the speed of the boat increases to levels above the wave speed. When this happens, there is a risk that the catamaran will semi-surf down the wave and hit the next one. This will slow the boat down, increase apparent wind, and create a rotational force that will make the boat invert if big enough.
Pitchpoling can happen in two ways, symmetrically or asymmetrically. According to the testing in the study, it is more common for one of the bows to dig down into the water and then diagonally flip.
Factors That Affect Pitchpoling
To increase the rotational forces needed for pitchpoling to happen, the center of weighing needs to be shifted aft. This means that a catamaran that is improperly balanced, for example, the bows filled with gear instead of empty, will increase the risk of burying the bows and potentially flipping over. More on weigh issues below!
Another way to offset your balance is to allow water inside the bows; this can happen after repeated slamming of waves onto the hatches. Once filled up, they can hold tons of water and be a severe threat due to buoyancy loss and shift in the center of weight.
Surfing a wave is cool, but it is much safer to lower the speed through reefing early; this reduction in speed makes it less likely to sail into the next wave or trough and risk pitchpoling.
If the boat speed is still too high, the next option is to deploy a drogue that will break the boat and add some directional stability. If this, for some reason is not possible, the study suggests that the vessel should hit the waves head-on.
What is a drogue?

Trampolines
We have already discussed the issue of burying the bows; the effect is massively increased with a solid deck that almost makes the boat into a spoon(a terrible thing if you do want thousands of kilos of water onboard). A better way to dissipate water is with trampolines that lets the water through in a much faster way, like eating soup with a fork.
The effect of having trampolines is twofold; firstly, it will reduce the time the bows are submerged. Secondly, it will decrease the weight of the water on top of the bows and, therefore, how deep the bows will dive.
What is a trampoline on a catamaran?

Hull Shape and Freeboard
There is a discussion that too narrow hulls can increase pitchpoling risk since the hulls might easier dive into the water. I understand the logic, but I am unavailable to find any data to support that claim.
You could also make the claim that wider hulls would increase the braking effect and therefore add to rotational forces. As said, we need more data on this!
Freeboard is the distance between the water and the deck; the bigger this is, the less chance of burying the bows, and vice versa. Same here, It makes sense logically, but there are little data to understand what is enough freeboard.

Real Cases of Catamarans Capsizing
Some news sites have reported on catamarans flipping in different parts of the world. Unfortunately, there is not much data, so drawing well-grounded conclusions is hard.
The previously named study mentions only one report of a catamaran capsizing due to waves hitting its side precisely at the moment of breaking. The cat was 9 m long, and the owner had modified the boat by adding keels.
The study consists of a data set of over 120 incidents reported, of which only 33 are catamarans showing that catamaran capsizing is something very uncommon.
The reason for a catamaran sailboat capsizes;
- 28% Gust of wind
- 16% wave and wind
- 12% Pitchpoled
- 4% Braking Wave
It is also worth noting that most catamaran incidents happened in the range between 6-9 of wind force(Beaufort). Most incidents were on boats smaller than 11m.
News reporting and other articles
While researching this piece, I came across several relevant news articles regarding incidents and a few well-written case studies. I have incorporated these in this article as a point of discussion rather than factual claims. At the bottom of this page, you’ll find the links if you want to read the articles in full length.
2019 Australia, 39ft catamaran capsizes. The daggerboards can be seen and appear to be fully extended; considering the discussion above with keels, daggerboards will decrease the possibility of sideways movement even further. This is also indicated in the study.
There is a discussion on whether or not to leave one daggerboard deployed and one raised, but once again, the discussions of which one and when vary. And I have not been able to find any scientific support for these claims.
2010 Tonga, 57 ft Atlantic catamaran. The crew describes the situation to be very gusty, with winds up to 60kts! A full report on this incident would be very interesting and could really add to the knowledge database. 57ft is a huge ship, but a boat of this size also has a lot of sail area, and during this incident, the autopilot was steering the ship under reefed sails.
A ship of this size should be wide enough to be able to handle some very big waves, and it would be interesting to see whether the crew stuck to the wind charts. I think there is a lesson to be taught here on autopilot and being on the lookout for bad weather.
You should definitely be behind the helm if there is a squall coming so that you are ready to compensate for a change in wind pattern and quickly put in another reef if the initial assessment was wrong.
Chris White, the designer of Atlantic Catamarans shares his thought on this incident;
To summarize: 1) Neither captain thought capsize was even a possibility until way too late 2) Both boats were under autopilot, which had the helm all the way through the capsize 3) The main sheet was never eased or released Chris White of Chriswhitedesigns.com
Mythbusting!
The first part of this article takes its trustworthiness from a scientific study backed by the United Kingdom government; in this next section, I will use that knowledge to address some common myths and misconceptions.
A Charter Is Harder to Flip Than a Performance Cat.
As far as I understand, this argument is based on the following premises; the charter boat is heavier than the racing cat; therefore, it is more stable . As we have come to understand from above, it is a matter of total kilograms and where it is located.
A low and centered center of gravity means better stability. A cruising cat can easily be weighed in the wrong places due to all the extra gear that is usually brought along, such as generators or extra food for a long passage.
Moving the center of weight forward increases pitchpoling risk, and moving the weight up makes it vulnerable to breaching by breaking waves.
There is no need to believe a cruising cat is safer in that aspect inherently. Another common argument I hear is that the rigging would never be able to flip a fully loaded cruising cat since the standing rigging will break before lifting a hull.
What is standing and running rigging?
In theory, this might be true (I don’t have the data available), but in reality, this is certainly not the case; the data in the study clearly shows that catamarans can flip with their rigging intact.
Taking the combined factors of wind, waves, and the keels’ braking effect, there is not necessarily much force needed on the rigging for the boat to capsize. Yes (once again, in theory), a lighter catamaran will be easier to flip under some circumstances, but I would then argue that is more of a sailor error than due to the boat’s construction or weight.
Capsizing a Catamaran vs. Monohull
These two types of boats work in very different ways when it comes to stability; one significant factor is the ability of self-righting of a monohull due to its large and heavy keel.
On the other hand, the catamaran will stay bottom-up and mast down until intentionally righted by another ship.
Once the monohull starts leaning to its side, it will start to dissipate the pushing force that the wind acts upon the sails. This is an automatic way for a monohull not to become overpowered.
This lack of feedback (no or little heeling) on a catamaran means the sailor needs to rely on wind speed charts to tell him or her when to reef. If these charts are not followed, chances are the cat will get overpowered.
Another interesting aspect is that even though a catamaran is flipped upside down, it will still float due to the massive air compartments and low weight, something that a monohull will not. It will even stay afloat if there is a hole in one of the hulls.
What are the differences between monohulls and catamarans?
Catamarans Capsize More Often Than Monohulls
This is a wild debate in many online forums; some argue that it is less safe since it doesn’t have a keel, and some argue that I would rather be floating atop my inverted catamaran than alone in the middle of the ocean with a sunken monohull (while obviously totally missing the point of the discussion).
The truth is that there are no real data to back these claims, at least not that I am aware of. I have tried the insurance companies, but there doesn’t seem to be any big data available, only stories and myths.

The Skills of the Crew
When trying to avoid a catastrophe like a capsize, the most critical aspect is avoiding putting yourself in a bad spot, sailing above your skillset, and more winds and waves than the boat can handle.
This is evident, of course, but it is worth mentioning in detail what this actually means; planning to avoid bad weather and learning how to plan a sail safely and not rush is one of the best safety skills you can have. Once you’re out on the water, surprises will always come your way, so when that happens, use the radar to try to stay away and outrun the weather.
Outrun, you say, no boat is that fast. Well, the idea is to outrun it at an angle, not outrun it like Indiana Jones outruns a rolling stone. At least try to hit the part of the squall or bad weather with lower wind speeds.
Reef Often, Reef Early
Considering the data above, that most boats capsize during gusts of wind, there is a need to respect that data and make that old saying more accurate than ever. Reef early reef often. Make sure you turn off your autopilot; if there is a squall coming, you better be behind the helm to control your ship. Autopilot is stupid, your not!
Also, remember that reefing not automatically reduces speed!
As mentioned above, reducing sail area doesn’t necessarily reduce speed, but it reduces the area where the wind’s pushing can turn into rotational forces. Keep your speed so that you do not overtake the weaves and risk burying the bows.

Keels, Daggerboards, Centerboards
Before you decide on your standing operating procedures for heavy weather, make sure that you understand how your daggerboards will affect the boat handling. The research suggests that you might want to raise them, but make sure you understand why you do it and when.
Using fully deployed daggerboards while getting hit by a breaking wave to the side will increase the rotational force making a capsize more likely.
Heavy Weather Strategies
The boat’s performance is one thing; the crew’s skills are another; make sure you practice those skills and read up on the actual data that exists instead of reading too many forums and listening to know-it-alls. Ensure that your drills are based on science and not someone’s best guess! I encourage you to read the full article, it will be linked below, and go out there and look for more high-quality content.
- https://catamaranguru.com/top-6-characteristics-of-a-good-catamaran/
- http://www.wumtia.soton.ac.uk/sites/default/files/1441_merged.pdf
- https://shuttleworthdesign.com/NESTalk.html
- https://www.chriswhitedesigns.com/25-news/112-what-we-can-learn-from-anna-s-capsize
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/250304001_Model_Tests_To_Study_Capsize_and_Stability_of_Sailing_Multihulls
News articles
- 2020 https://voilesetvoiliers.ouest-france.fr/securite-en-mer/disparition-en-mer/le-catamaran-hallucine-de-regis-guillemot-chavire-au-large-de-vigo-un-mort-trois-rescapes-491bc45c-237e-11eb-97e1-64af5fb563fa
- 2019 https://www.news.com.au/national/nsw-act/news/three-dead-two-rescued-after-catamaran-capsized-in-newcastle/news-story/8f94be3543c41368a4fd83b9b661033b
- 2010 https://www.chriswhitedesigns.com/25-news/112-what-we-can-learn-from-anna-s-capsize
- https://www.sailingtoday.co.uk/uncategorized/bullimores-33m-catamaran-capsized/
Owner of CatamaranFreedom.com. A minimalist that has lived in a caravan in Sweden, 35ft Monohull in the Bahamas, and right now in his self-built Van. He just started the next adventure, to circumnavigate the world on a Catamaran!
2 thoughts on “ Why Catamarans Capsize, A Scientific Explanation (For Beginners) ”
Hi , Thanks for the advice, very good to know. Look forward to having a look at links. Best of luck on the trip, have fun. Mike
Thanks, Mike! Let me know if you have any other questions 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Must-Have Boat Gear for Catamaran Sailors!
Sailing is probably the most gear-intensive activity I've ever done; there are so many decisions to be made about what gear to buy now, for tomorrow, and what to definitely never buy. The gear on...
6 Best Trailerable Trimarans For Bluewater and Coastal Sailing
Having a boat costs a lot of money, even when you are not using it, marina fees, etc. And once it is in the water most sailors never go very far from their "home marina" and sailing will be somewhat...
Can a Catamaran Capsize? The Surprising Answer
Capsizing often happens with small boats like canoes, kayaks, and sailboats. But even for bigger boats like catamarans, which have an established reputation for stability and safety, it's still normal to wonder if they can capsize too. To give you peace of mind and prepare you for the worst, let's answer that question in this article.
A catamaran can capsize under extreme conditions, just like any other boat. Even the most stable catamaran can capsize if it's hit by a large wave, caught in a sudden gust of wind, or if the rotational force has overcome the stability of the boat. However, it's not something that happens frequently.
It can be a scary experience if a catamaran capsized, but you have to stay calm and know that most modern catamarans are designed to self-right. This means that they can turn themselves back over after capsizing. Let's continue reading to know what else can we do to recover from a catamaran capsize.
- A catamaran's stability is attributed to its center of gravity, its freeboard, and its pendulum-like behavior. However, despite its stability and speed, a catamaran can still capsize due to strong winds and capsizing waves.
- There are factors that can contribute to the likelihood of a capsize happening, such as wind speed, wave height, weather conditions, breaking waves, and the overall sailing conditions.
- The best thing to do to quickly recover from a capsize is to stay calm and position the boat to make it self-right quickly.

On this page:
A catamaran can capsize despite its stability, factors influencing catamaran capsizing, safety measures to prevent capsizing, recovering from a capsized catamaran.
A catamaran can capsize. However, it's not very common, and most catamarans are designed to be stable and safe in a variety of conditions.
Despite their stability and speed, catamarans can still capsize under certain conditions. Strong winds, large waves, and imbalance can all cause a catamaran to capsize. When a catamaran is caught in a gust of wind, the increased wind pressure on one side of the catamaran can cause it to lean to one side, which can lead to a capsize if not corrected.
Any boat can technically capsize , but there are specific factors that can contribute to a catamaran capsizing. One of the main reasons for catamaran capsizing is the effect of rotational forces. When these forces overcome the stability of the boat, it can lead to capsizing.
A catamaran is a type of multihull boat that has two parallel hulls connected by a deck or bridge. They are well known for their stability and speed, making them a popular choice for sailors and boaters.
One of the key advantages of their twin hulls is that it gives them a larger base and makes them less likely to tip over . It also helps to distribute the weight of the boat more evenly, providing greater stability. This is especially helpful in rough seas , where the catamaran's stability can help keep you safe and comfortable. Below are factors that contribute to the stability of catamarans:
Their center of gravity makes them stable
In a catamaran, the center of gravity is typically lower than in a monohull, which helps reduce the likelihood of capsizing. This is because the lower the center of gravity, the more stable the boat will be.
The freeboard also adds up to their stability
Their freeboard of a catamaran is typically lower than a monohull's, which helps to reduce the windage and the chances of the boat being pushed over by strong winds.
Their pendulum-like behavior helps them to be stabilized
When they encounter waves, the two hulls move independently of each other, which helps to reduce the rolling motion of the boat. This is because the weight of the boat is distributed between the two hulls, which act like pendulums, swinging in opposite directions to counterbalance the motion of the waves.

Aside from stability, another advantage of a catamaran is its speed. Because they have two hulls, they create less drag than a single hull and can move through the water more quickly and efficiently. This can be especially useful if you're trying to get somewhere quickly or if you're racing.
The height of the wave can affect the chance of capsizing
Wave height is a significant factor when it comes to catamaran capsizing. The higher the waves, the greater the risk of capsizing. This is because the waves can exert a significant amount of force on the boat, causing it to tip over.
Wave capsize occurs when a boat overtakes a wave and sinks its bow into the next one, causing it to capsize. However, this is also not very common and can usually be avoided by keeping an eye on the waves and adjusting your speed and course accordingly.
Wind speed is another important factor to consider
The stronger the wind, the more likely it is that a catamaran will capsize. The wind can create a lot of pressure on the sails, which can cause the boat to lean to one side and potentially capsize. To know more about the ideal wind speed in sailing, read this article.

Weather conditions can also play a role in catamaran capsizing
If there is a storm or other severe weather conditions, the risk of capsizing is much higher. Perhaps consider checking the weather forecast before setting out on a catamaran to ensure that conditions are safe. You may also try reading this article on the possible danger of sailing through thunderstorms.
Breaking waves can cause a catamaran to capsize
When waves break, they release a significant amount of energy, which can cause the boat to capsize. Try to keep an eye out for breaking waves and avoid them if possible.
The overall sailing condition can increase the likelihood of capsizing
You may need to be aware of the conditions and take appropriate precautions to ensure that you stay safe while on the water.
1. Ensure proper weight distribution
To prevent capsizing, you could check if the weight on your catamaran is evenly distributed, with heavier items stored low and towards the center of the boat. Try to avoid overloading your catamaran with too much weight.
2. Learn the right way of reefing
Reefing is the process of reducing the size of your sails to adjust to changing wind conditions. When the wind starts to pick up, you will need to reef your sails to prevent your catamaran from heeling over too much. You must learn how to reef your sails properly before you set out on your journey.
3. Know how to properly anchor and use the right anchor
An anchor can help keep your catamaran in place and prevent it from drifting in strong currents or winds. You need to know how to properly anchor your catamaran and always use an anchor that is appropriate for the size of your boat. Learn different anchoring techniques in tough conditions through this article: Boat Anchoring Techniques Explained (Illustrated Guide)

4. Utilize your catamaran's engine
Your engine can be a valuable tool for preventing capsizing. If you find yourself in a dangerous situation, such as strong winds or currents, you can use your engine to help keep your catamaran stable and prevent it from capsizing.
5. Use your boat tools to prevent it from capsizing
Keels, daggerboards, and centerboards all help stabilize your catamaran and prevent capsizing. You may need to check if these are properly installed and maintained.
6. Use the drogue to slow down the boat
A drogue is a device that can help slow down your catamaran and prevent it from capsizing in heavy seas. You can check if you have a drogue on board and learn how to properly use it in case you need to.
7. Make sure to have safety equipment onboard
Always make sure you have the proper safety equipment on board, including life jackets, flares, and a first aid kit. Everyone on board must also know where the safety equipment is located and how to use it.
8. Use an autopilot
Autopilot can help keep your catamaran stable and prevent it from heeling over too much. Consider learning how to properly use your autopilot before you set out on your journey.
Capsizing a catamaran can be a scary experience, but with proper preparation and practice, you can easily handle it. When the boat flips upside down, all the loose gear in the boat floats away (or sinks), and you are left with a capsized boat. Here are some steps that can help you recover from a catamaran capsize:
The first thing to do when your catamaran capsizes is to remain calm. Take a deep breath and assess the situation. Check if everyone on board is safe and accounted for.
Position the catamaran to self-right
Catamarans are designed to self-right, which means that they can turn themselves back over after capsizing. To self-right, the boat needs to be positioned in a certain way, usually with the mast pointing downwind.
Help the catamaran to self-right using the righting lines
If your catamaran doesn't self-right, you can help it by using the righting lines. These lines are attached to the bottom of the hulls, and they can be used to pull the boat back upright.
The buoyancy of the catamaran can help you recover
Catamarans are designed to be buoyant , which means that they can float even when they are upside down. This makes it easier to recover from a capsize.
Be prepared
The best way to prepare for a capsize is to practice recovering from one. Set aside some time to practice capsizing your catamaran in a controlled environment, like a calm lake. This will help you build confidence and prepare you for the real thing.
Leave a comment
You may also like, catamaran vs monohull in rough seas: which is better.
Catamarans and monohulls have different designs that affect how they handle rough sea conditions. In fact, they have an advantage over each other when sailing in …

Are Catamarans Safer than Monohulls? - Not Always

The Perfect Size Catamaran to Sail Around the World

What is the Ideal Wind Speed for Sailing?

The Illustrated Guide To Boat Hull Types (11 Examples)
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:
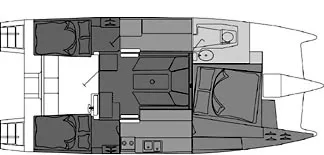
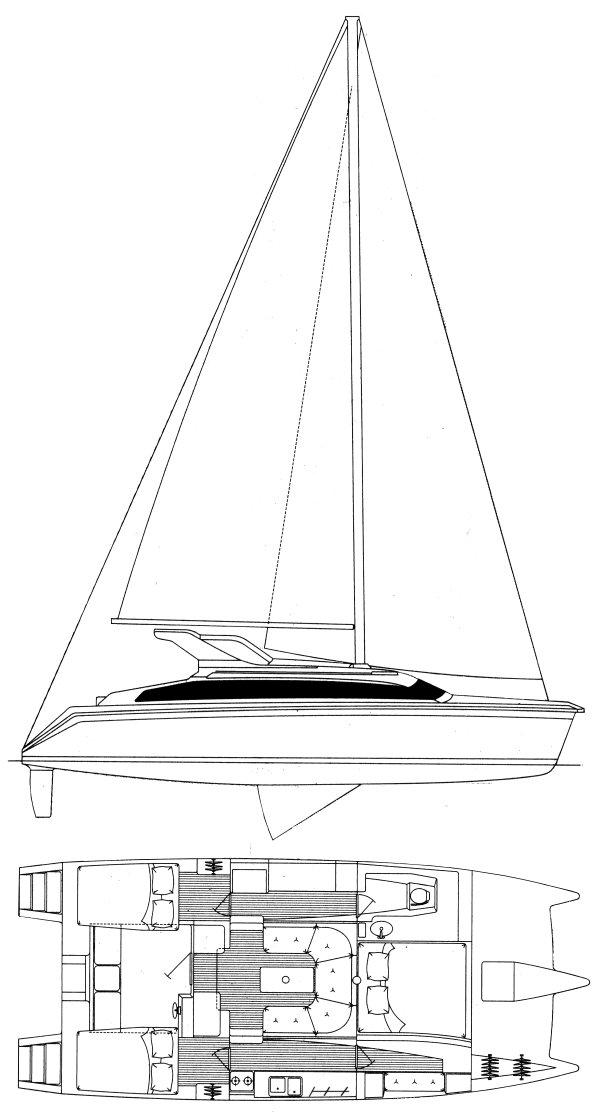
Gemini 105m
The gemini 105m is a 33.5ft masthead sloop designed by tony smith and built in fiberglass by performance cruising between 1995 and 2000., 110 units have been built..
The Gemini 105m is a light sailboat which is a high performer. The fuel capacity is originally small. There is a short water supply range.

Gemini 105m for sale elsewhere on the web:

Main features
Login or register to personnalize this screen.
You will be able to pin external links of your choice.
See how Sailboatlab works in video

We help you build your own hydraulic steering system - Lecomble & Schmitt
Accommodations
Builder data, other photos.
Modal Title
The content of your modal.
Personalize your sailboat data sheet
Great choice! Your favorites are temporarily saved for this session. Sign in to save them permanently, access them on any device, and receive relevant alerts.
- Sailboat Guide
2001 Gemini Catamaran 105Mc
- Description
Seller's Description
Coddiwomple: Gemini Catamaran 105Mc The Gemini, Perfected! Read tinyurl.com/wompler Full VIDEO review 50 Facebook pics Upgrades and Fixes In the Pacific Northwest In the Bahamas In the East Coast 400 detail pics
Equipment: Literally EVERYTHING you can think of. Please click tinyurl.com/5cc3b7yx to view the document. Check out over 400 pics of everything here: tinyurl.com/2fu2cmav
New engine New paint, inside and out! New instruments New safety gear New dinghy New windlass New windows New LED lighting New galley New dining table New entertainment New lifelines New ground tackle 385 watts solar So many tools Spares galore Full documentation Manuals, manuals, manuals!
Rig and Sails
Auxilary power, accomodations, calculations.
The theoretical maximum speed that a displacement hull can move efficiently through the water is determined by it's waterline length and displacement. It may be unable to reach this speed if the boat is underpowered or heavily loaded, though it may exceed this speed given enough power. Read more.
Classic hull speed formula:
Hull Speed = 1.34 x √LWL
Max Speed/Length ratio = 8.26 ÷ Displacement/Length ratio .311 Hull Speed = Max Speed/Length ratio x √LWL
Sail Area / Displacement Ratio
A measure of the power of the sails relative to the weight of the boat. The higher the number, the higher the performance, but the harder the boat will be to handle. This ratio is a "non-dimensional" value that facilitates comparisons between boats of different types and sizes. Read more.
SA/D = SA ÷ (D ÷ 64) 2/3
- SA : Sail area in square feet, derived by adding the mainsail area to 100% of the foretriangle area (the lateral area above the deck between the mast and the forestay).
- D : Displacement in pounds.
Ballast / Displacement Ratio
A measure of the stability of a boat's hull that suggests how well a monohull will stand up to its sails. The ballast displacement ratio indicates how much of the weight of a boat is placed for maximum stability against capsizing and is an indicator of stiffness and resistance to capsize.
Ballast / Displacement * 100
Displacement / Length Ratio
A measure of the weight of the boat relative to it's length at the waterline. The higher a boat’s D/L ratio, the more easily it will carry a load and the more comfortable its motion will be. The lower a boat's ratio is, the less power it takes to drive the boat to its nominal hull speed or beyond. Read more.
D/L = (D ÷ 2240) ÷ (0.01 x LWL)³
- D: Displacement of the boat in pounds.
- LWL: Waterline length in feet
Comfort Ratio
This ratio assess how quickly and abruptly a boat’s hull reacts to waves in a significant seaway, these being the elements of a boat’s motion most likely to cause seasickness. Read more.
Comfort ratio = D ÷ (.65 x (.7 LWL + .3 LOA) x Beam 1.33 )
- D: Displacement of the boat in pounds
- LOA: Length overall in feet
- Beam: Width of boat at the widest point in feet
Capsize Screening Formula
This formula attempts to indicate whether a given boat might be too wide and light to readily right itself after being overturned in extreme conditions. Read more.
CSV = Beam ÷ ³√(D / 64)
This listing is presented by SailboatListings.com . Visit their website for more information or to contact the seller.
View on SailboatListings.com
Embed this page on your own website by copying and pasting this code.
- About Sailboat Guide
©2024 Sea Time Tech, LLC
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Capsize accounts confirm what most small multihull sailors learn by instinct. Cats are more vulnerable to wind, and trimarans are more vulnerable to waves. ... Gemini 105mC. In 2018, the 34-foot catamaran was sailing in the Gulf of Mexico under full sail at about 6 knots in a 10-15 knot breeze. Squalls had been reported on the VHF. The crew ...
I have owned a 28 Sabre for the past 8 years and have enjoyed sailing this fine craft along the northeast coast. Recently came across a deal on a mid 90s 3400 gemini thats been sitting on the hard for a few years. Owner ill and needs to sell ASAP. Vessel needs work and good cleaning. my main concern is the drive unit, it sports a 27hp westerbeke diesel with a sillete sonic drive unit.
Gemini 105MC is a 33′ 5″ / 10.2 m catamaran sailboat designed by Tony Smith and built by Performance Cruising between 2003 and 2011. ... weight of a boat is placed for maximum stability against capsizing and is an indicator of stiffness and resistance to capsize. Formula. Ballast / Displacement * 100 ... GEMINI 105MC is a development of the ...
Capsize Screening Formula. ... In 2001 the owner, designer and builder of the Gemini catamaran series, Tony Smith, sailed a new Gemini 105Mc across the Atlantic Ocean for a delivery to Southampton, England topping out at 18 knots of speed (surfing down the face of heavy seas). Many more of these adventures are chronicled in the Gemini Gems ...
Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 7: should the worst happen - with Nigel Irens. Capsize is very unlikely in most modern catamarans, but should the worst happen it is as well to be prepared ...
Boat: Paper Tiger 14 foot, Gemini 105MC 34 foot Catamaran Hull no 825. Posts: 2,912. Re: 2012 Round The Island Race (& Gemini capsize) When I got washed up onto the beach at Broughton Island, I pumped my Fresh water tanks out to use as flotation tanks, They hold 60 gallons, 2 X 30 gallon tanks, Good idea, and it would have helped,
Capsize Screening Formula (CSF): Designed to determine if a boat has blue water capability. The CSF compares beam with displacement since excess beam contributes to capsize and heavy displacement reduces capsize vulnerability. The boat is better suited for ocean passages (vs coastal cruising) if the result of the calculation is 2.0 or less.
Construction of the Gemini, which is marketed as a comfortable, low-priced cruising catamaran rather than a spartan high-tech racing machine, is quite conventional. The hull is built of solid fiberglass—mat and woven roving. The deck is cored with balsa for stiffness. The new Gemini 3200 incorporates a layer of vinylester resin as a blister ...
In January, the Gemini Legacy 35 was the first fixed hull catamaran to exhibit at the Chicago Strictly Sail show. USCG Captains, veteran catamaran guys and Bay Breeze staffers Dave, Paul and Doug were there to field questions from the 4,000 folks that toured the boat. Below is a sampling of the most frequently asked questions:
GEMINI LEGACY 35. Made in America since 1981, the Gemini Legacy has proven to be the most family-friendly performance cruising catamaran in the world, and the reasons are obvious; A 34 inch draft that allows the boat to be pulled up right next to a beach or anchored inu0003 small, protected coves. A 14 foot beam, which means the boat can be ...
In 1993, the company launched the Gemini 3400, the first catamaran with a lifting underhung rudder system. It was eventually modified and reintroduced as the 105M, and the 105Mc is the most recent upgrade. With 800 boats on the water, the company claims to be the best-selling catamaran manufacturer in the US. In 2002 the company's 20 ...
Gemini production moved to FL in 2009 after the 2008 financial meltdown. In 2011, Gemini offered the Limited-Edition Design Touch TM models, whose upgrades included cherry veneer finishes, Corian countertops, and ducted air conditioning. In a partnership with Hunter Marine and a generous buyout from The Catamaran Company, Gemini was able to live on under the direction of Smith's daughter ...
The cat was 9 m long, and the owner had modified the boat by adding keels. The study consists of a data set of over 120 incidents reported, of which only 33 are catamarans showing that catamaran capsizing is something very uncommon. The reason for a catamaran sailboat capsizes; 28% Gust of wind. 28% Wind.
Summary. A catamaran's stability is attributed to its center of gravity, its freeboard, and its pendulum-like behavior. However, despite its stability and speed, a catamaran can still capsize due to strong winds and capsizing waves. There are factors that can contribute to the likelihood of a capsize happening, such as wind speed, wave height ...
Overview. Specifications. Gemini 105Mc Design Touch - The World's Best-Selling Single-Design Cruising Catamaran since 1980. For over 27 years and over 1000 deliveries, the Gemini 105Mc still remains one of the most proven and popular catamarans ever built. Her sailing performance is legendary yet still manages to surprise unsuspecting newcomers.
The Gemini 105m is a 33.5ft masthead sloop designed by Tony Smith and built in fiberglass by Performance Cruising between 1995 and 2000. ... Capsize: 2.80 ... Catamaran twin centerboard Construction: Fiberglass Waterline length: 31.75 ft ...
For Sale is my 1998 Performance Cruising Gemini 105M Cruising catamaran. I am asking $60,000 for this boat due to a change in my life situation. This is a VERY well kept example of a 105M and is a USCG DOCUMENTED VESSEL. Equipment 3 Lead Acid Deep Cycle Batteries, Brand New (Jan 2020) New Life Lines (Jan 2020) New UV covers for windows (Outland ...
Notes. The GEMINI 31 was the first of Gemini series of cruising catamarans that became the best selling boat of its type being built in the United States. Loosely Based on the earlier ARISTOCAT 30, designed by Musters and Shaw, the 31 was superseded by the very similar Gemini 3000, which remained in production until 1990, when it was in its ...
Notes. The GEMINI 3400 was the predecessor to the GEMINI 105 and the first in the series to have molded transom steps. A new kick-up rudder system was developed for the new transom design. Like all Gemini models the 3400 has kick-up centerboards which are housed in low aspect ratio fixed keels which serve as protection for the under-slung ...
Capsize Screening Formula. This formula attempts to indicate whether a given boat might be too wide and light to readily right itself after being overturned in extreme conditions. Read more. Formula. CSV = Beam ÷ ³√(D / 64) Beam: Width of boat at the widest point in feet; D: Displacement of the boat in pounds?
7Stay connected with Gemini Catamarans by subscribing to our newsletter. You'll receive important news, updates, and special offers right to your Inbox. Subscribe. Gemini Models . Gemini Freestyle 399 Power . Gemini Freestyle 37 . Gemini Legacy 35 . Gemini 105Mc Design Touch. Latest News. More News.
Come take a look at this catamaran with me in this Gemini 105 MC Catamaran Boat Tour and see what one of these cool Gemini 105 MC Catamarans really looks li...
Gemini 105Mc Design Touch. Overview; Specifications . Specifications: Manuf. Length: 34' ( 10.36 m) Beam: 14' ( 4.27 m)